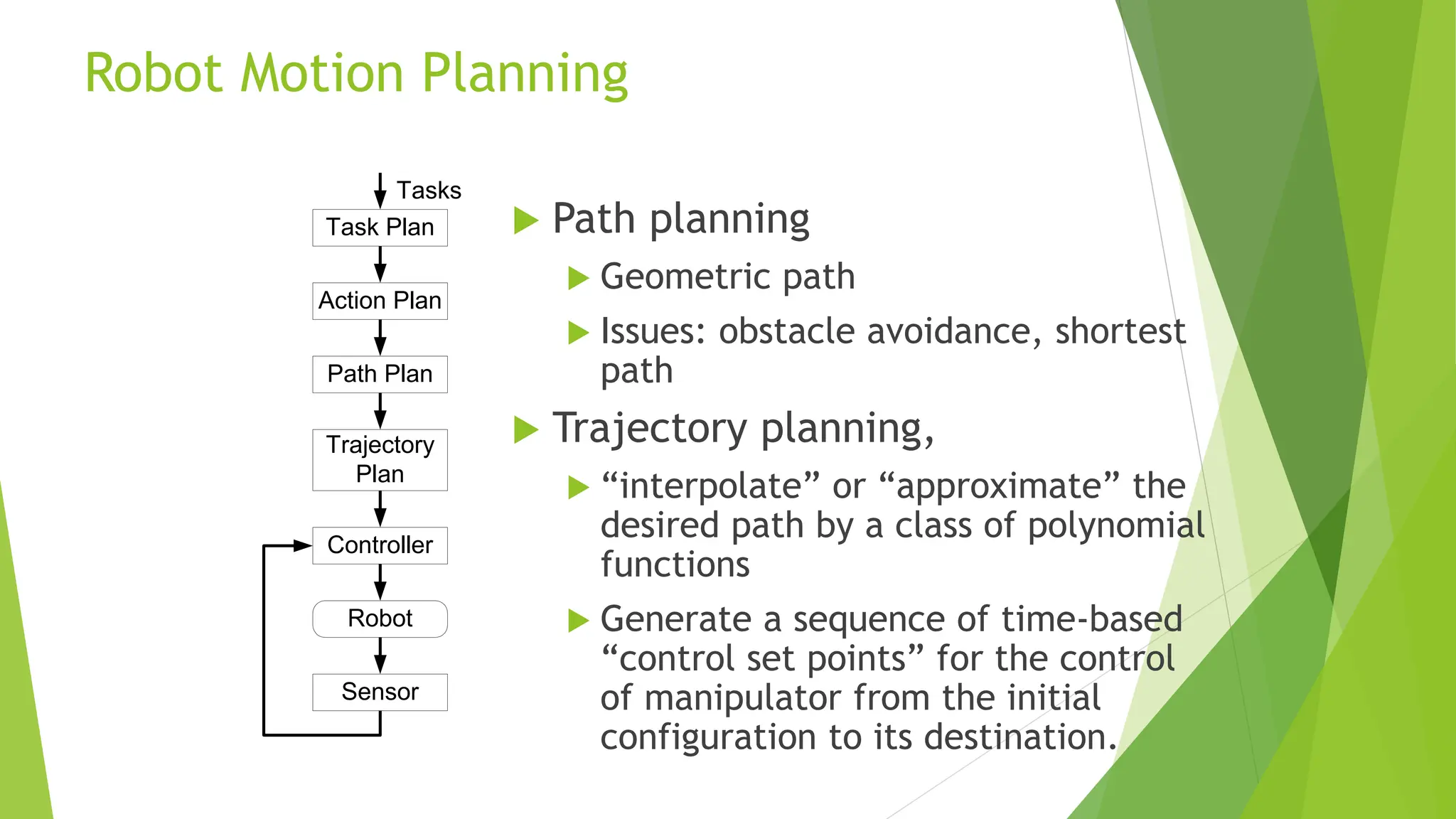
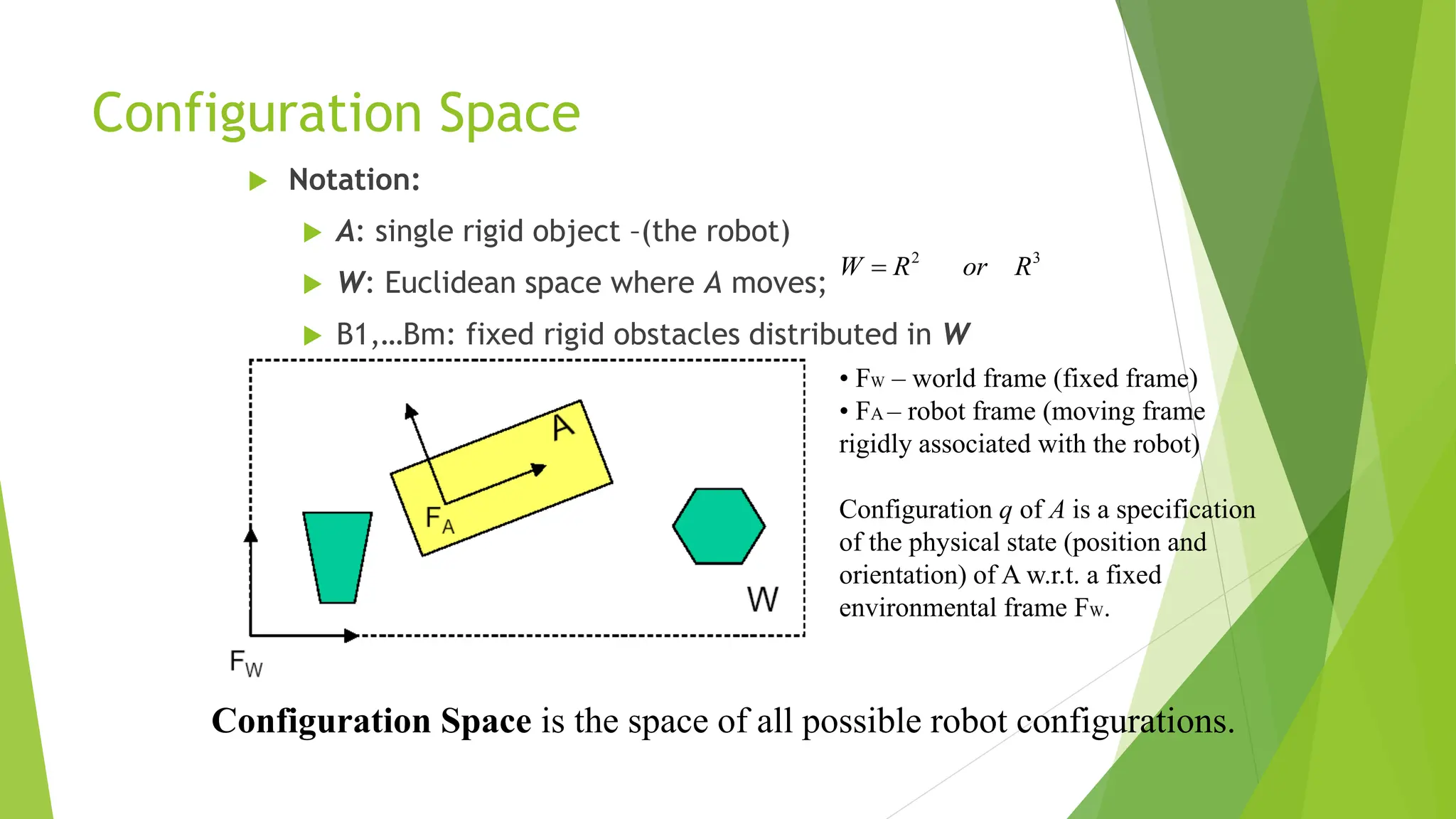
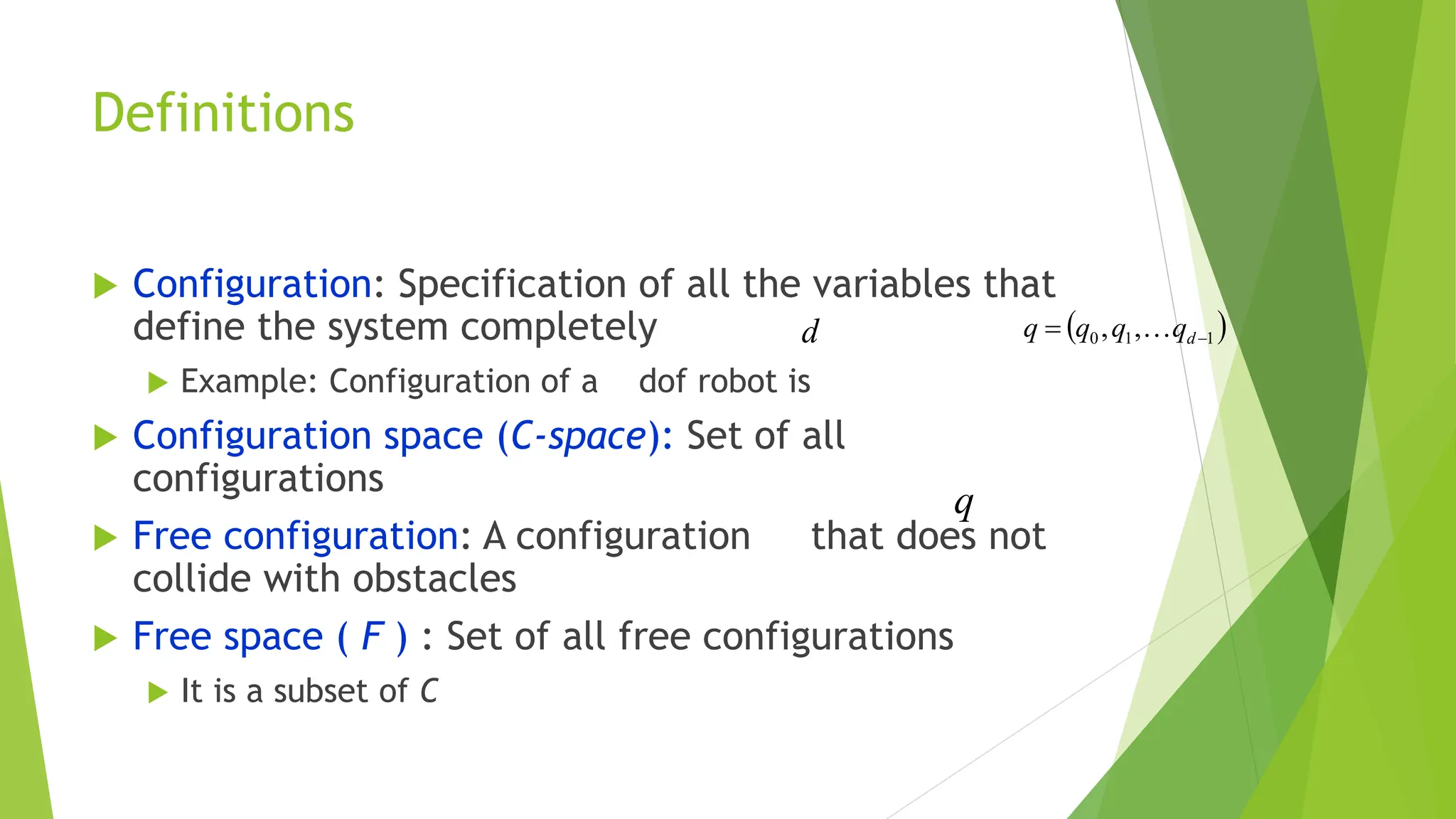
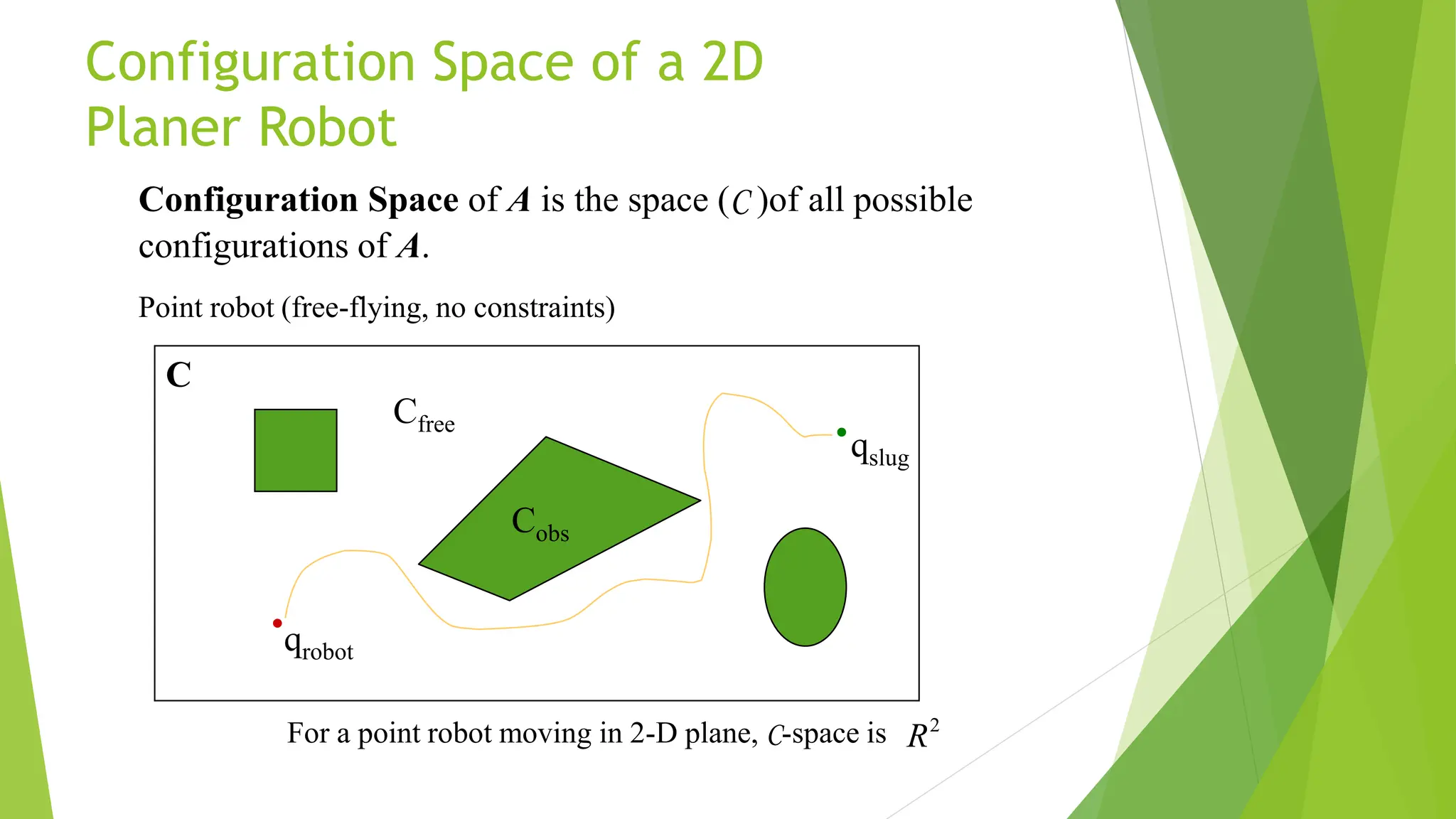
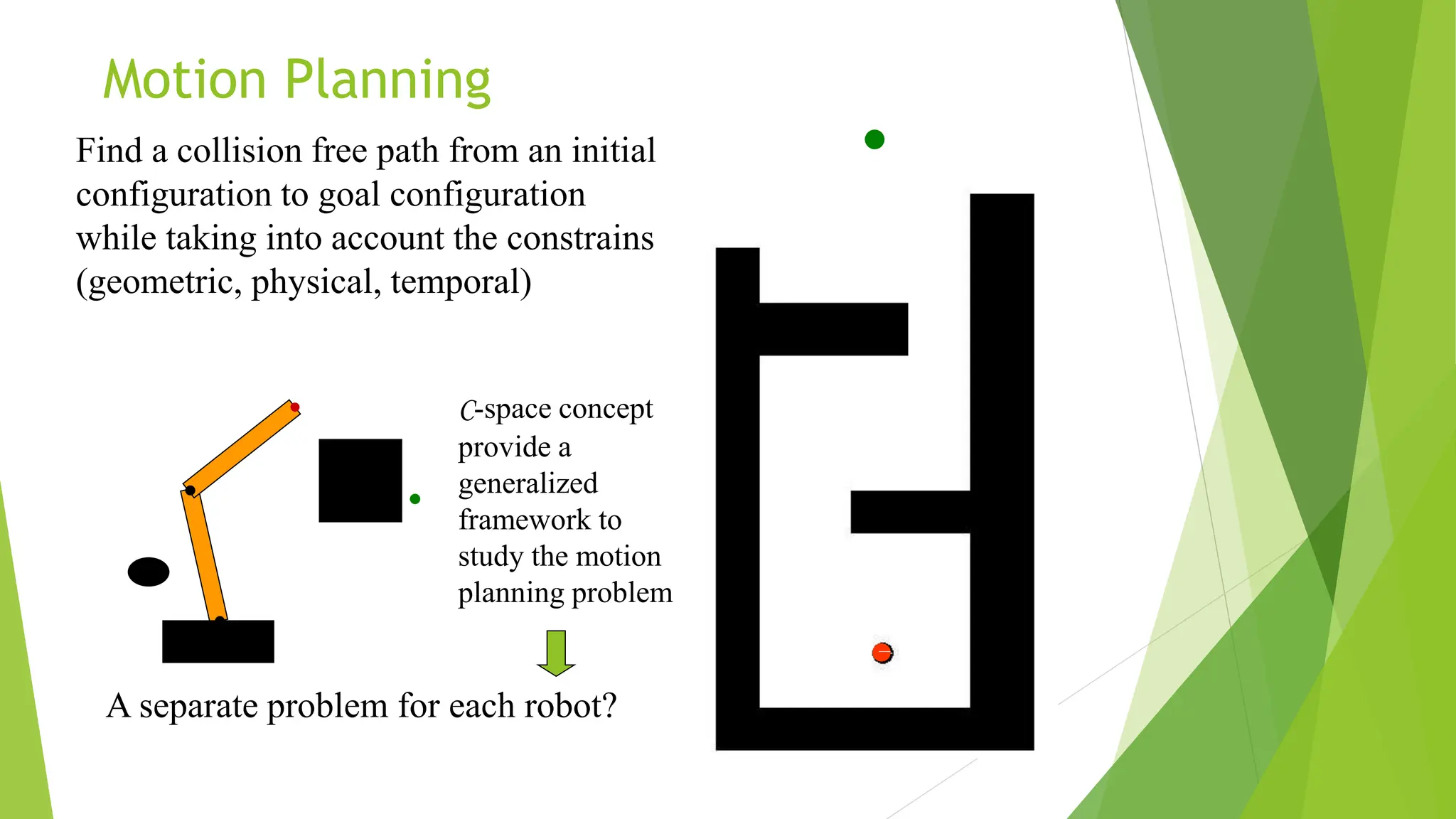
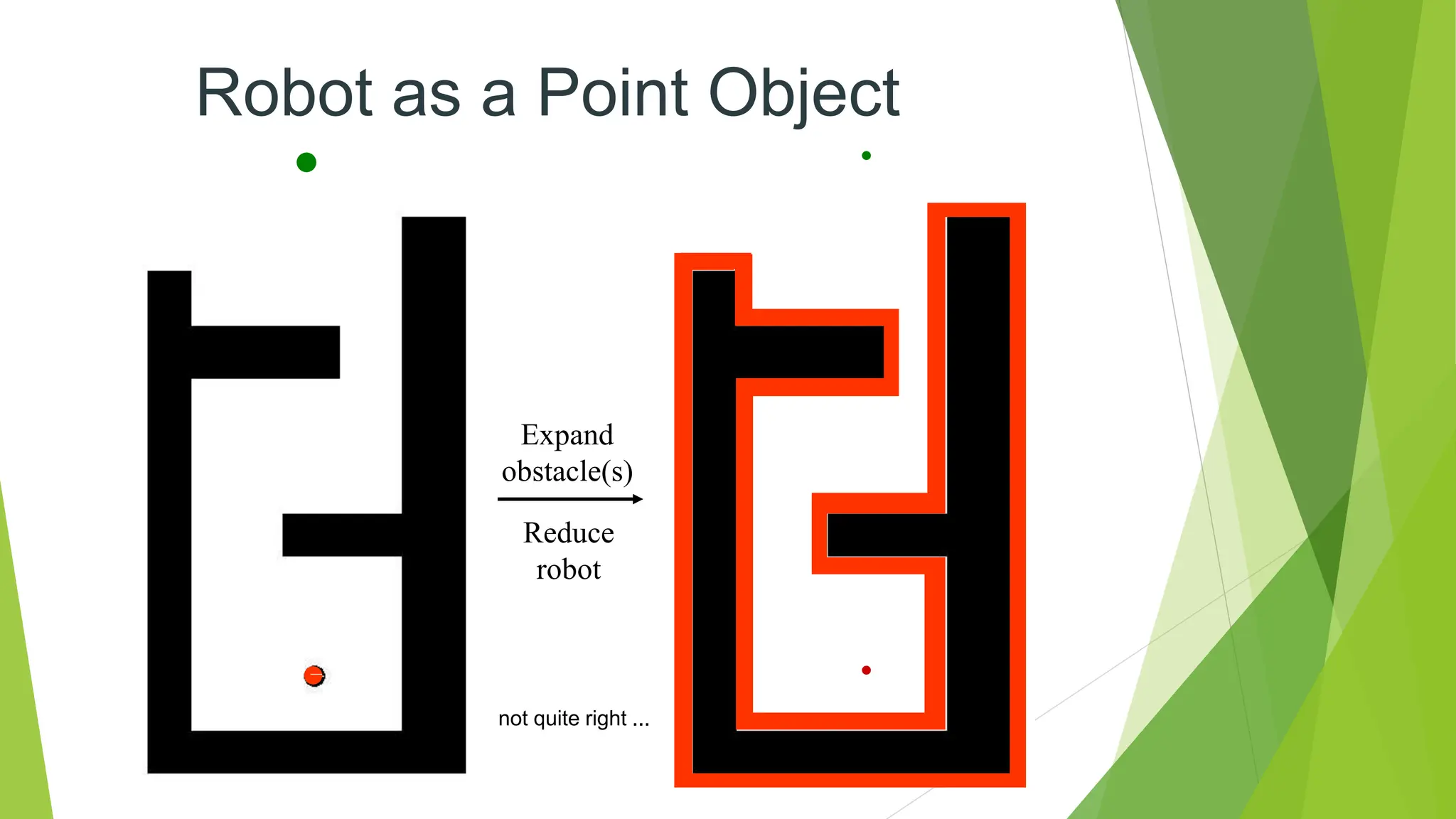
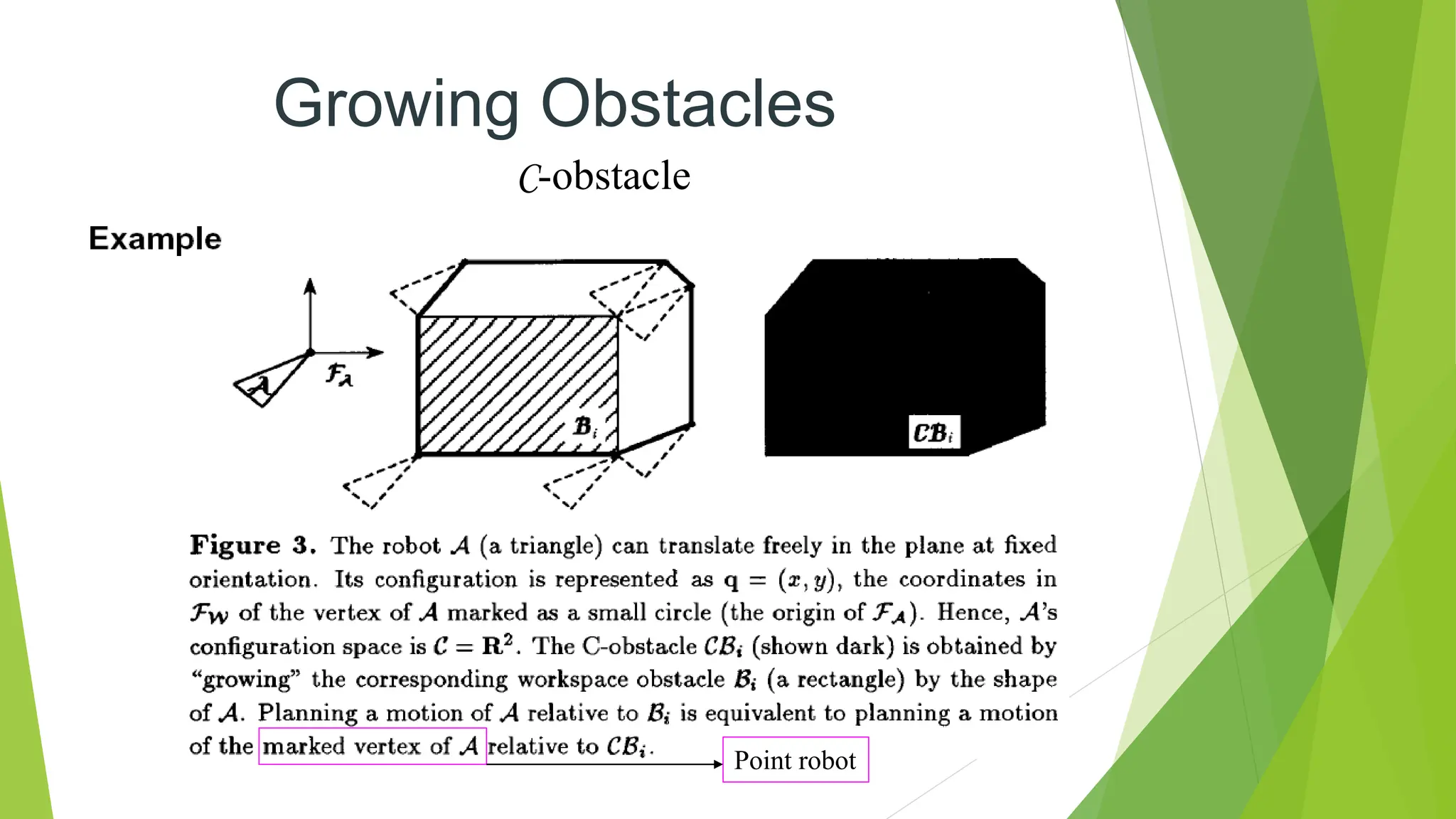
