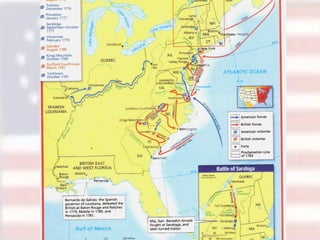
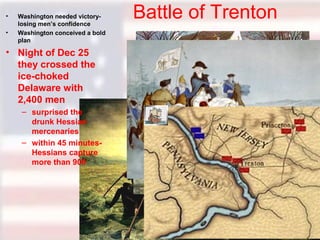
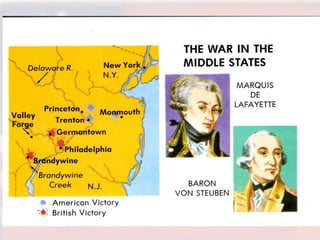
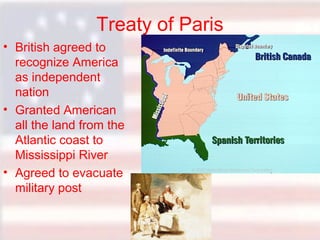
Committees of Correspondence warned neighboring colonies about incidents with the British. Paul Revere and others warned the militia about the arrival of British troops in Lexington. At the Battle of Concord, thousands of minutemen assembled and fired at the British from behind stone walls and trees, dropping dozens of Redcoats before they were rescued. This began the divide between Loyalists who supported the king and Patriots who supported independence. The Patriots had advantages of defending their homeland and using guerrilla tactics, while the British had experienced soldiers and strong naval support.