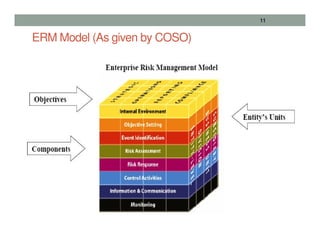
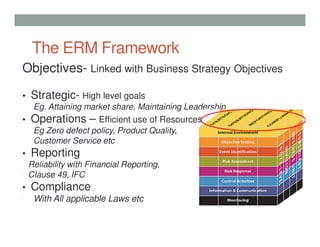
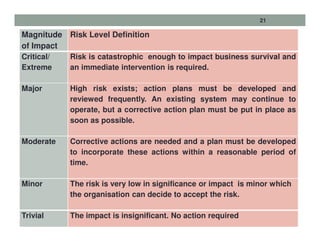
This presentation provides an overview of enterprise risk management (ERM). It defines risk and ERM, outlines the key components of an ERM framework including risk identification, assessment, and response. It discusses the roles of management, the board of directors, and internal auditors in ERM. The presentation traces the evolution of risk management from a focus on hazards to a holistic enterprise-wide approach. It emphasizes that strong internal controls are essential to effective ERM.