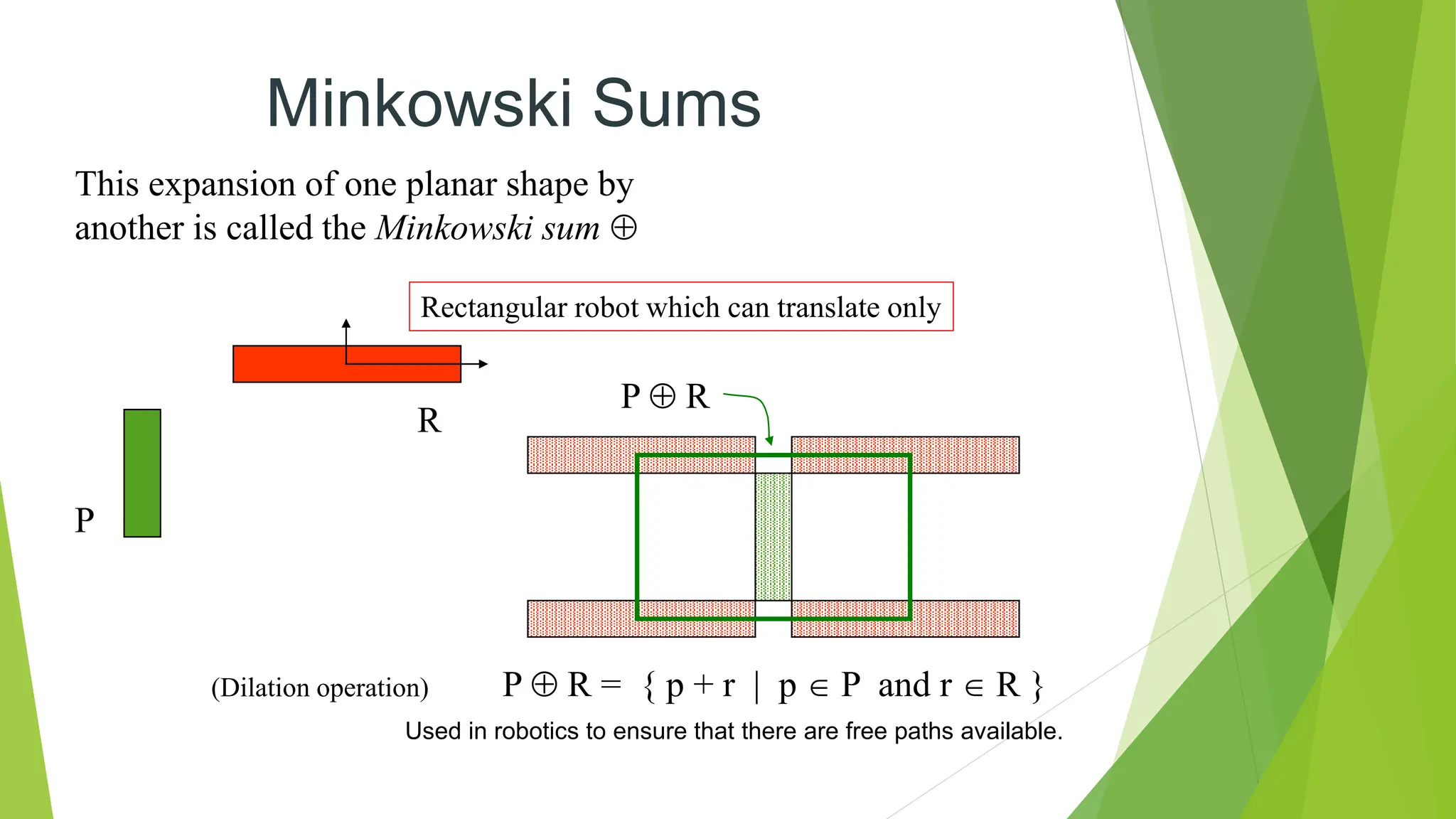
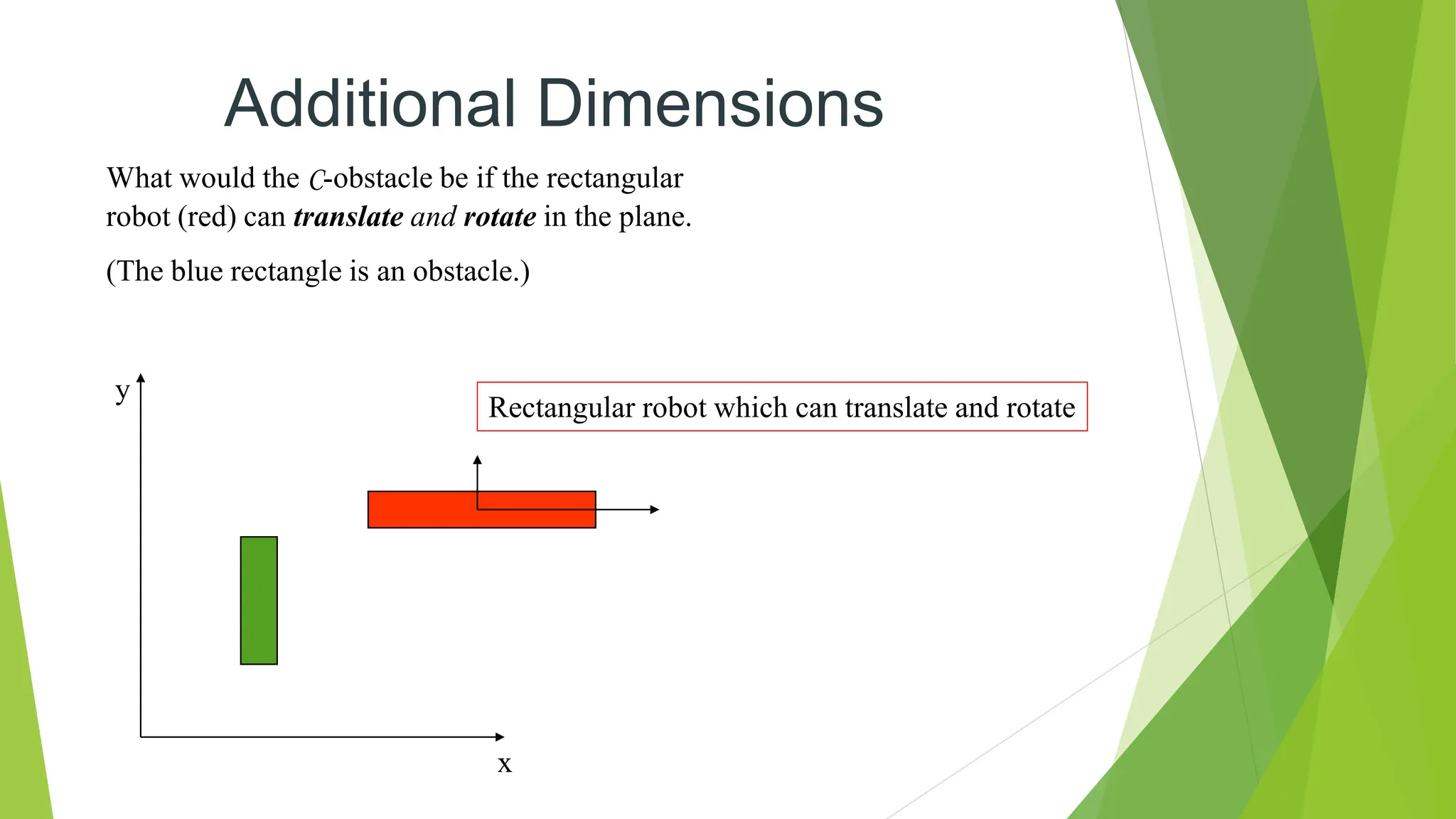
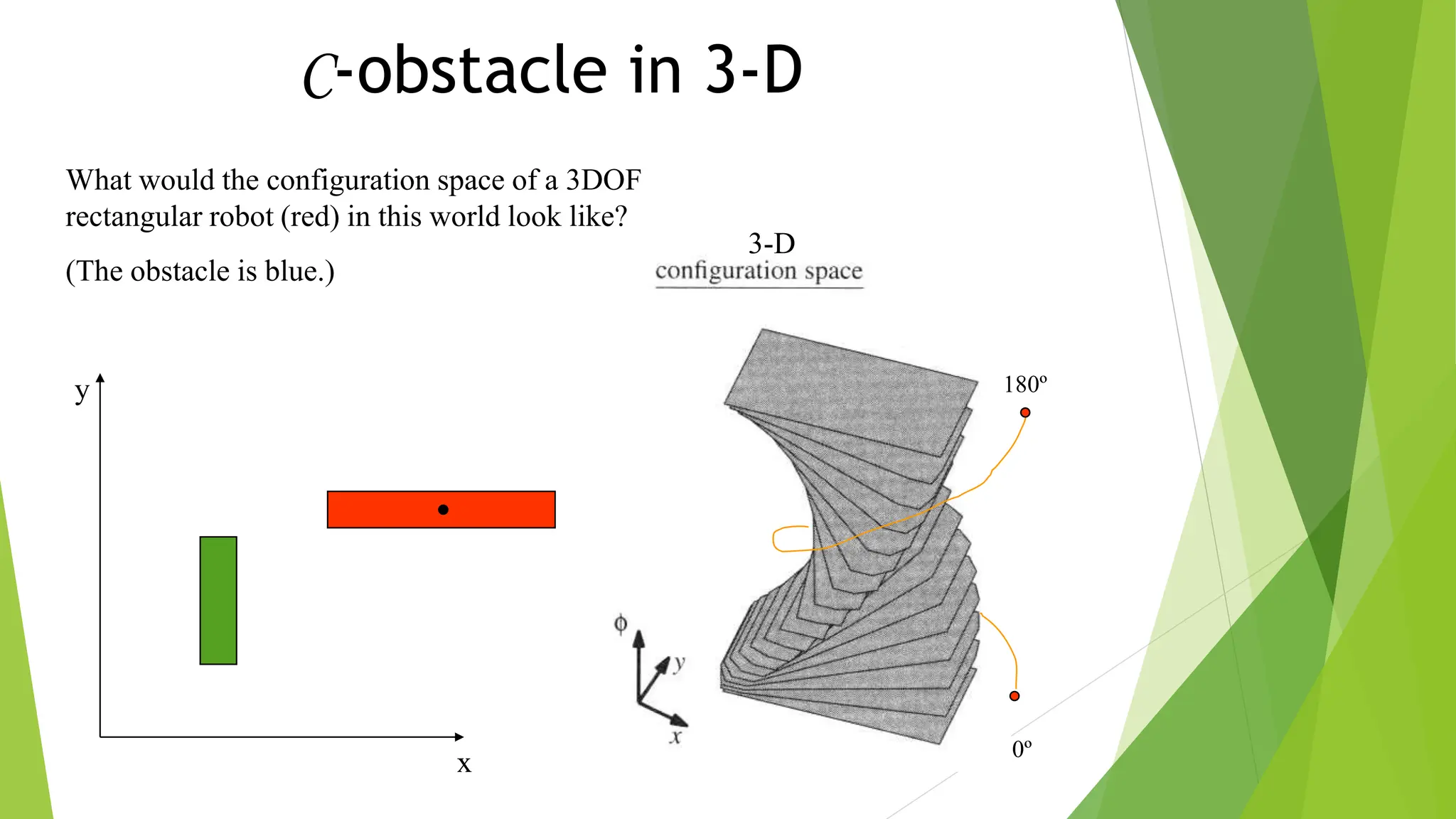
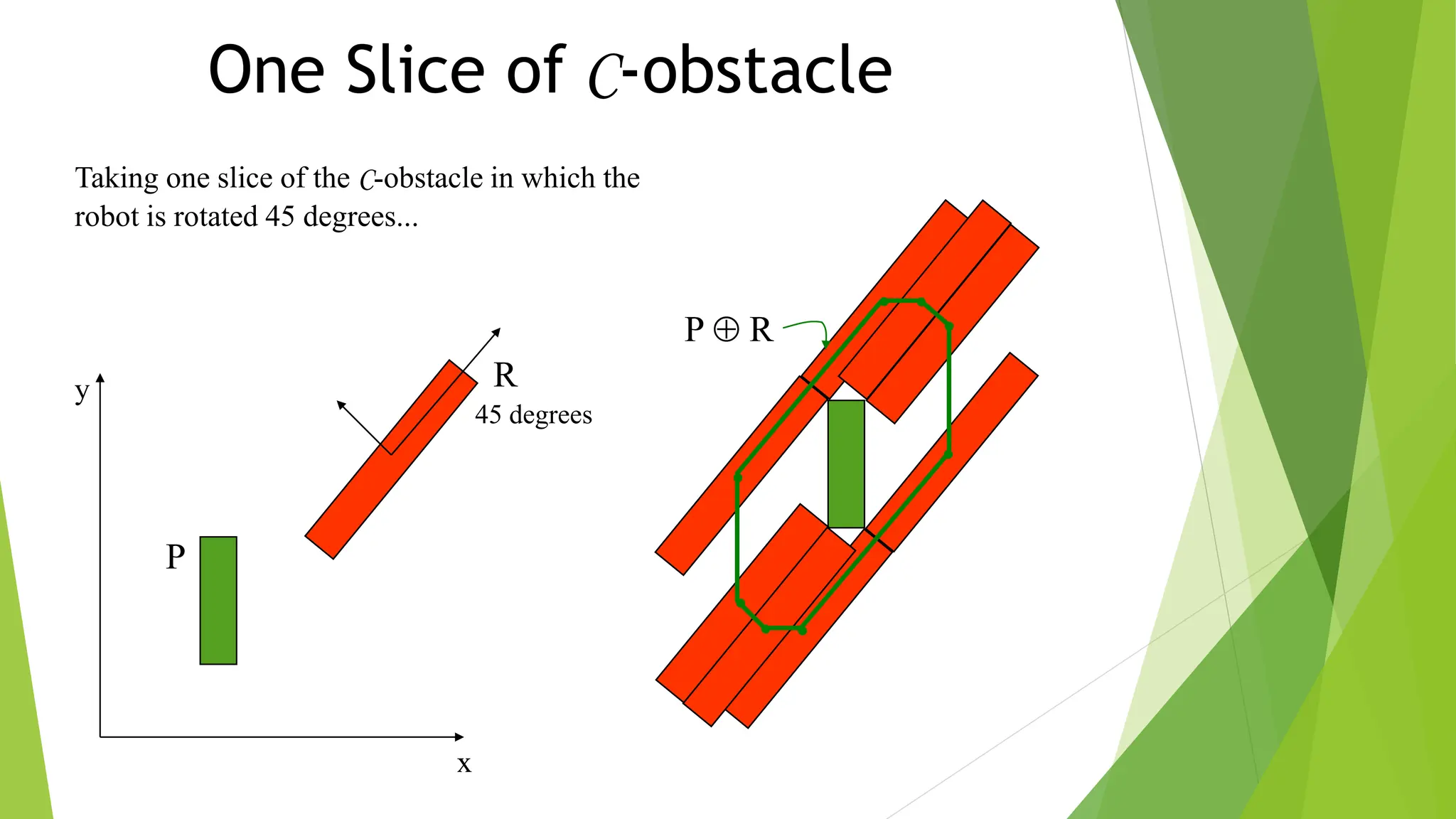
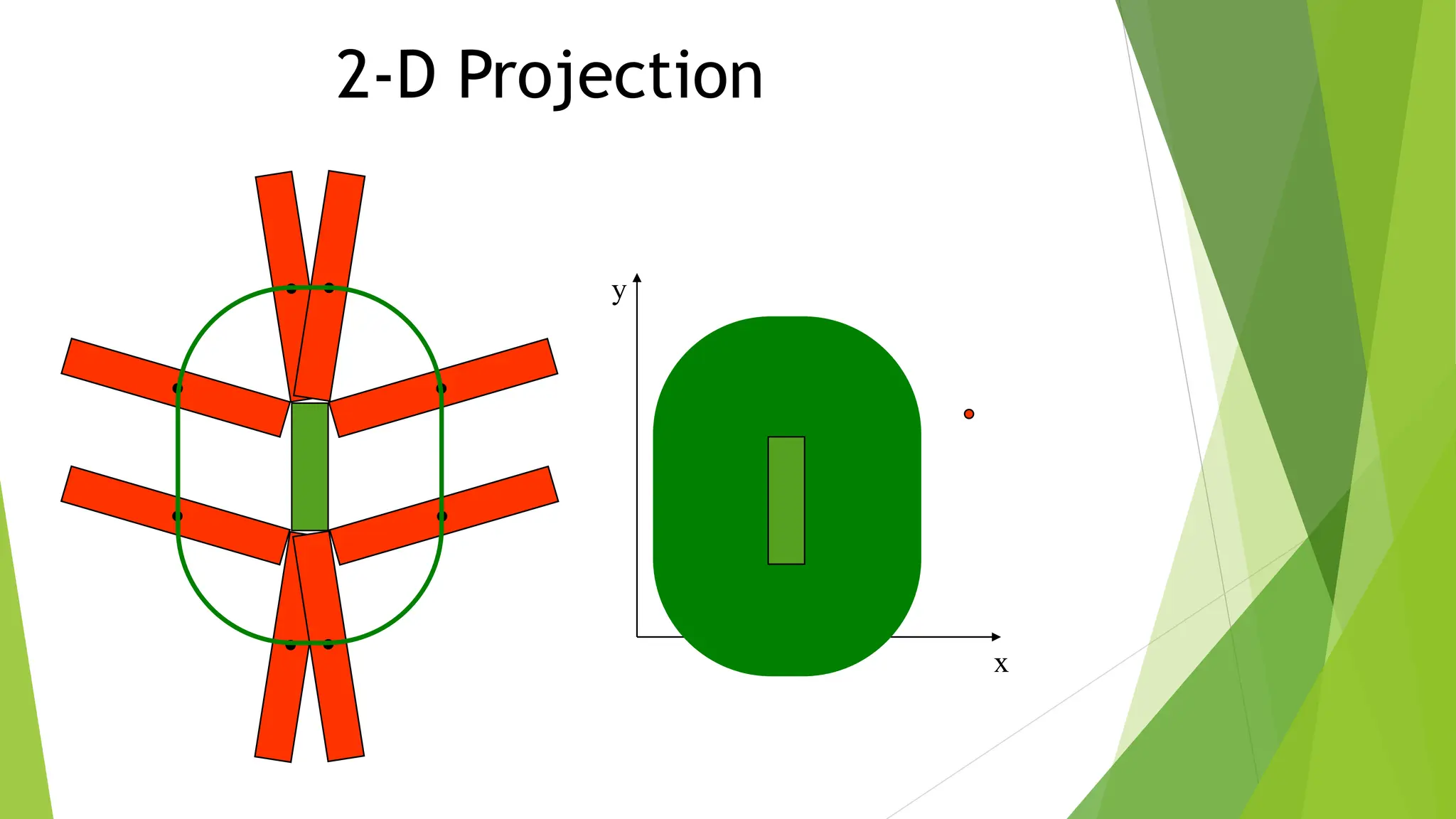
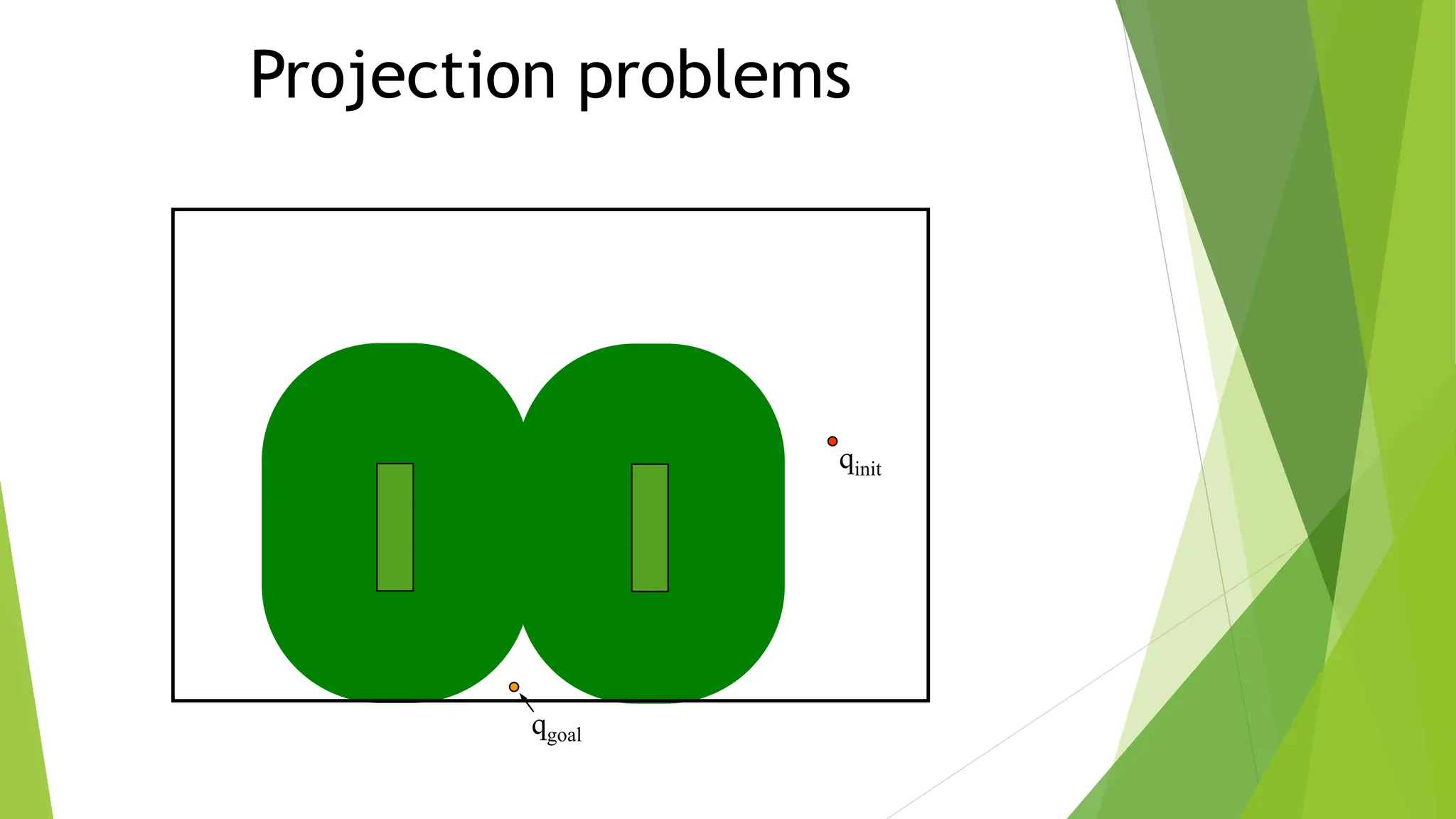
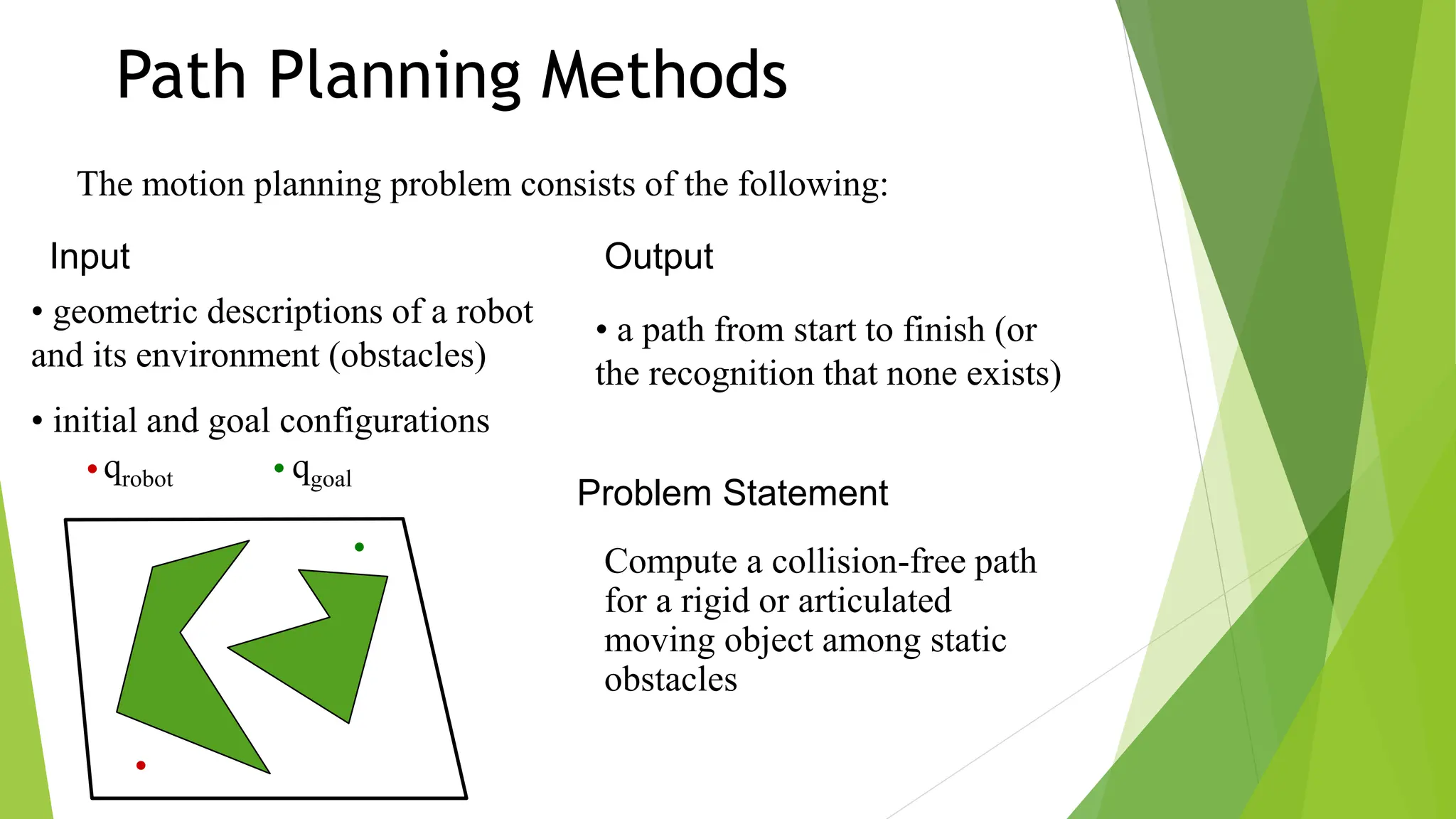
