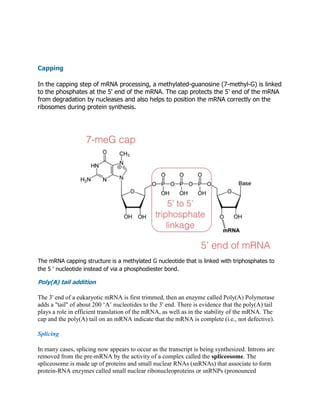
The three main processing steps for eukaryotic messenger RNAs are:
1. Capping at the 5' end, which involves adding a methylated guanosine nucleotide linked by triphosphates rather than a phosphodiester bond.
2. Addition of a poly(A) tail of about 200 adenine nucleotides to the 3' end, which aids in translation and stability.
3. Splicing to remove introns by a spliceosome complex that recognizes splice junction sequences to correctly cut out introns and join exons.