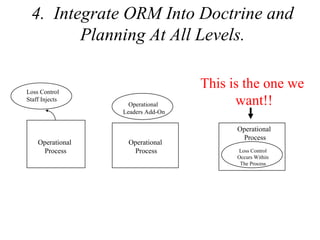
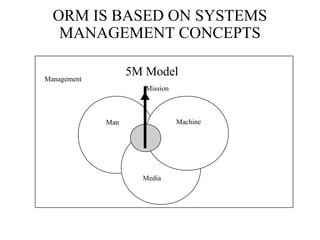
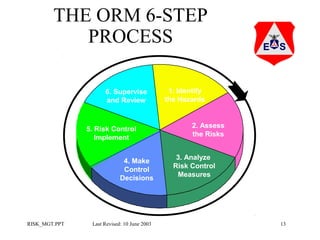
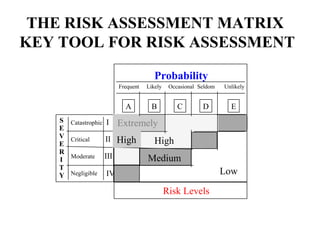
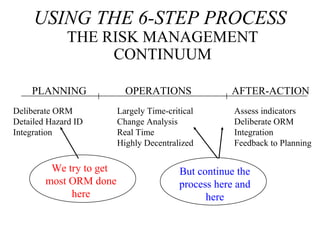
This document provides an overview of operational risk management (ORM). It describes the 6-step ORM process which includes identifying hazards, assessing risks, analyzing risk control measures, making control decisions, implementing controls, and supervising/reviewing. The goal of ORM is to systematically balance risk costs and benefits to ensure necessary risks are taken while preventing losses. Tools like risk matrices and various hazard identification techniques help objectively evaluate and mitigate risks.