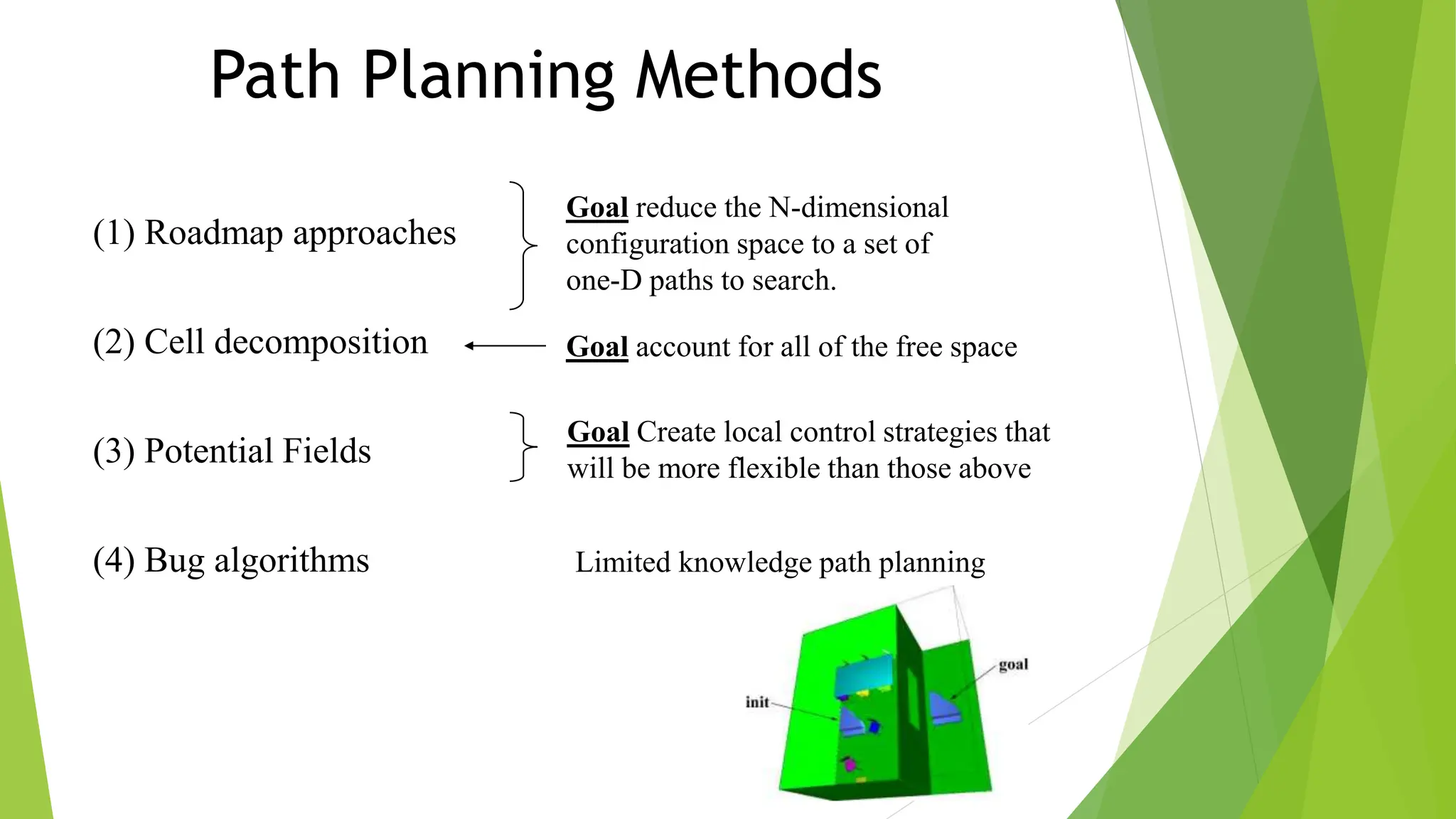
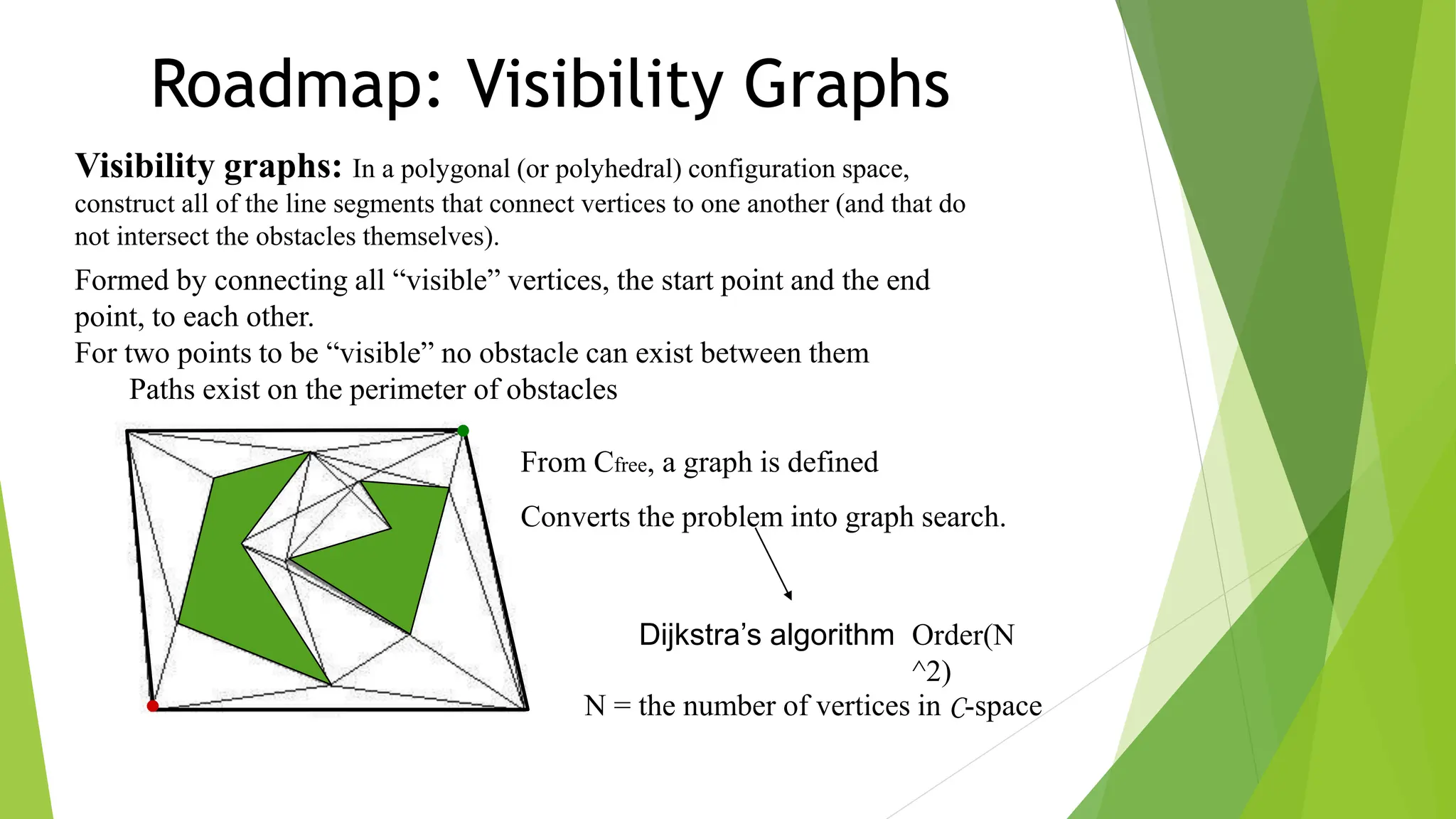
Robot path planning involves generating a collision-free path for a robot to follow between an initial and goal configuration. Key aspects of path planning include:
