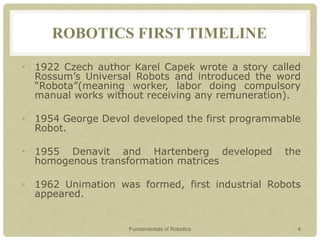
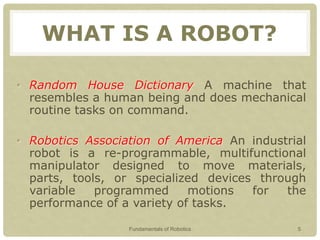
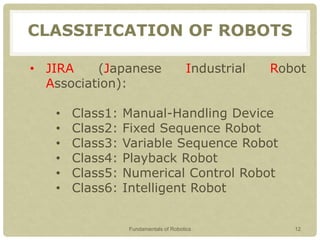
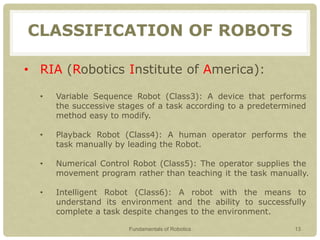
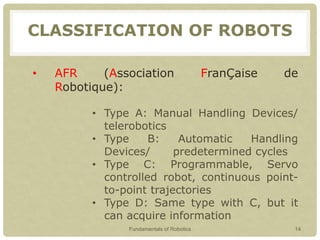
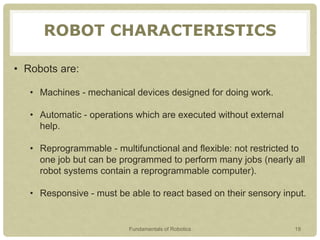
This document provides an introduction to robotics, covering key topics such as the definition of a robot, the history and timeline of robotics, classifications of robots, Isaac Asimov's Three Laws of Robotics, examples of robots around the world, characteristics of robots, advantages and disadvantages of robots, and why robots are used. The presentation aims to explain what a robot is, its types, characteristics and classifications, as well as the field of robotics and what tasks robots can perform.