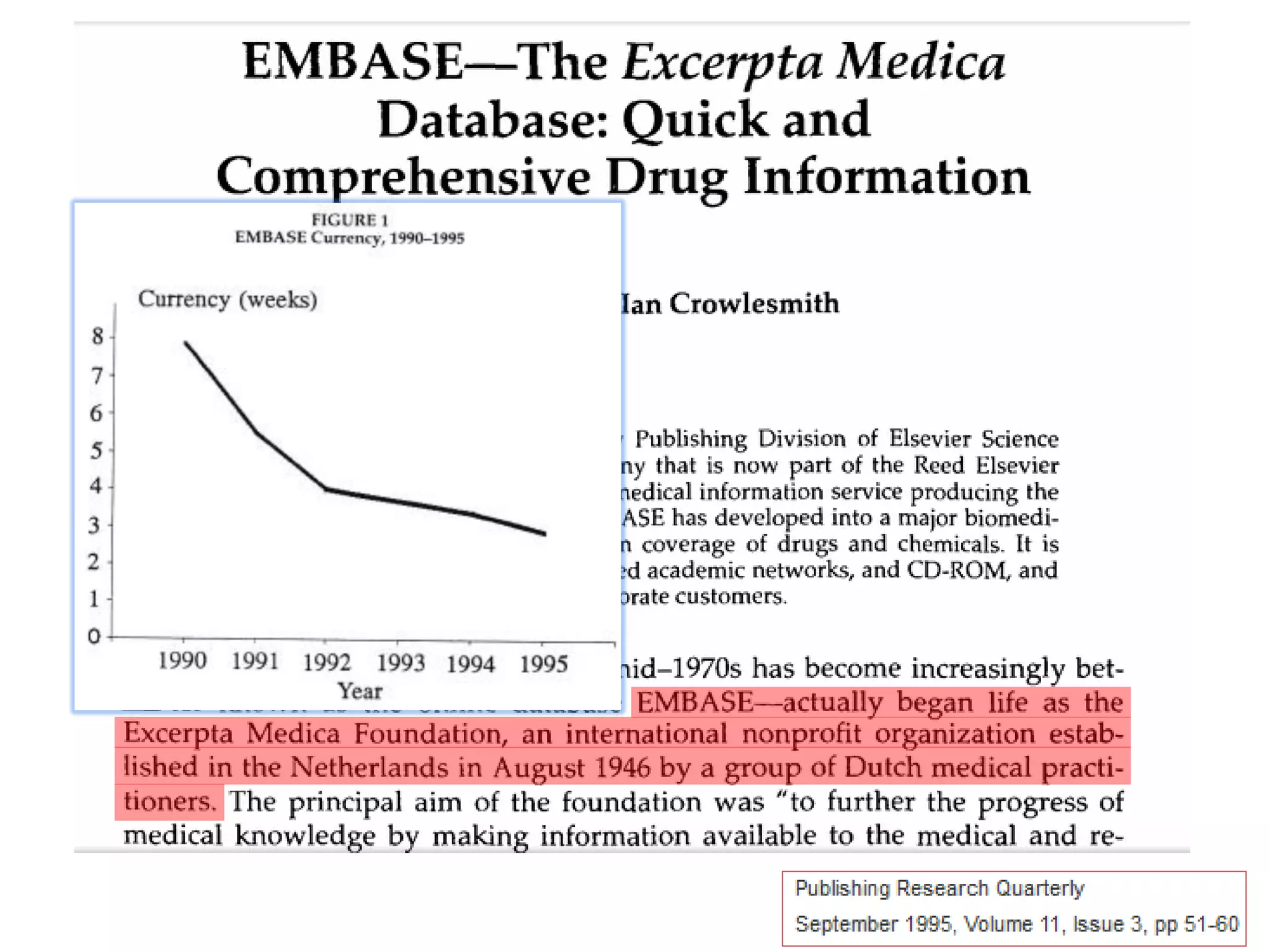
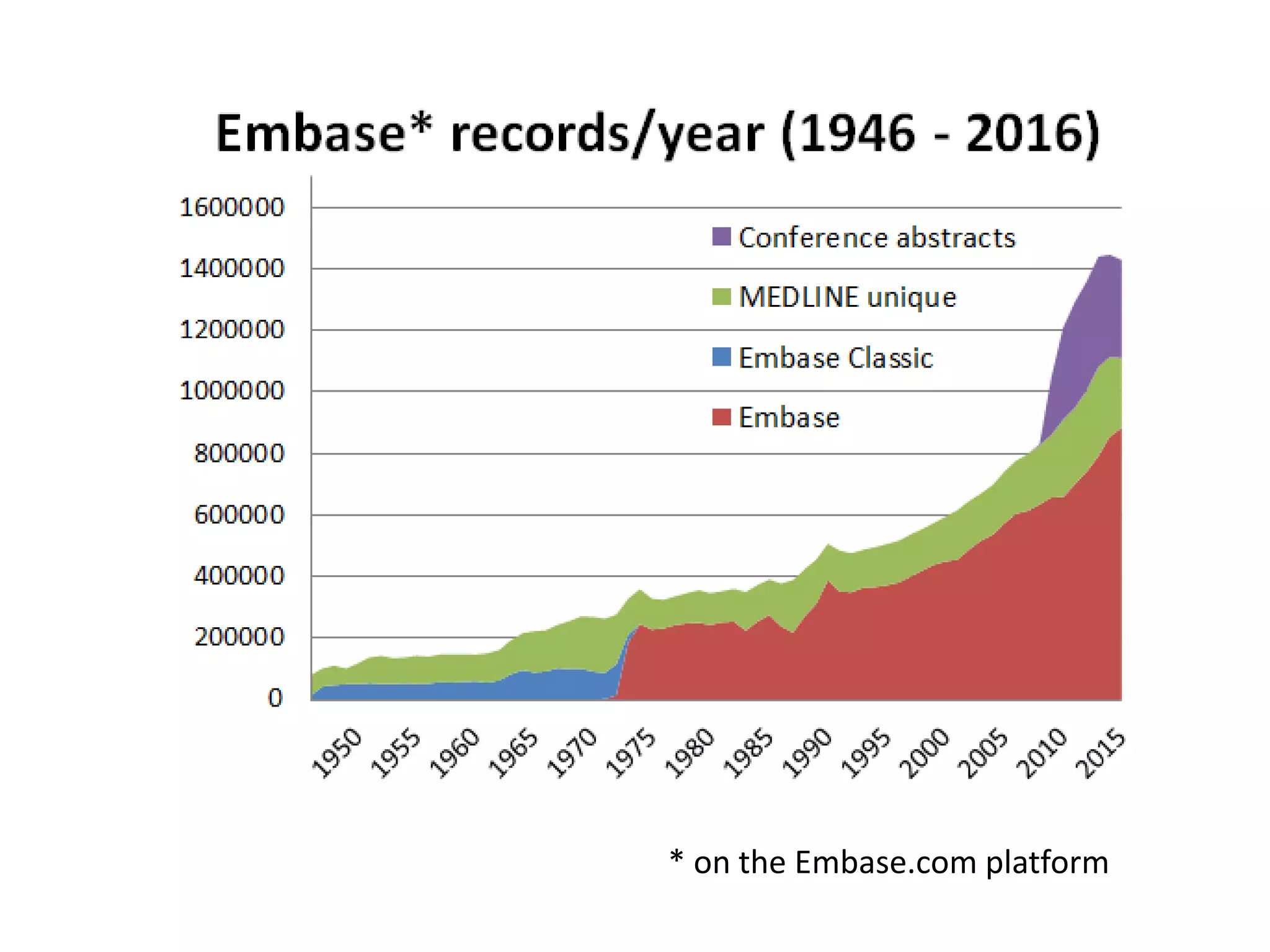
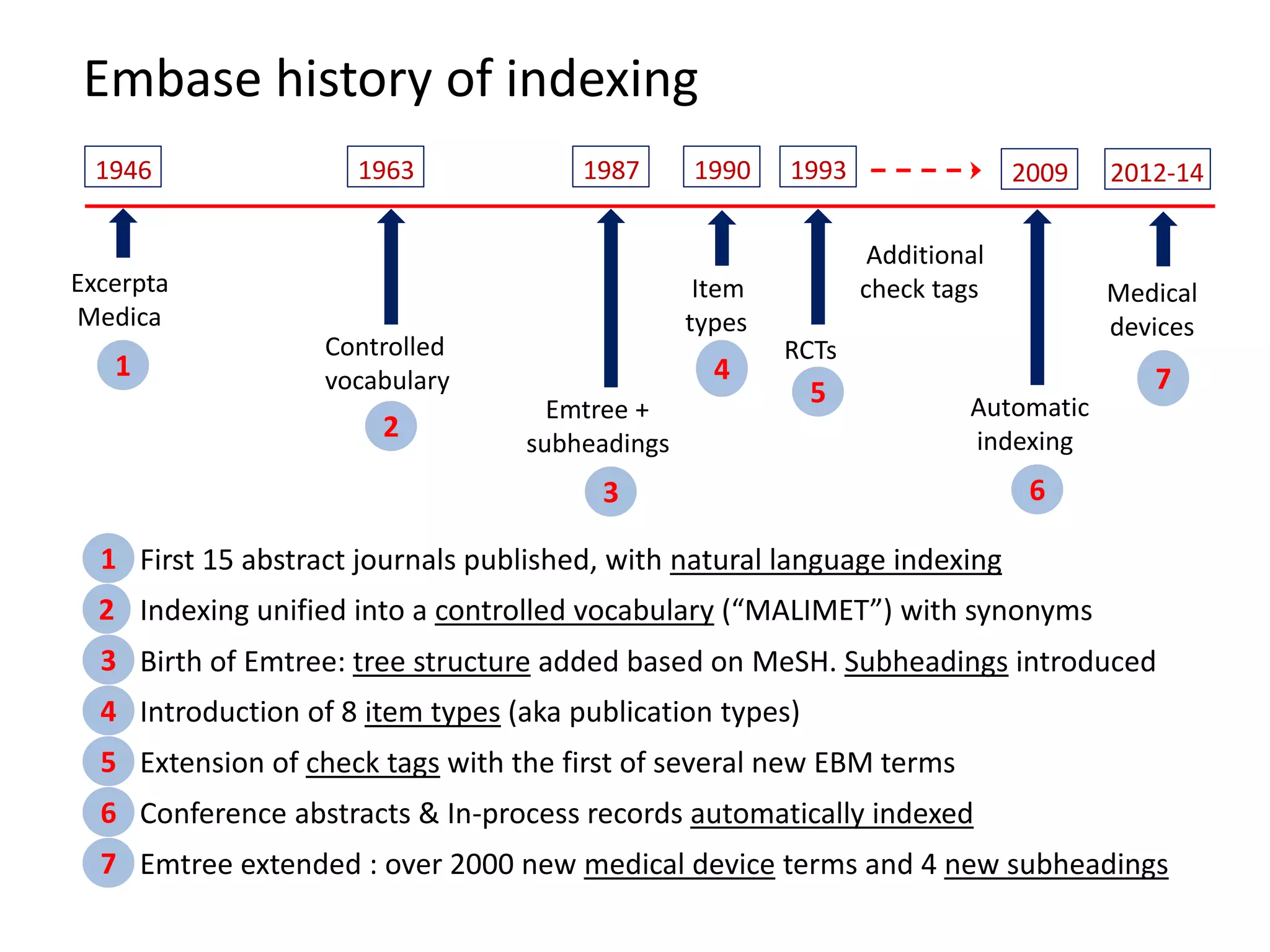
Embase began in 1946 as Excerpta Medica, founded to provide medical abstracts. It was acquired by Elsevier in 1971 and became available online in 1978. Key developments included introducing a controlled vocabulary called Emtree in 1987 and adding item types and check tags for evidence-based medicine in 1990. Currently, Embase indexes articles in great depth using natural language and extensively covers drugs and devices. The taxonomy Emtree is regularly updated to reflect new terms.