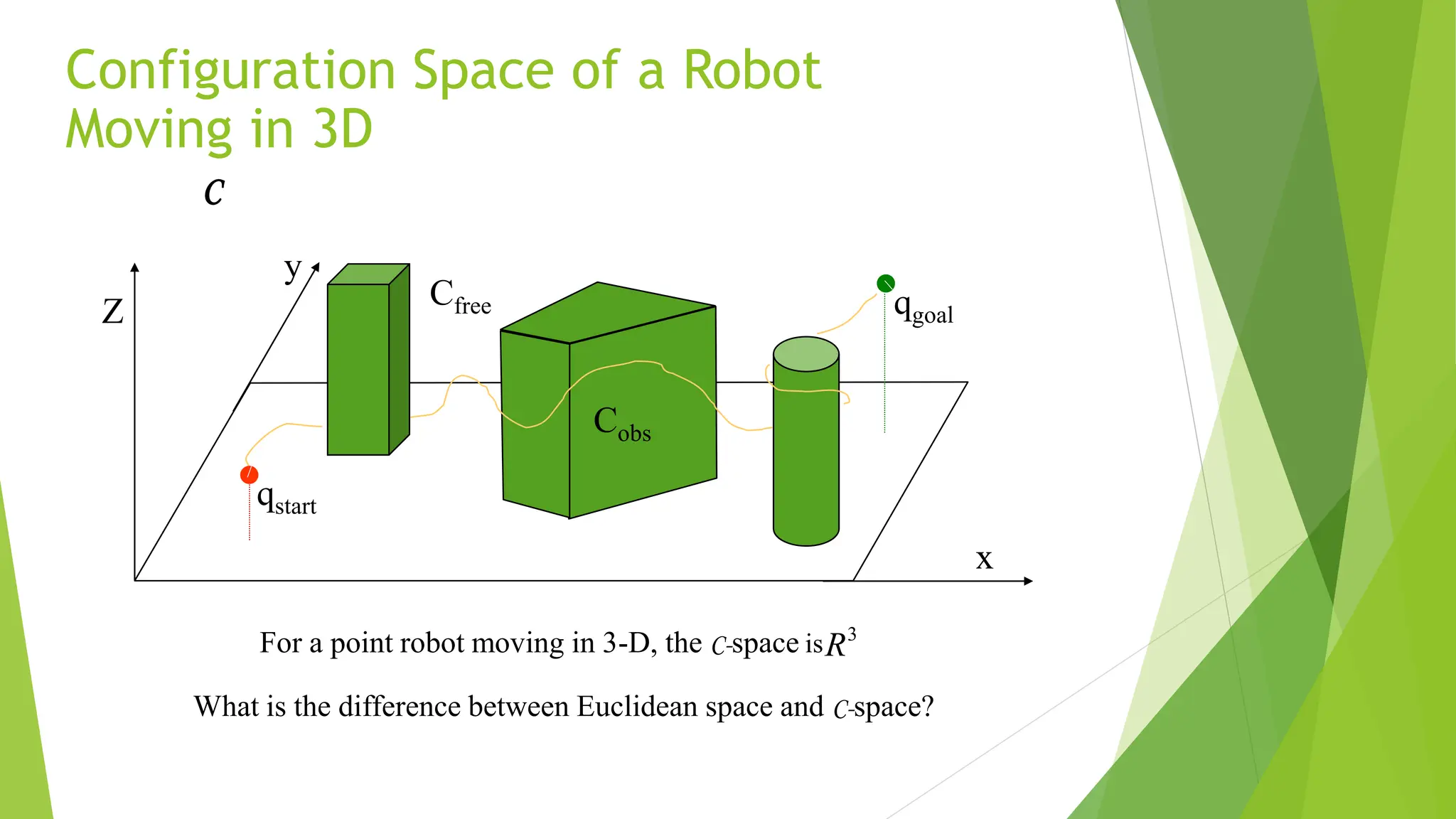
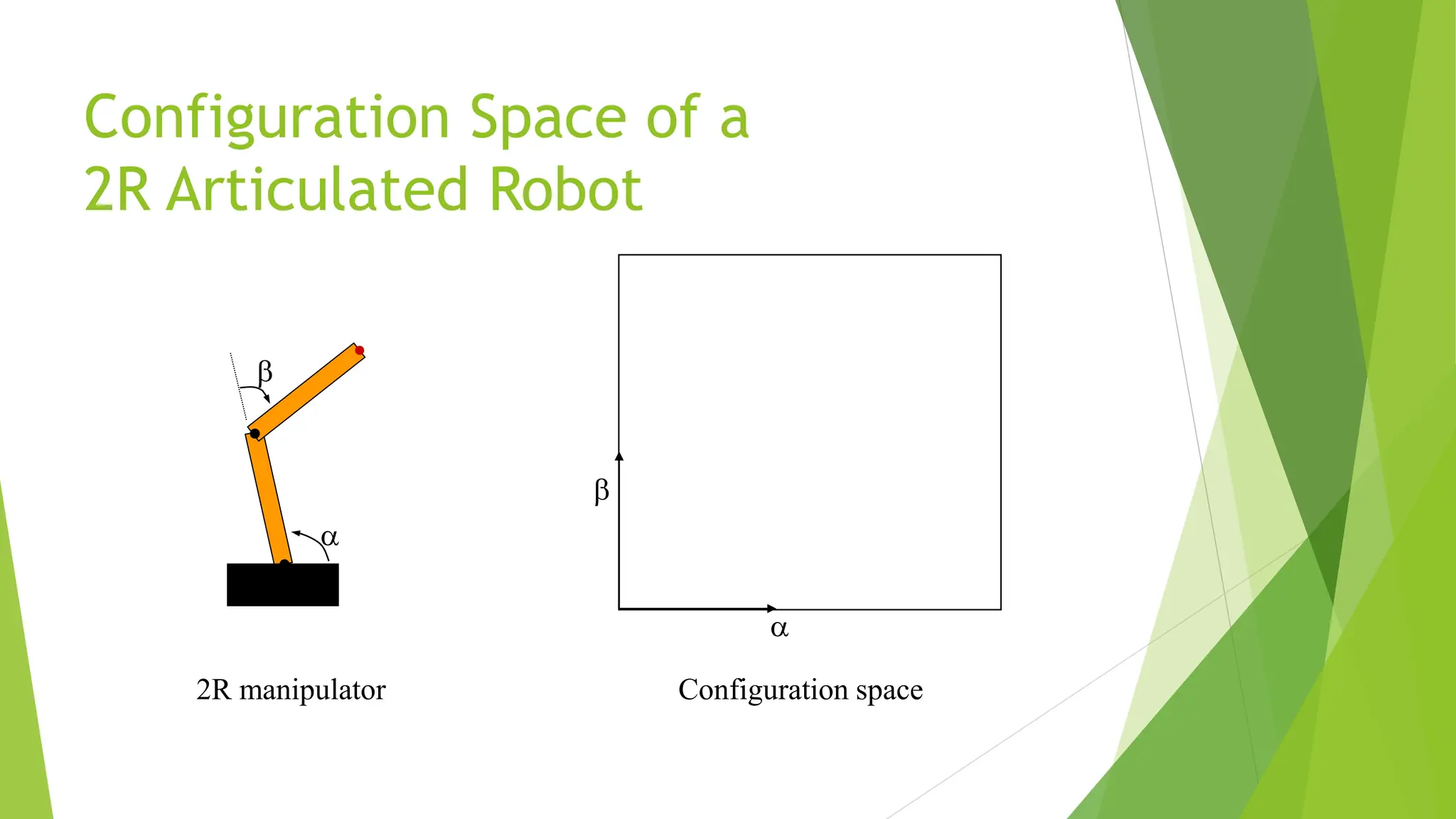
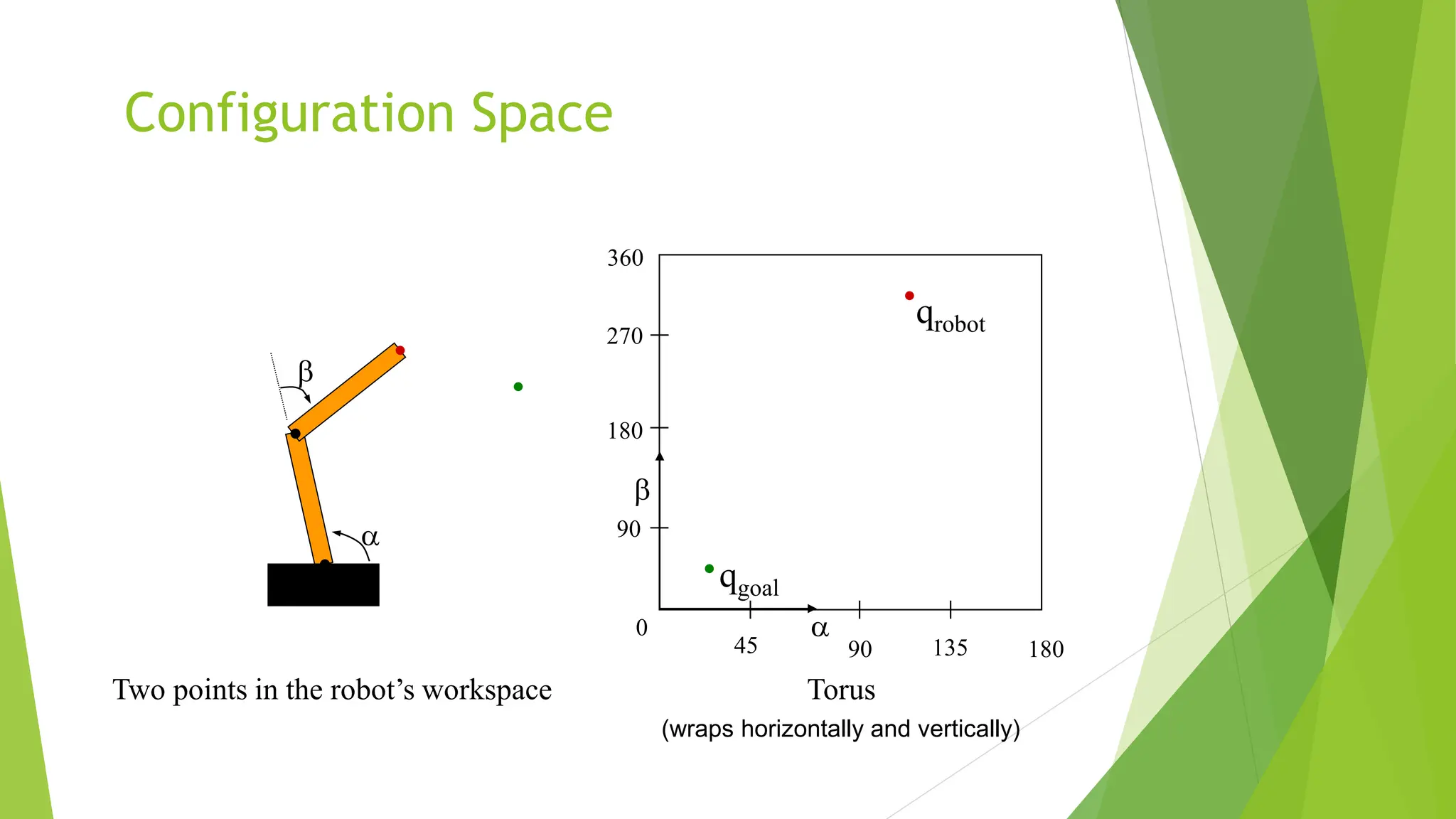
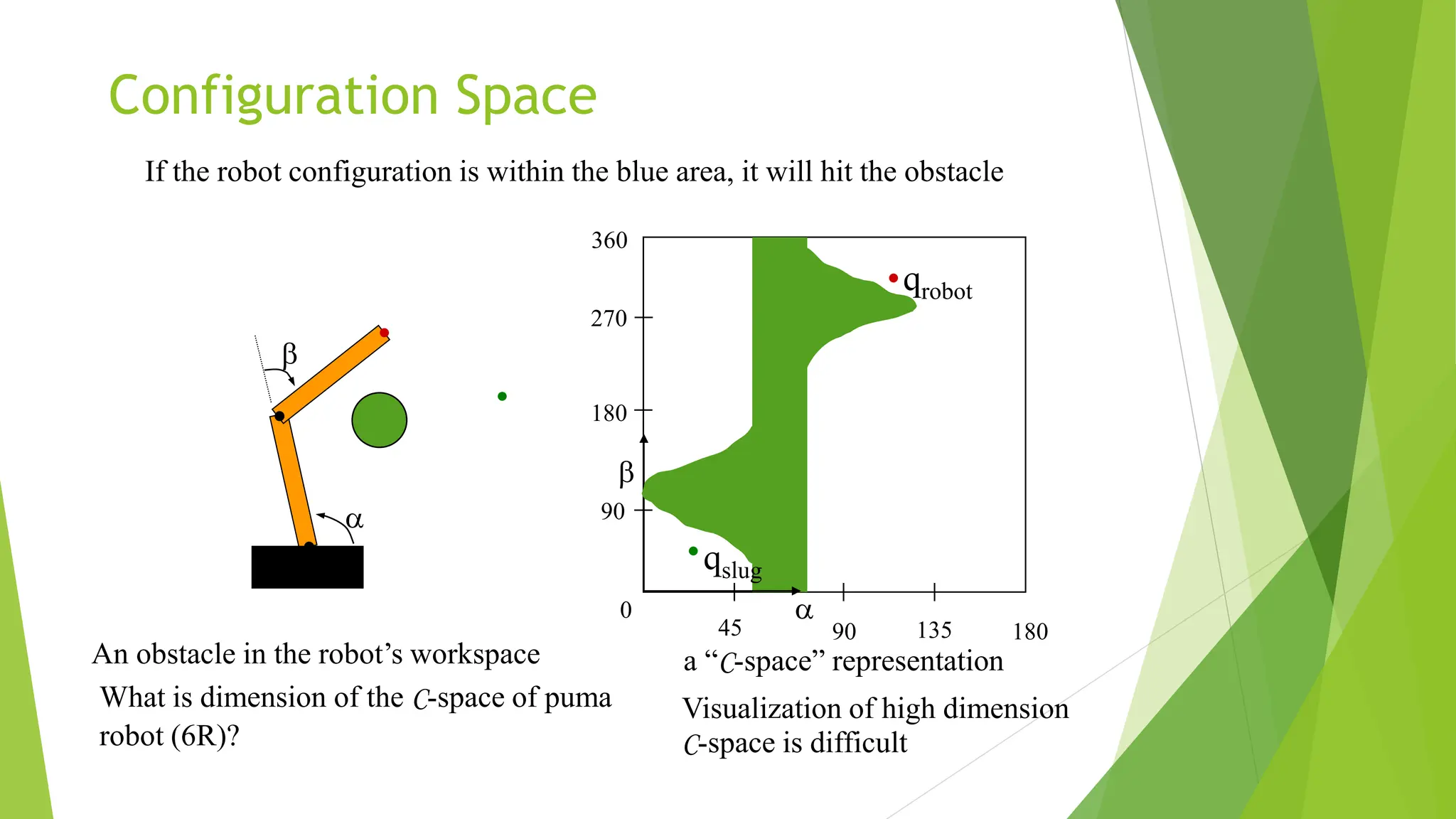
1) Representing the robot and obstacles in a configuration space (C-space) that accounts for all possible robot states. This allows the