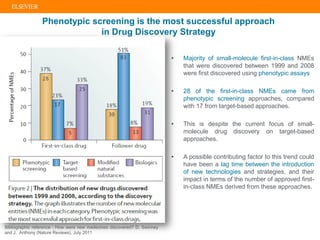
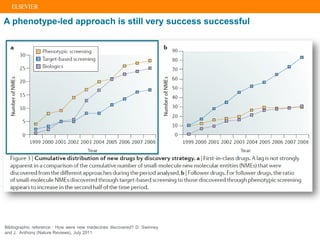
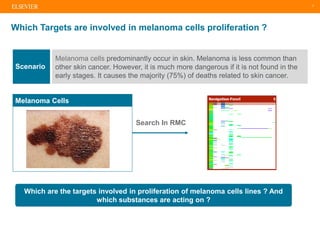
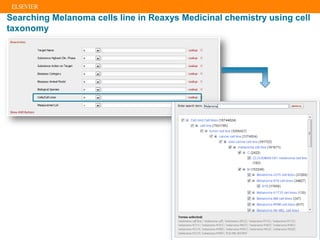
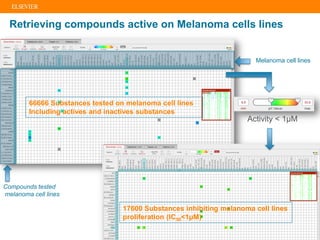
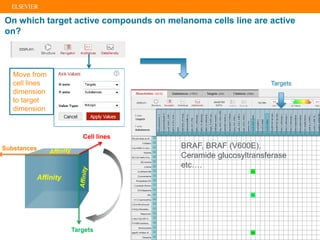
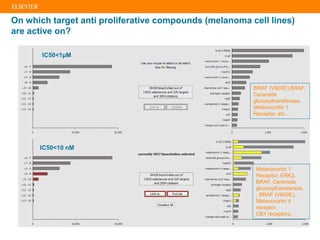
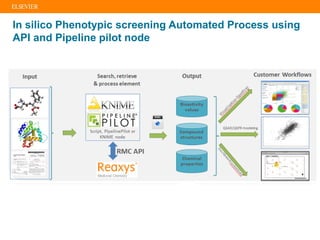
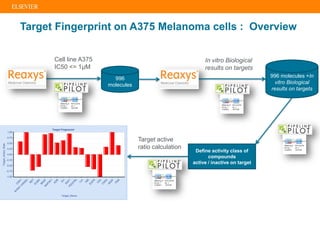
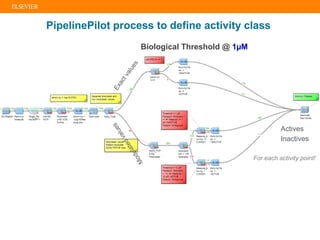
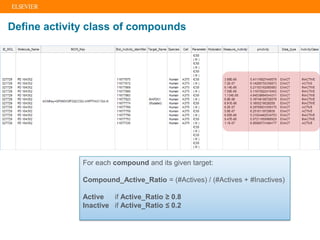
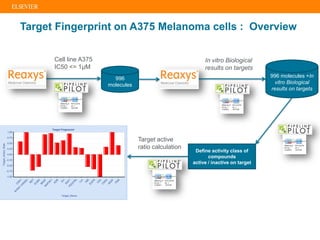
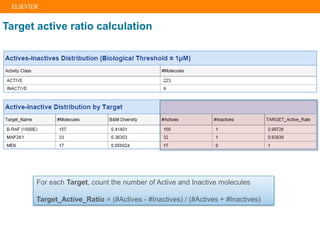
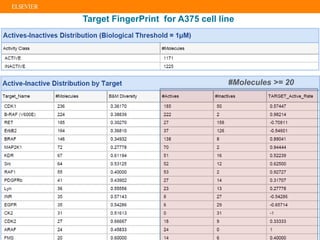
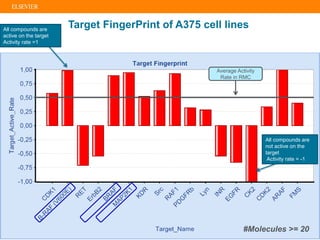
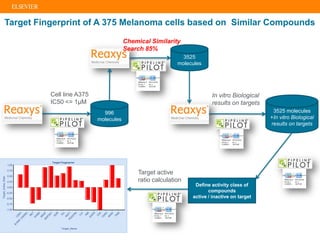
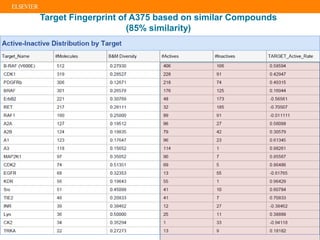
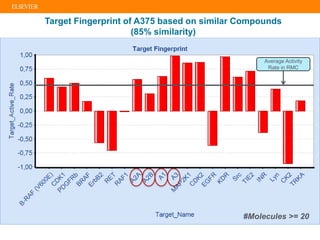
The document describes building an in-silico phenotypic screening approach using Reaxys. Phenotypic screening identifies compounds that produce a biological response in cells and has proven successful in drug discovery. The approach develops a target fingerprint for disease-specific cell lines to identify pharmacological targets and molecular mechanisms of action. As a scenario, the target fingerprint is generated for melanoma A375 cells based on 996 compounds with IC50 < 1μM, identifying targets like BRAF, ERK2 and melanocortin receptors. Literature also links the melanocortin receptor A3R to reduced proliferation in A375 cells.