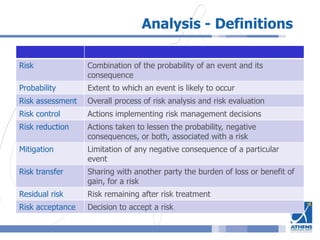
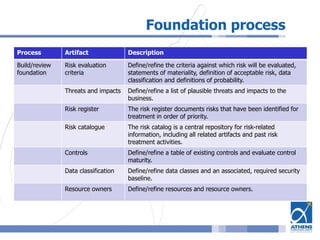
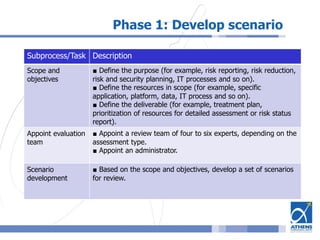
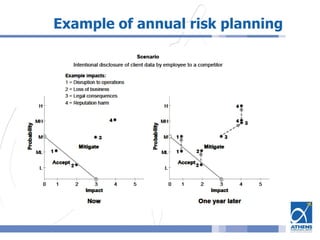
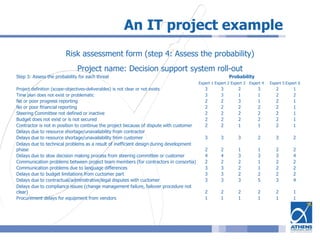
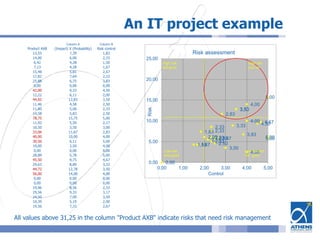
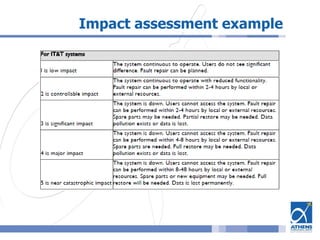
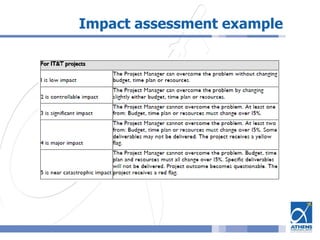
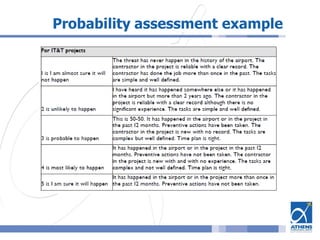
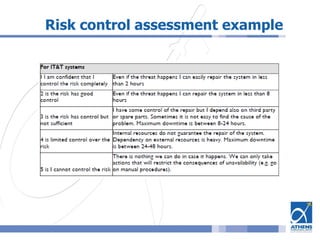
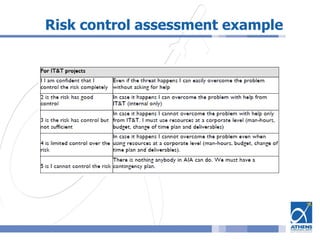
This document outlines a risk assessment methodology for organizations. It discusses how risk assessments are often not implemented formally or do not provide practical advice. The presented method uses foundation documents, risk evaluation criteria, and a multi-round review process called the Delphic Technique to provide a standardized risk assessment. It recommends developing reusable templates, defining assessment scope and objectives, using the methodology to identify and evaluate risks, and creating formal treatment plans. Time is included as a variable to show changing risks over time. The goal is for assessments to identify practical risk reduction options.