path planning problem to be generalized across different robots.
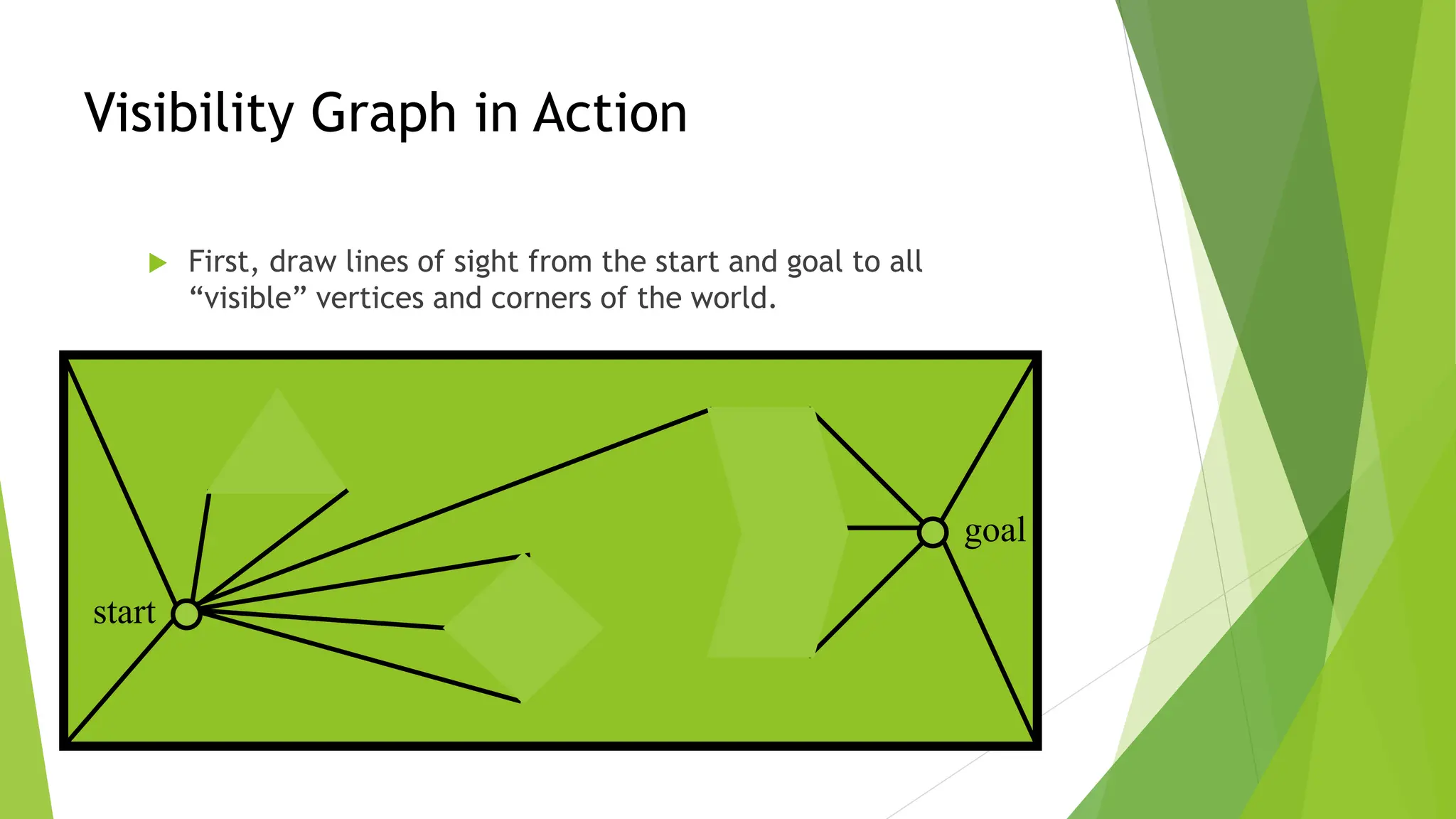
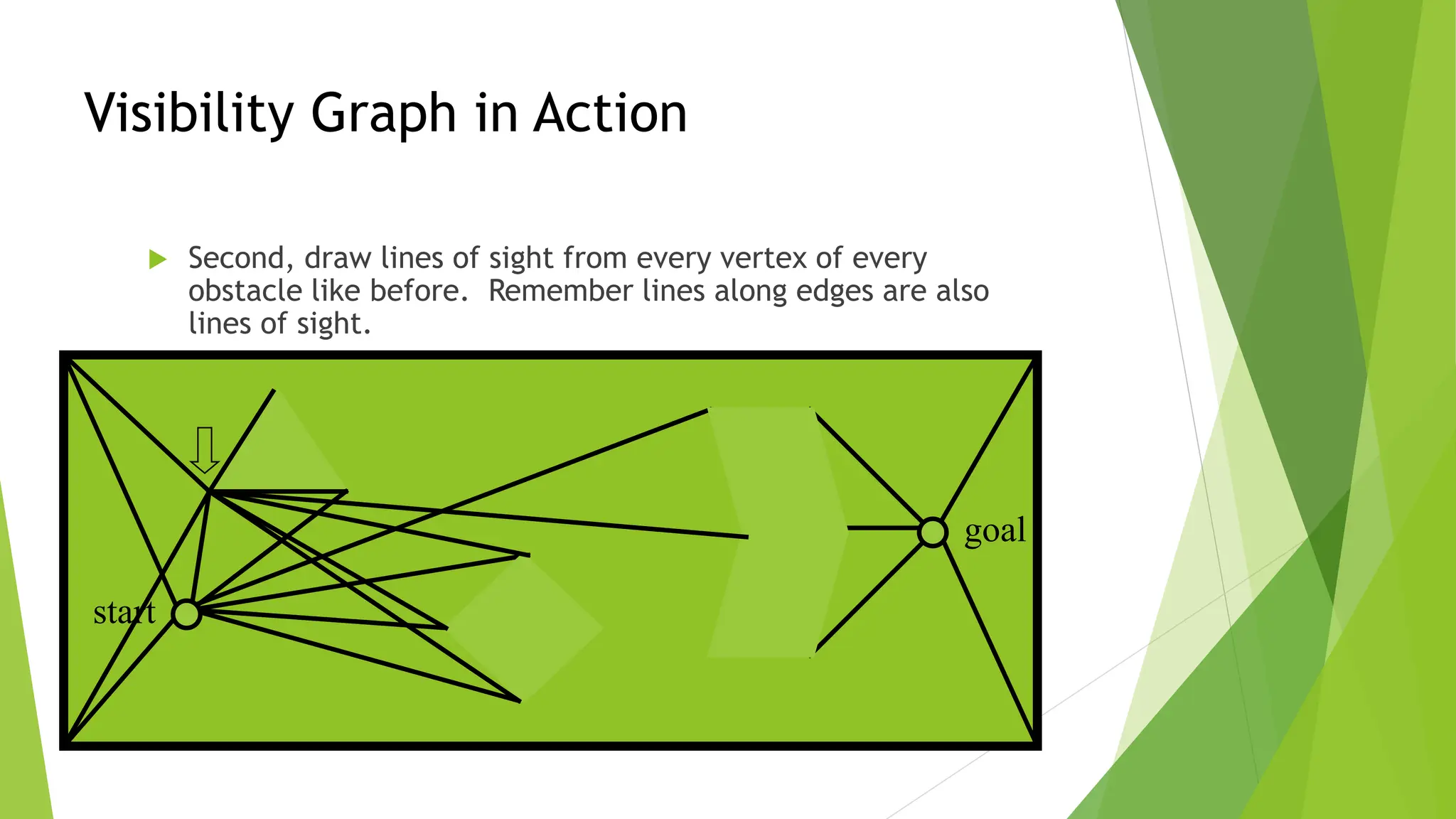
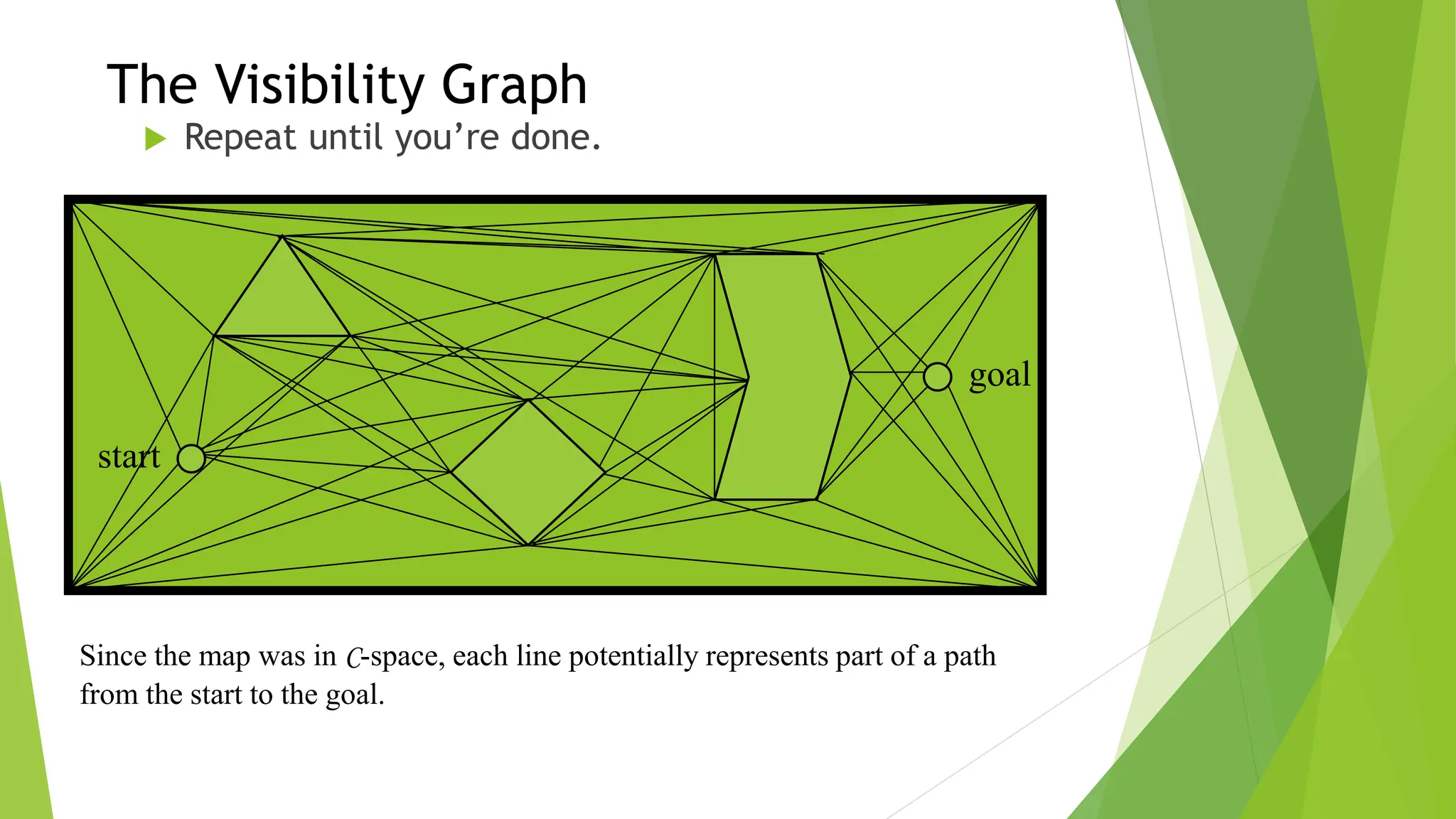
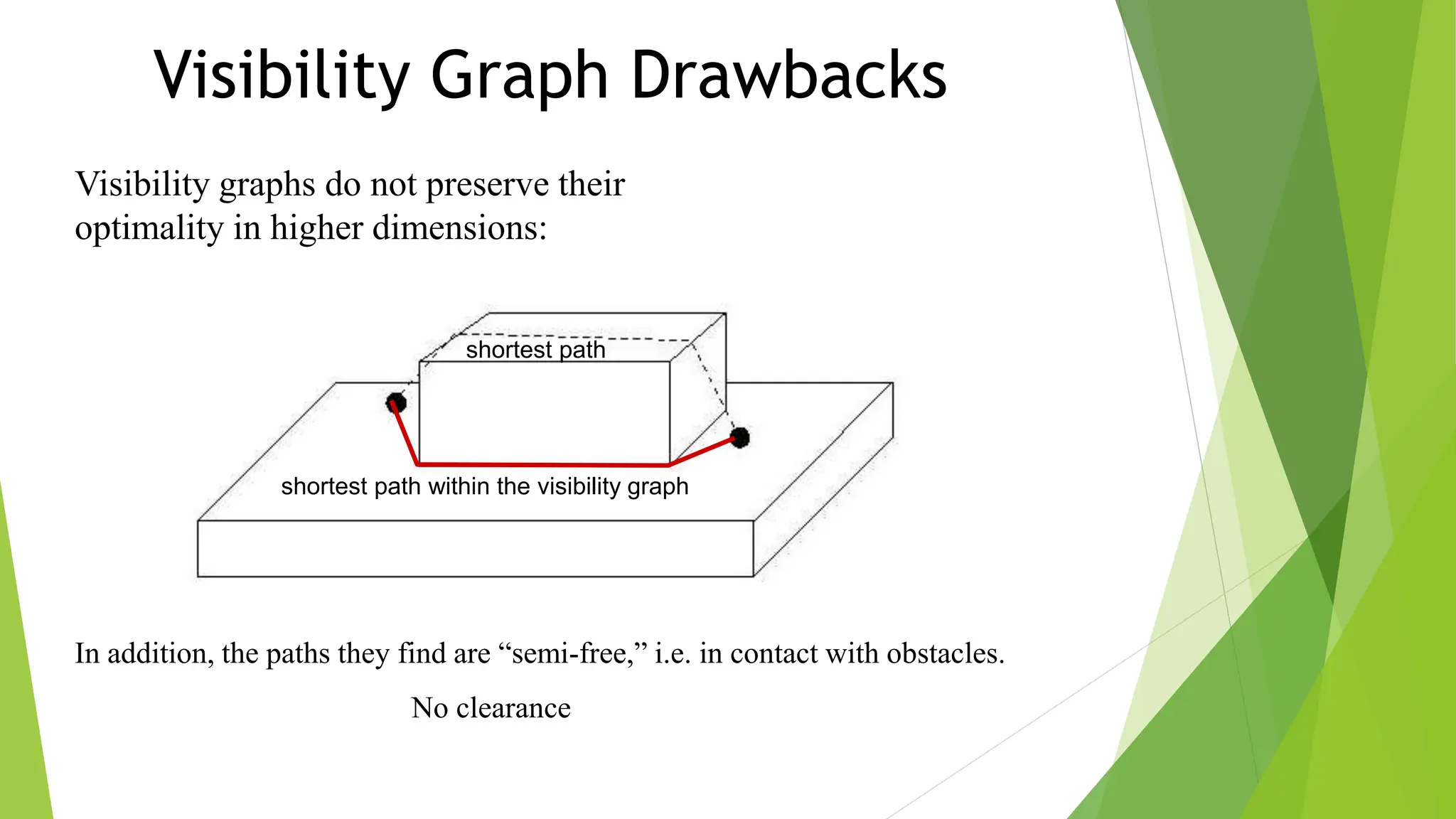
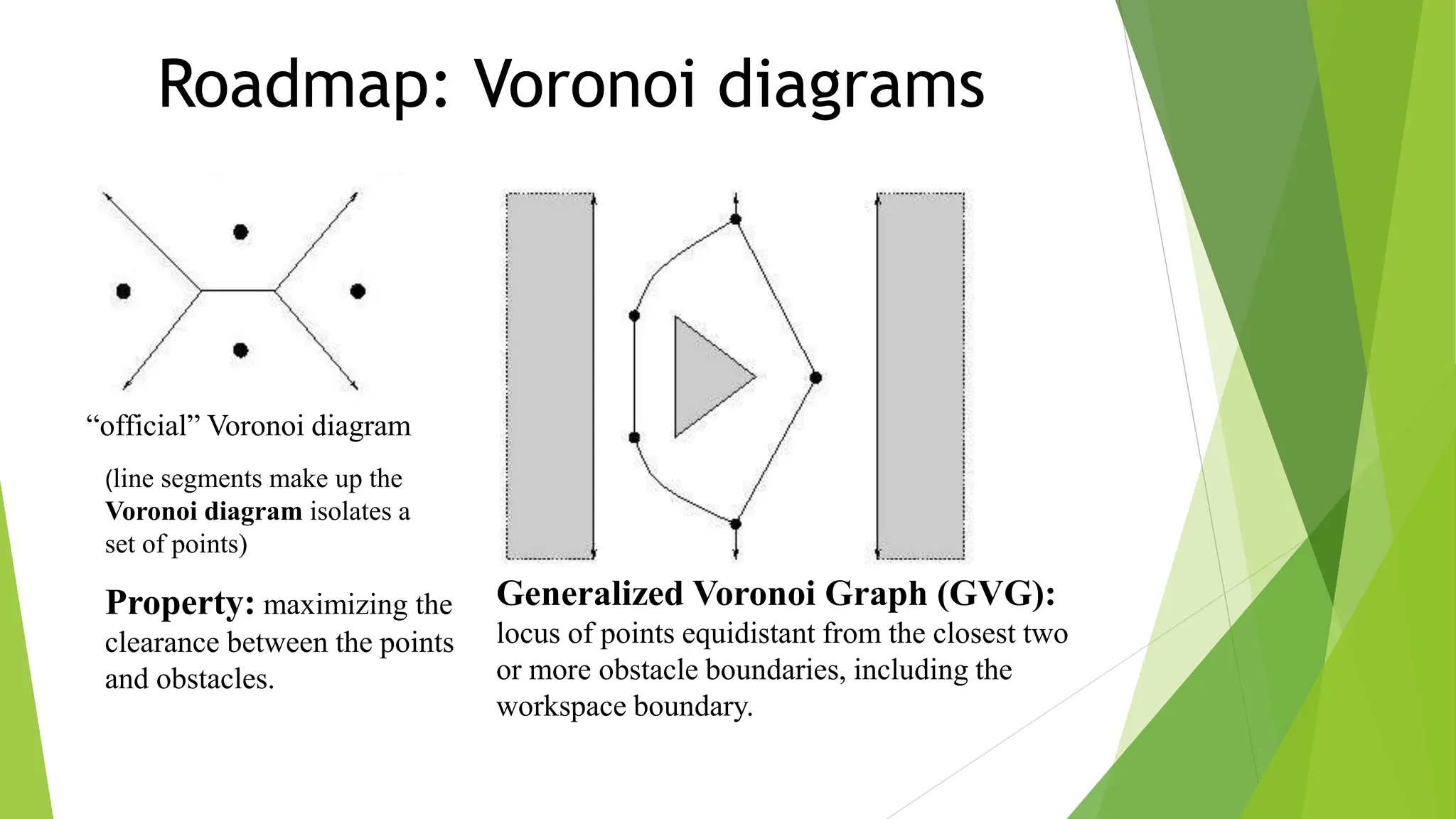
