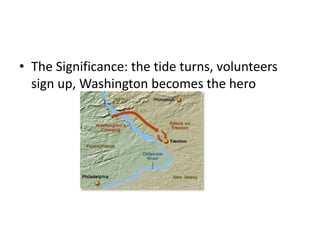
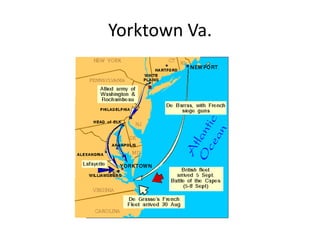
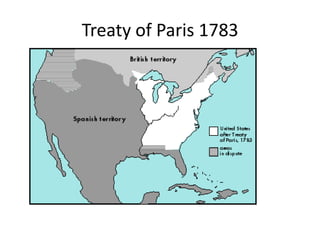
The American Revolution between 1775-1783 saw the colonies struggle to win independence from Britain through war while also working to establish stable state and national governments. It involved both a military conflict with Great Britain and an internal political struggle. Key events included the Declaration of Independence in 1776, difficulties financing the war under the weak Articles of Confederation, pivotal American victories at Trenton, Princeton, Saratoga, and Yorktown, and eventual recognition of American independence in the 1783 Treaty of Paris after over seven years of war. The outcome was influenced by factors like America's use of guerilla tactics on its home turf against Britain's conventional army, the colonists' resolve to fight for freedom and self-govern