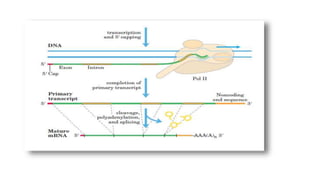
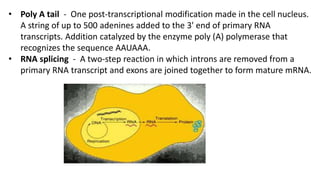
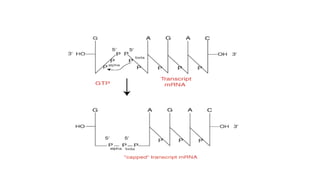
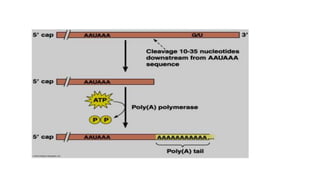
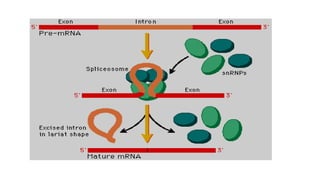
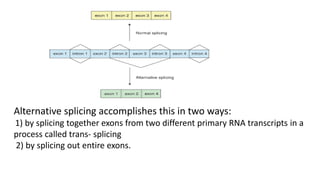
Post-transcriptional modifications help process primary transcripts into mRNA in eukaryotes. This involves 5' capping, addition of a poly-A tail, and splicing of introns. 5' capping adds a guanine cap to protect the 5' end from degradation. Poly-A polymerase adds around 200 adenine bases to the 3' end. Splicing removes introns and ligates exons by the spliceosome, producing mature mRNA that can be translated into protein. Alternative splicing allows different mRNA and protein isoforms from a single gene.