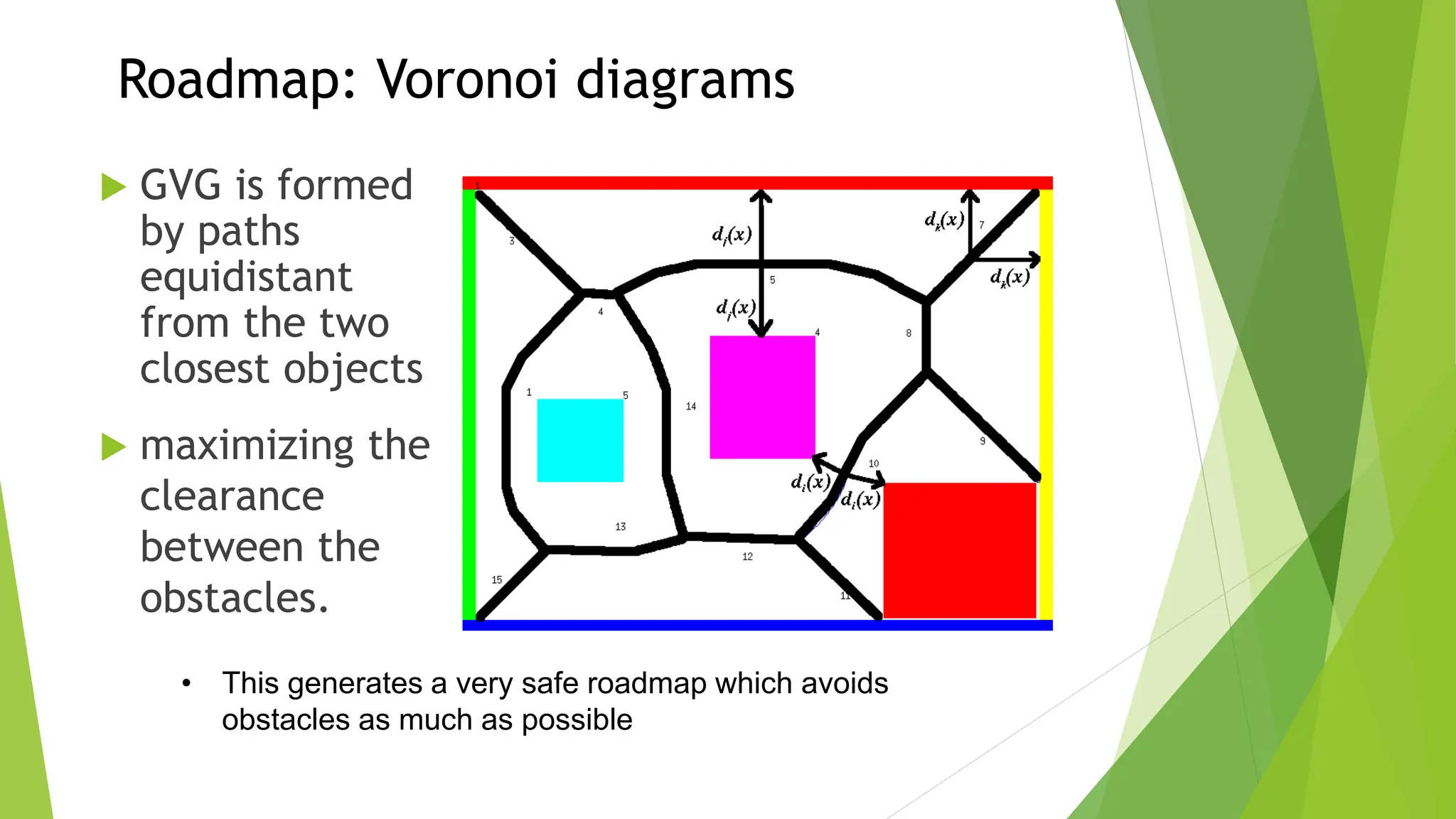
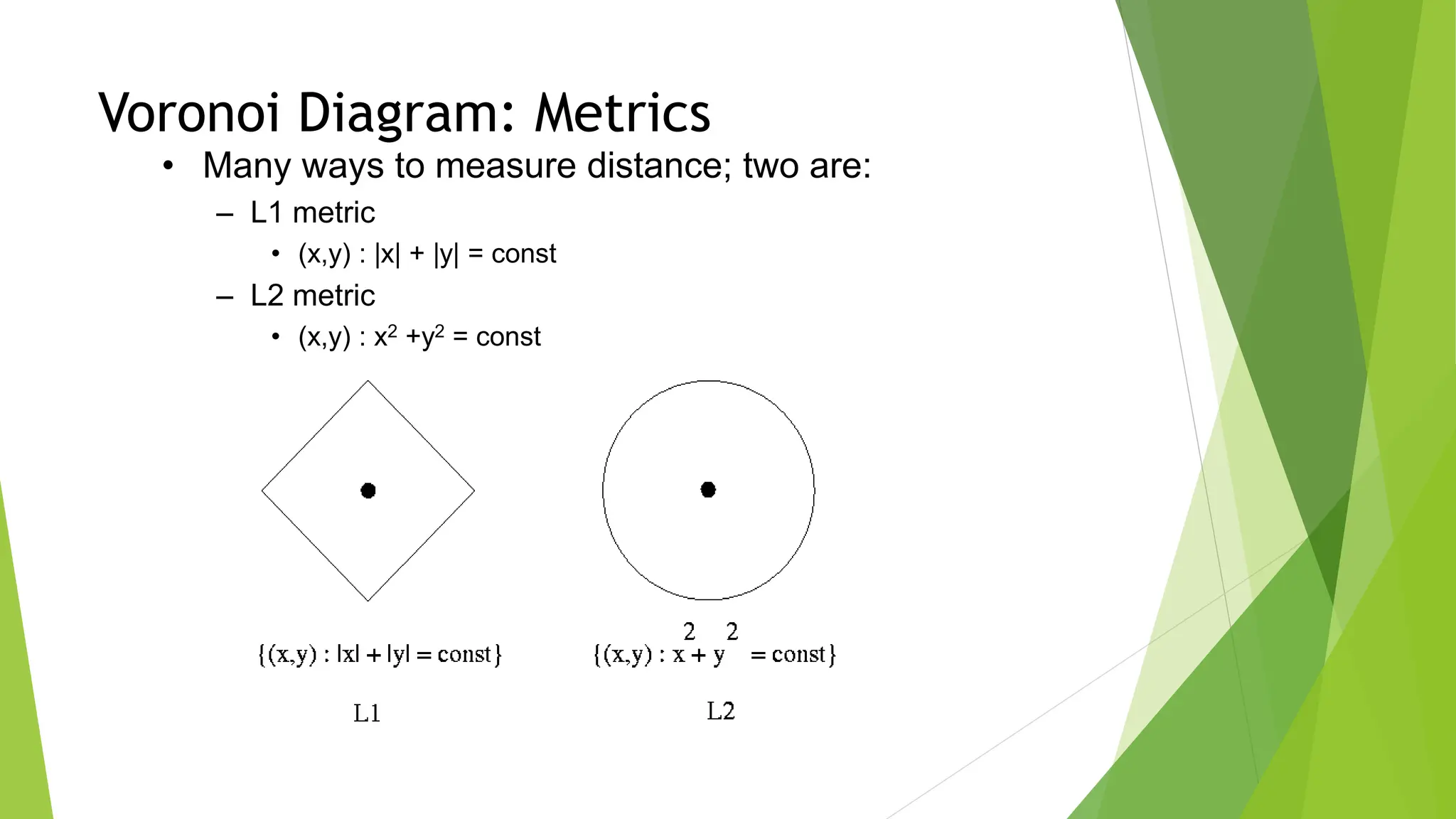
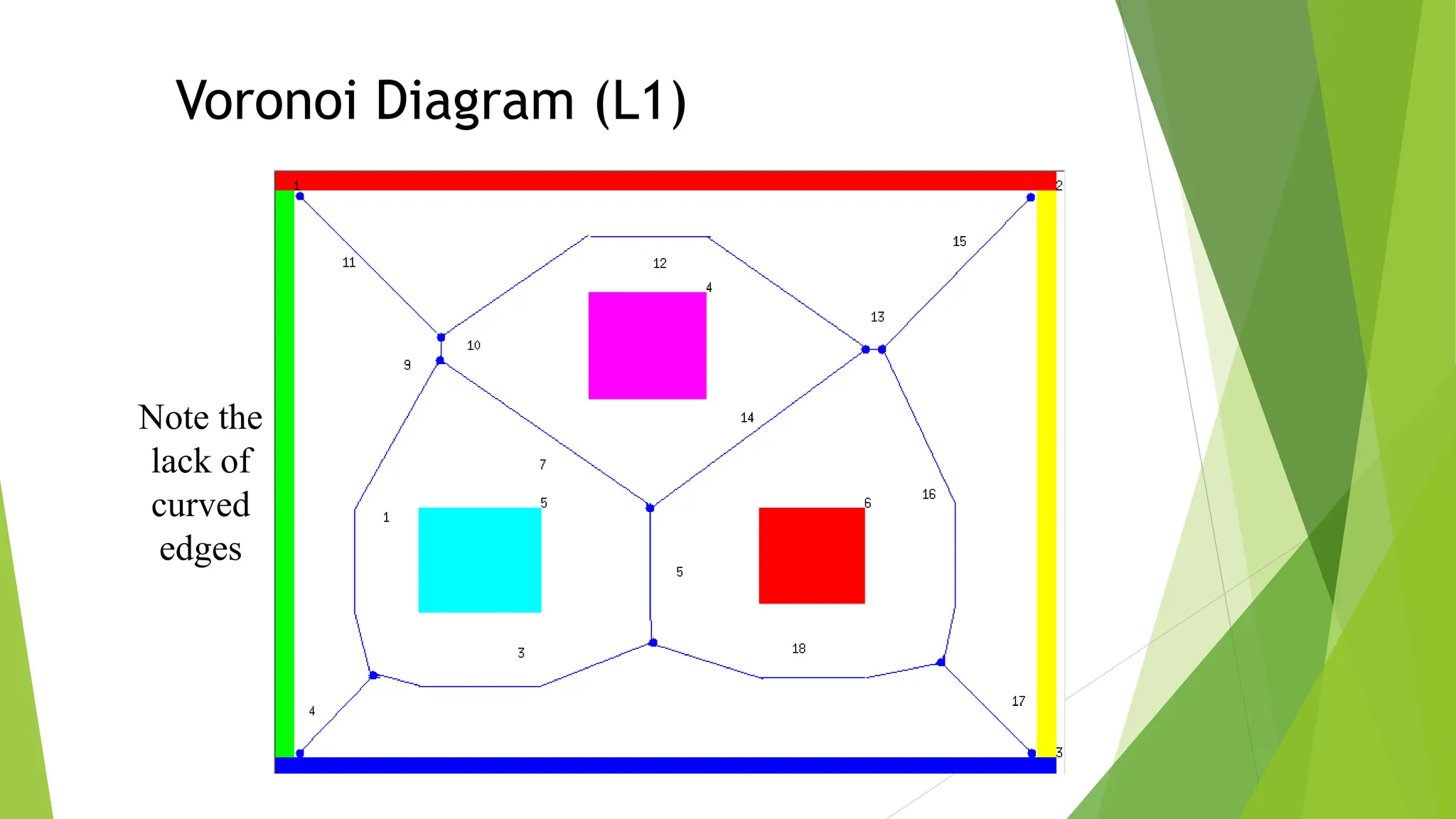
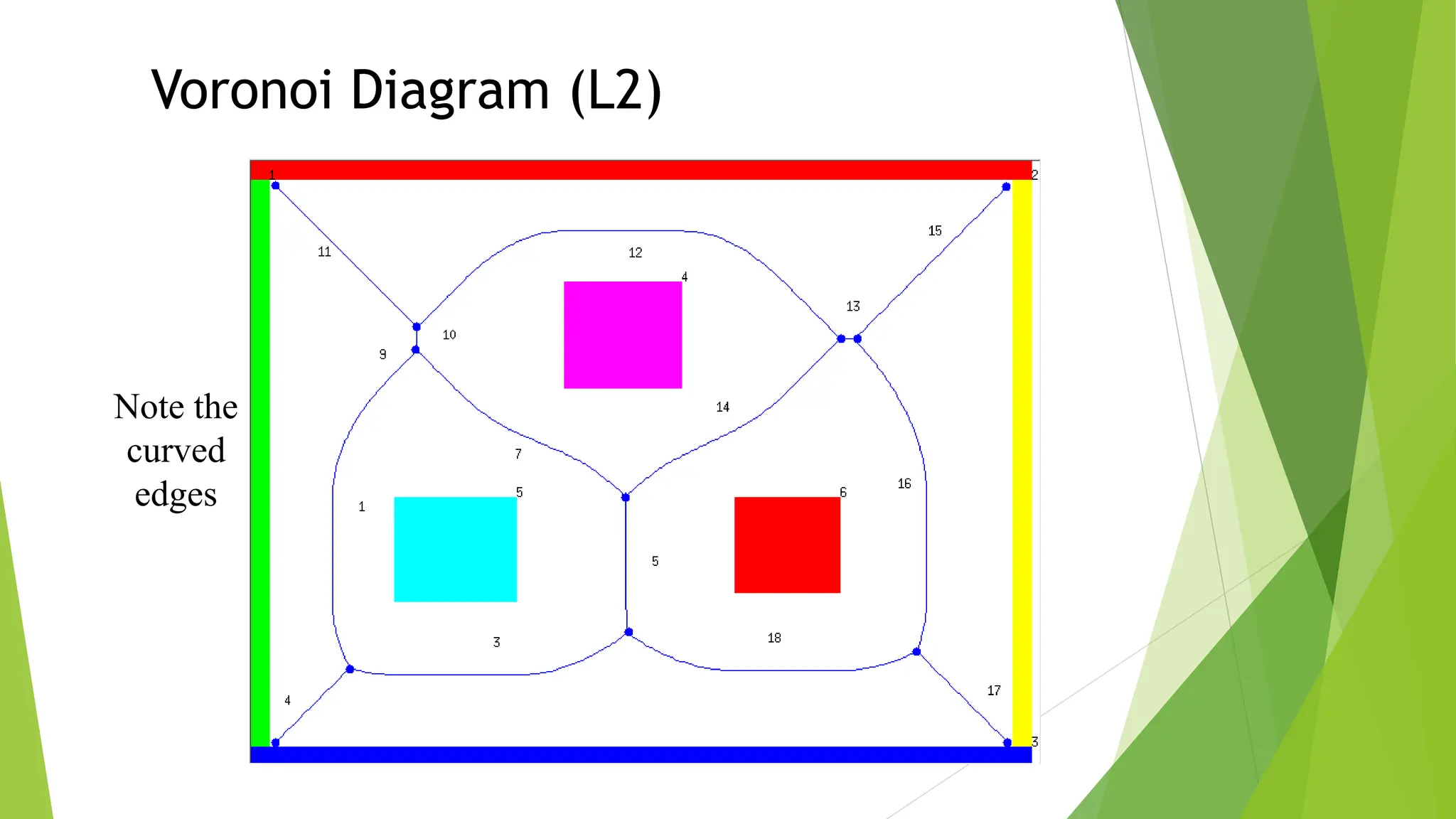
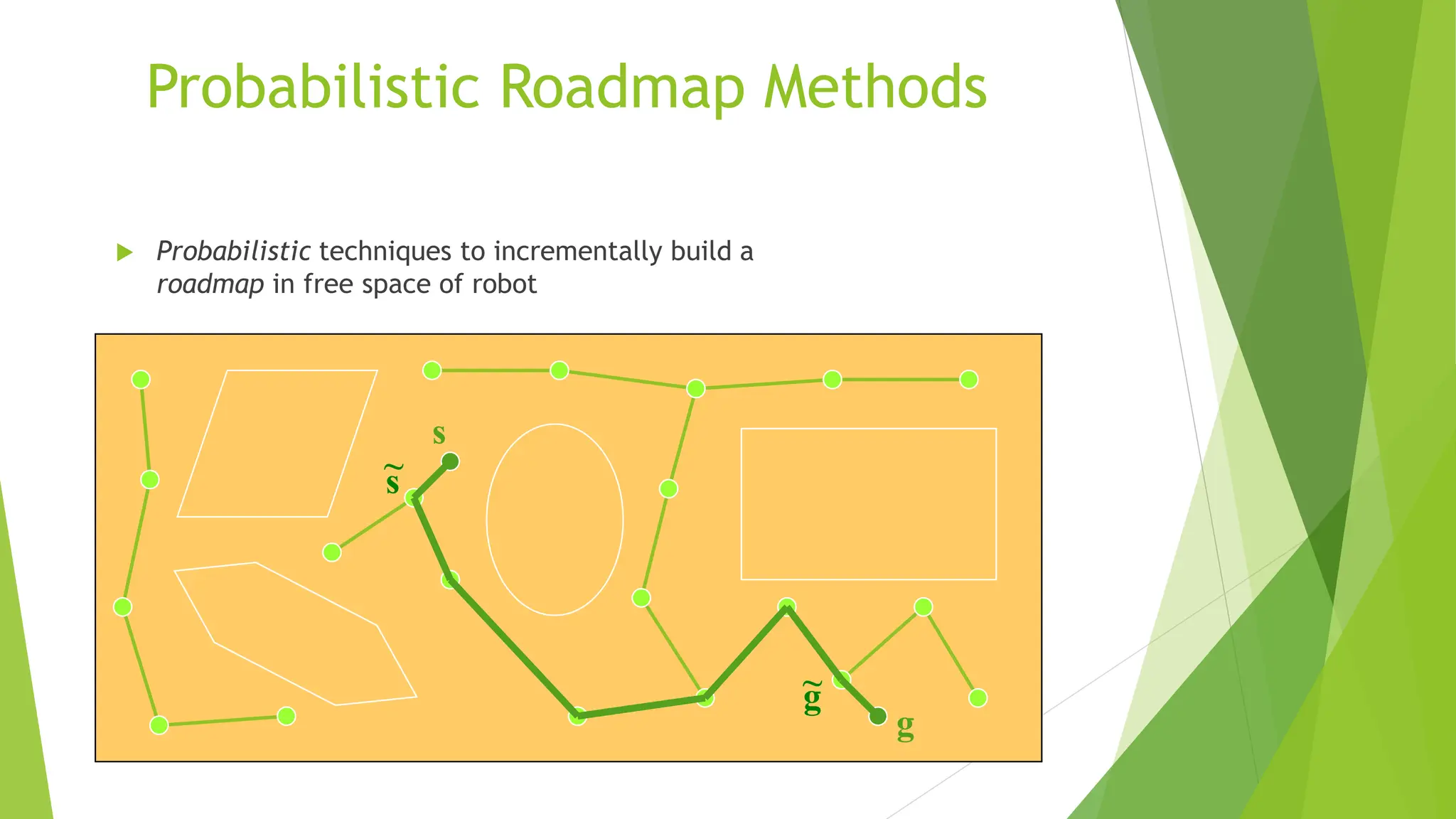
2) Using roadmap approaches like visibility graphs or Voronoi diagrams to reduce the high-dimensional C-space to a graph that can be searched to find paths.
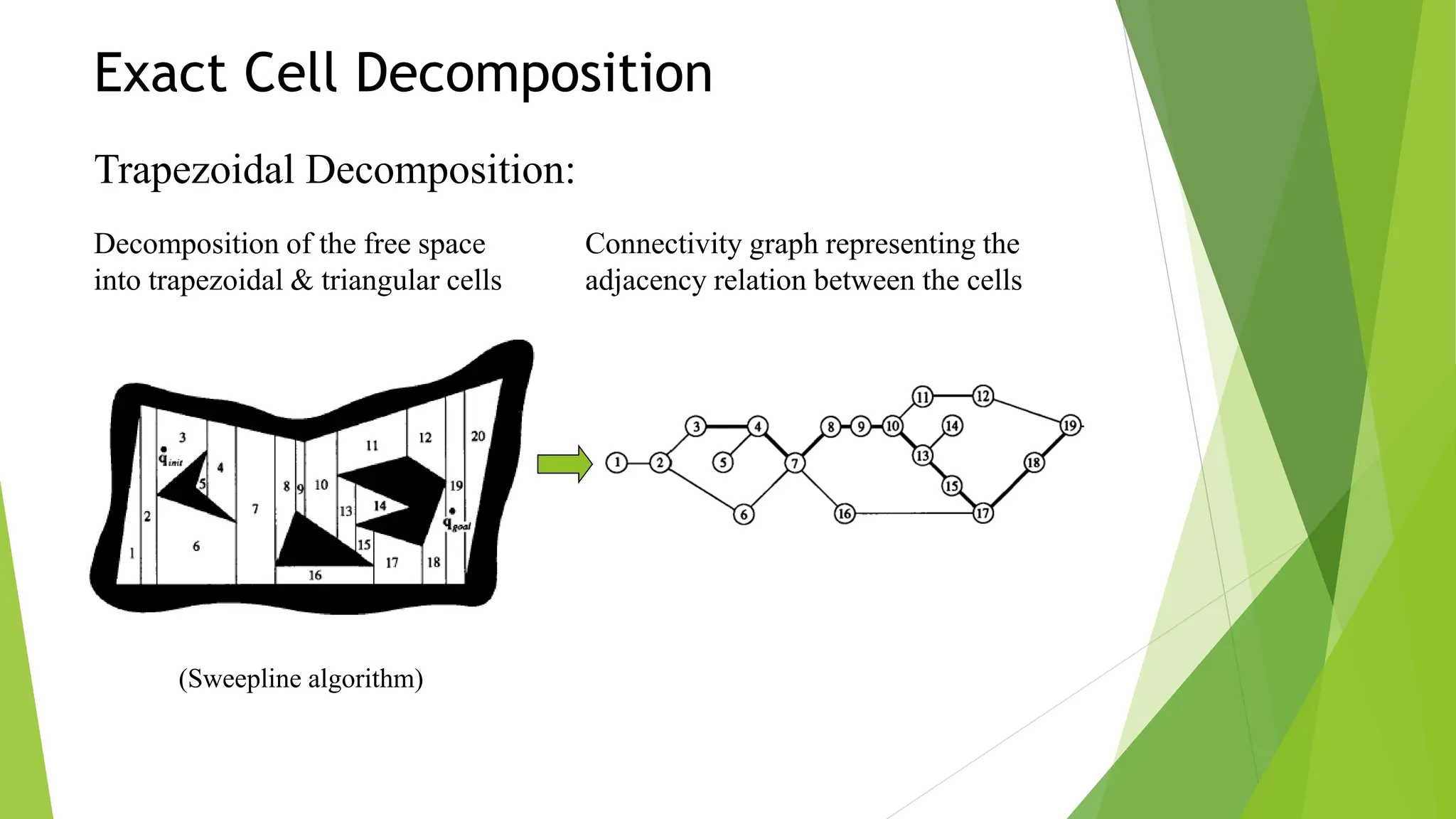
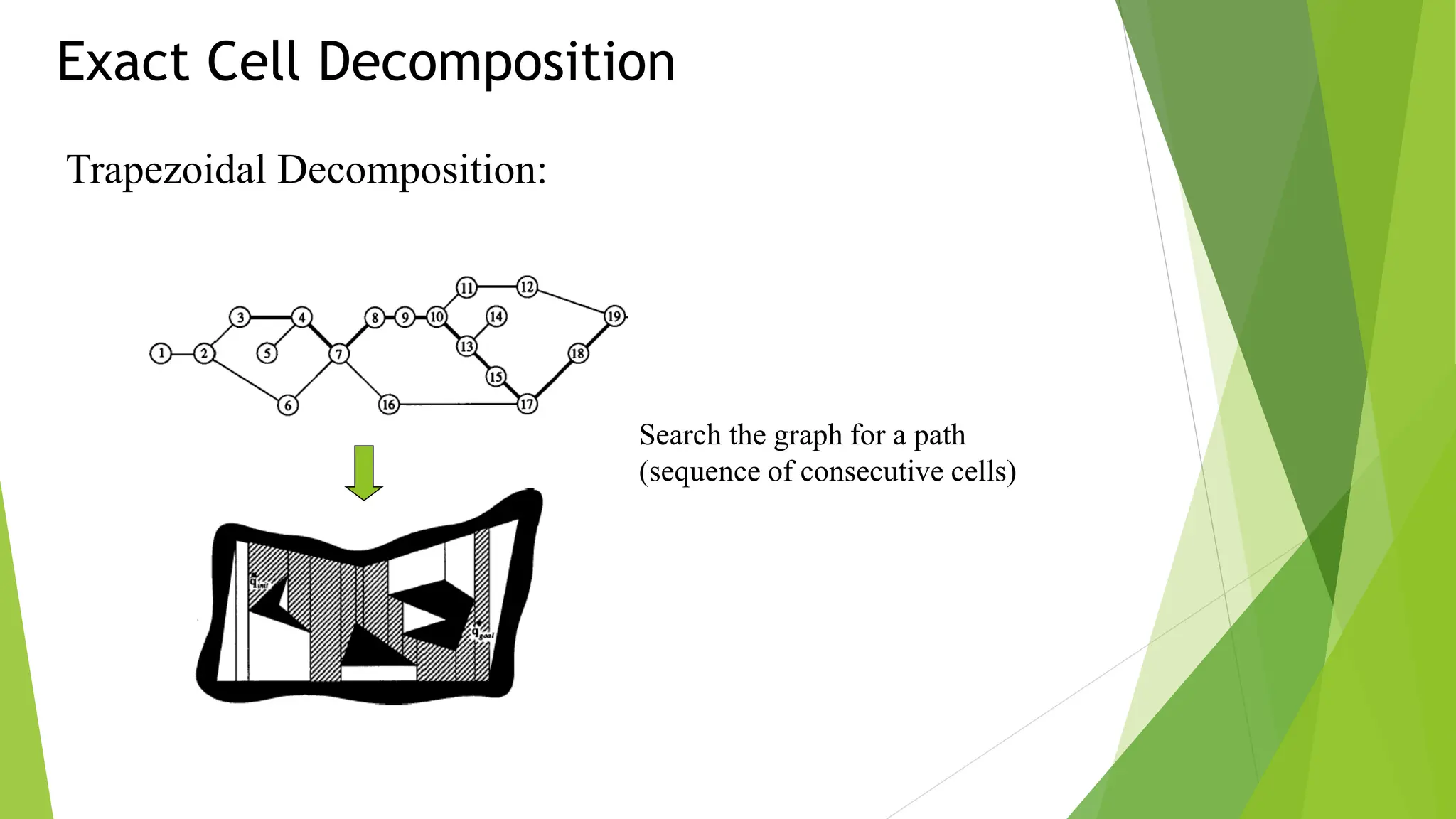
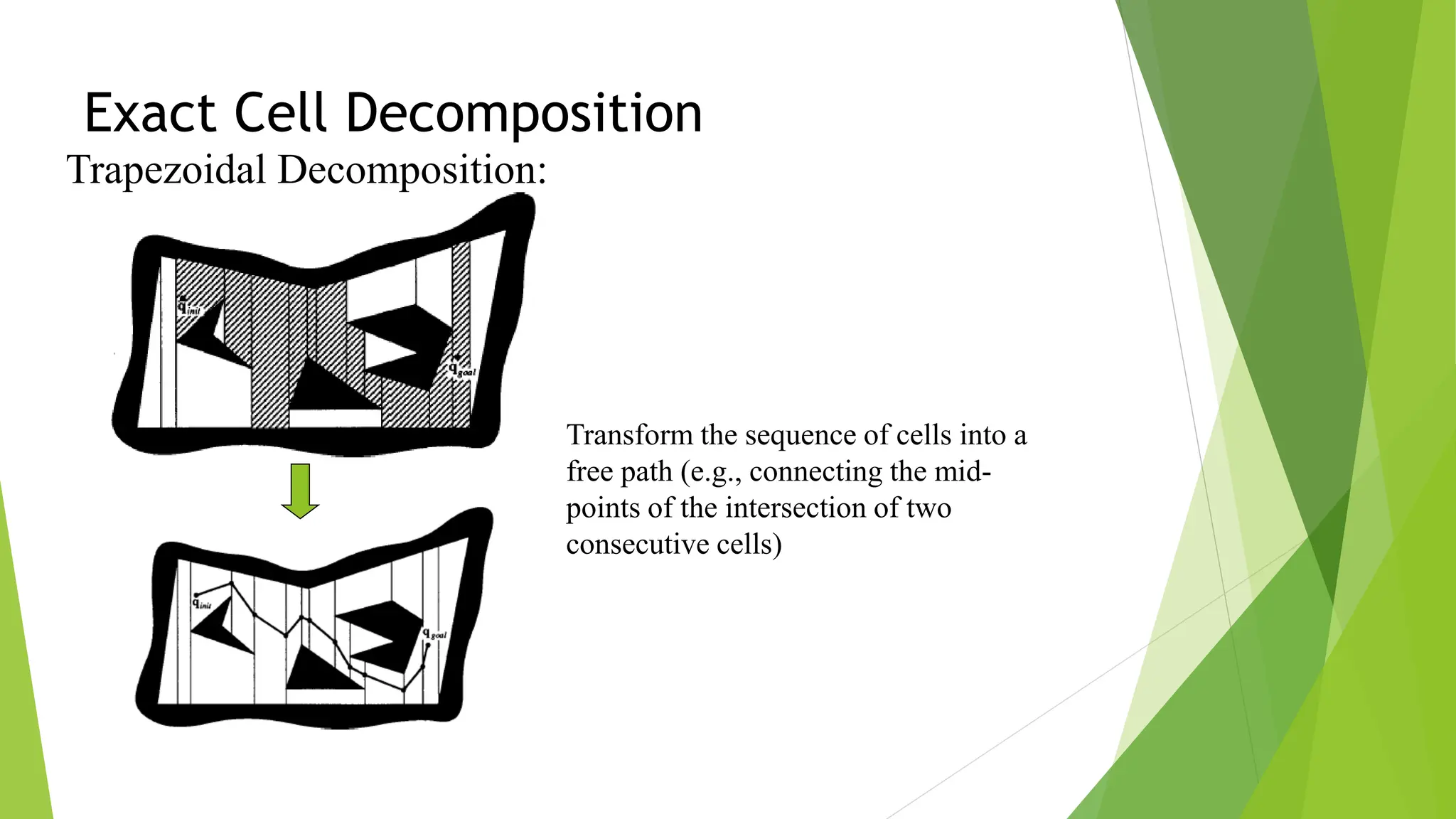
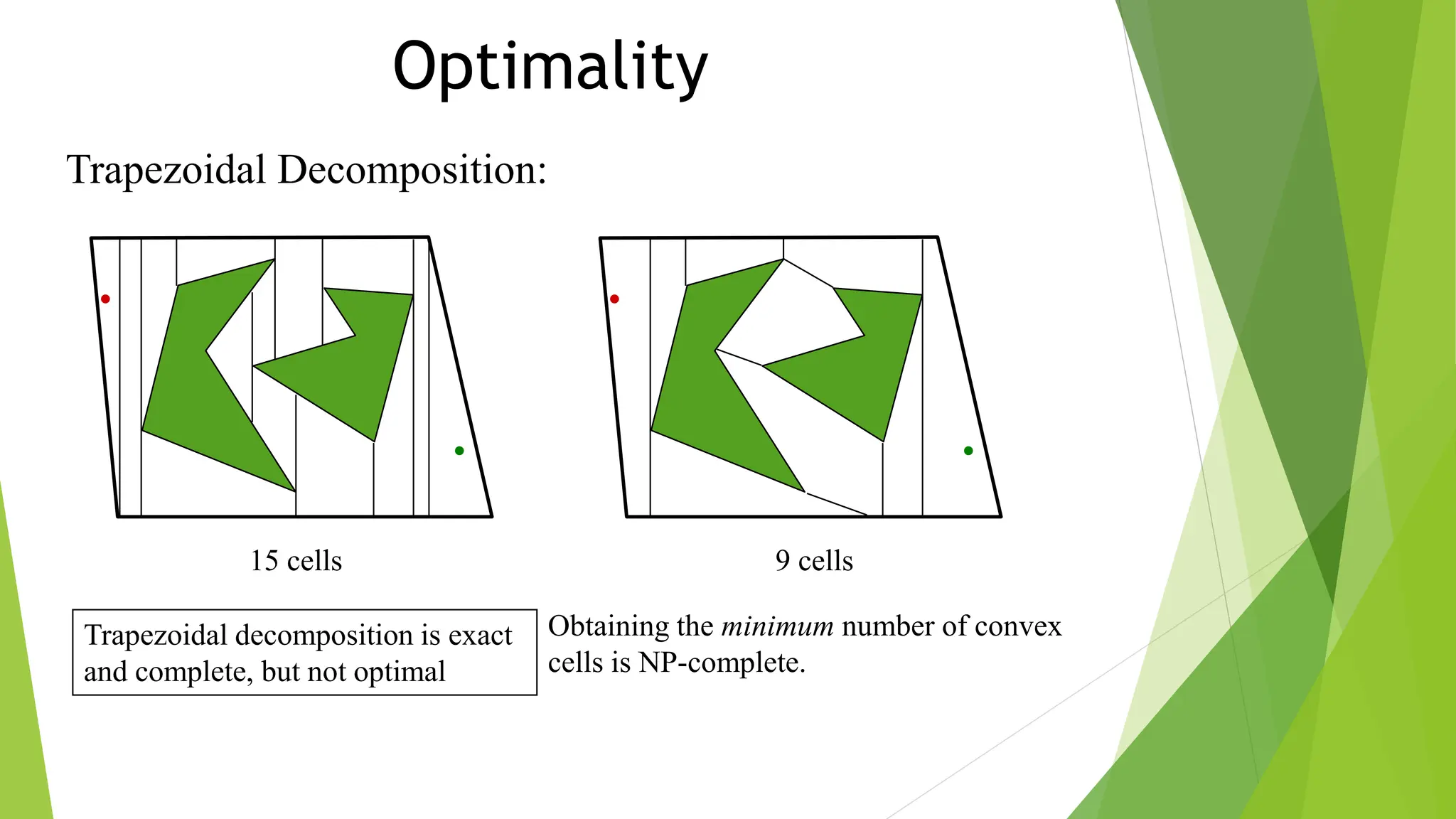
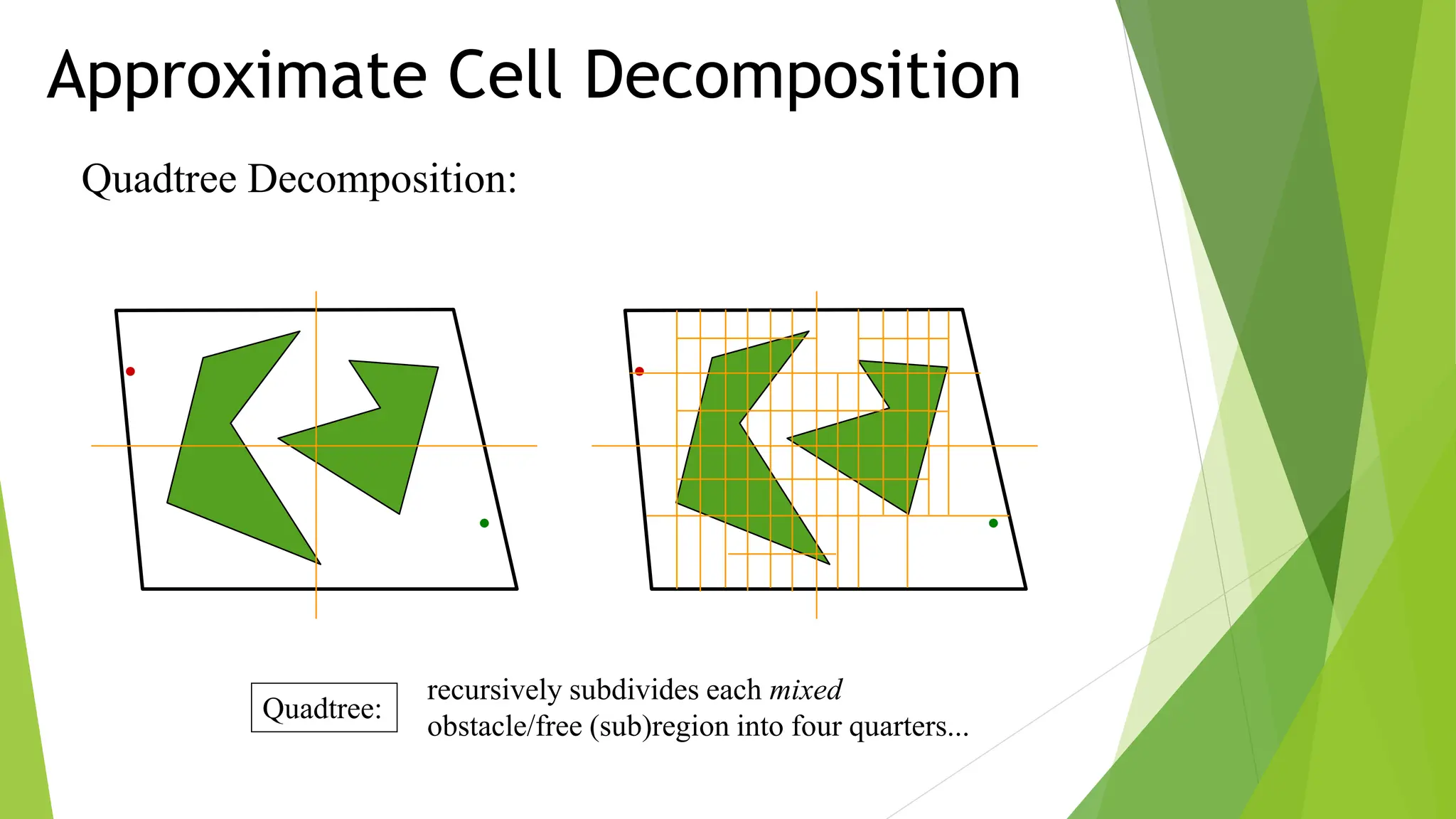
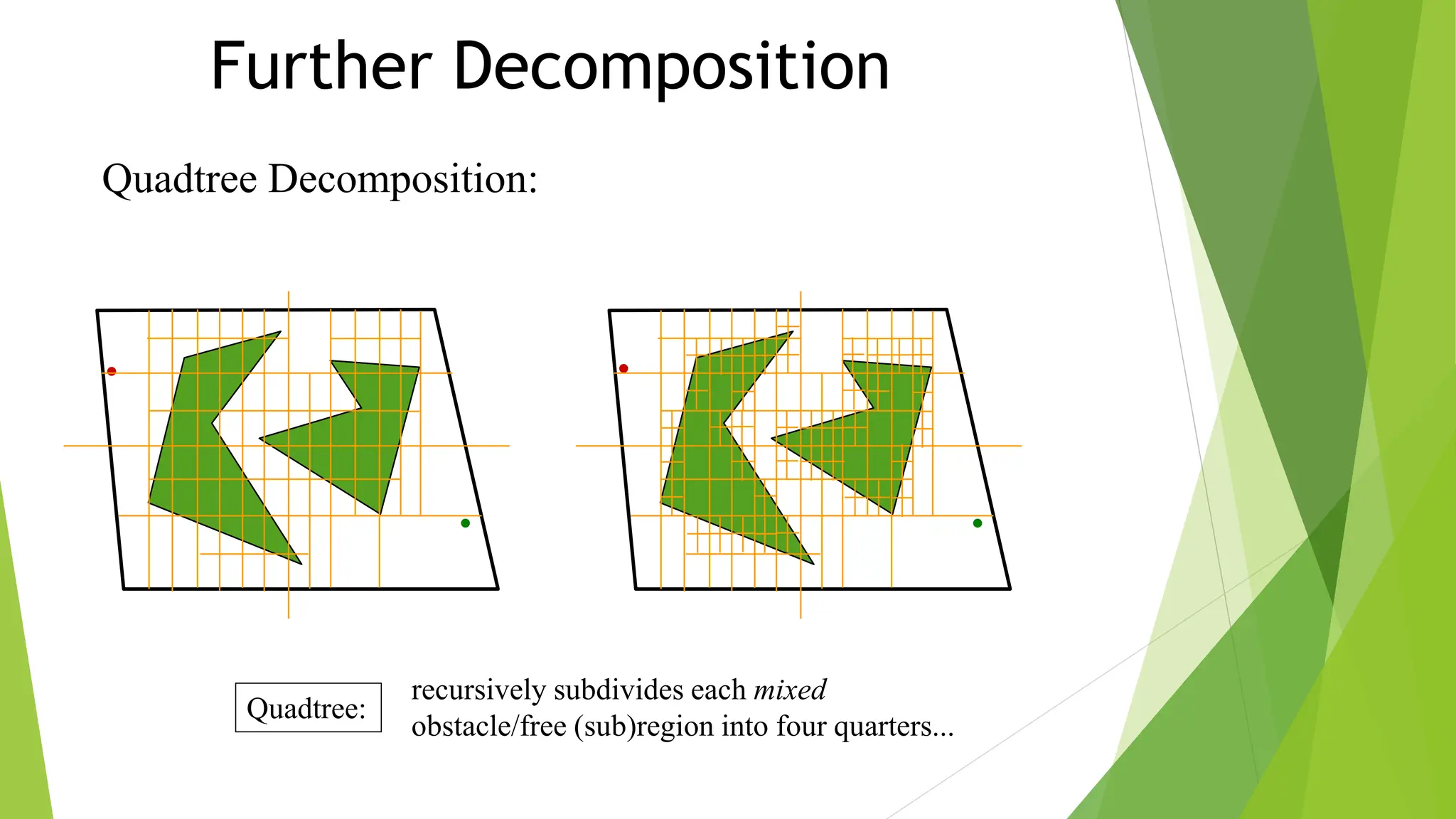
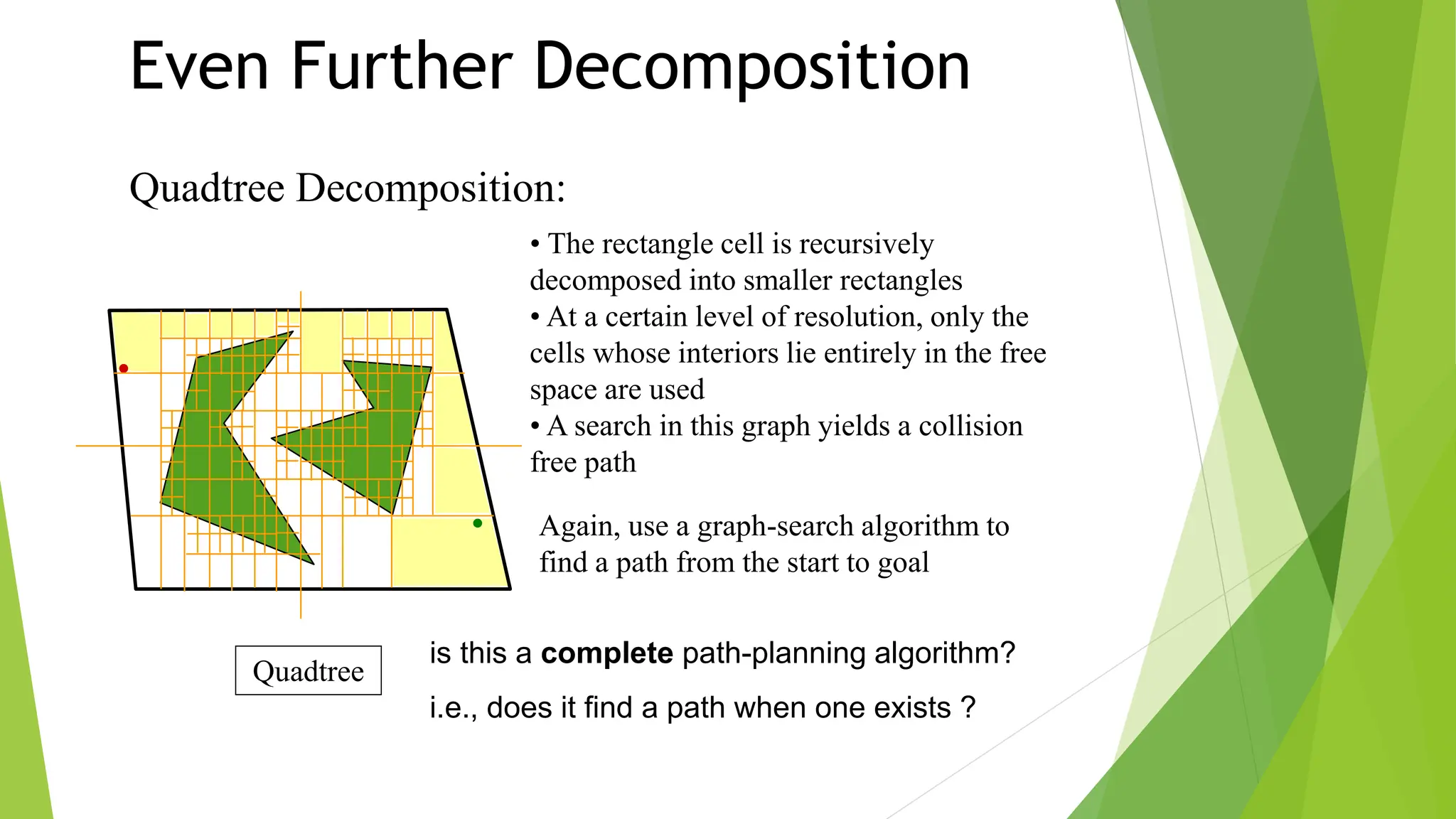
3) Cell decomposition methods like trapezoidal decomposition or quadtree decomposition that partition the C-space into simple cells and connect adjacent free cells to form a connectivity graph.
4) Prob