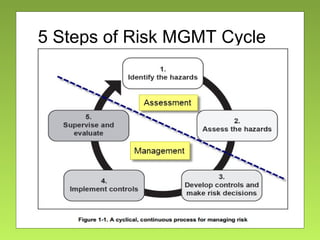
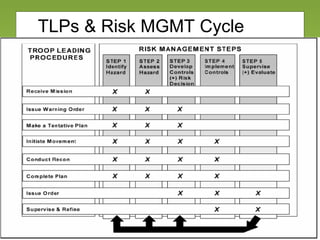
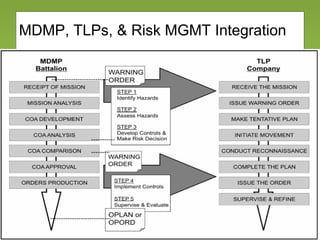
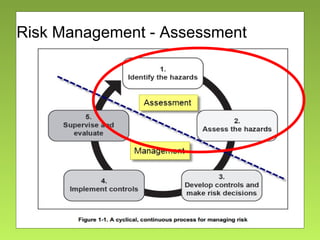
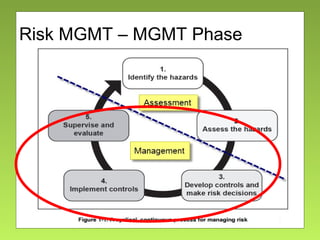
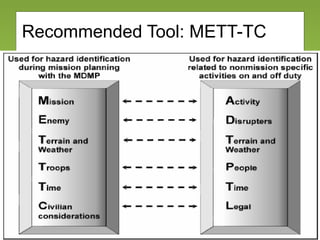
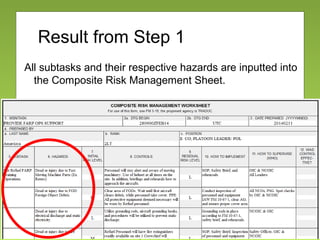
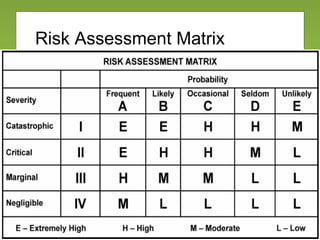
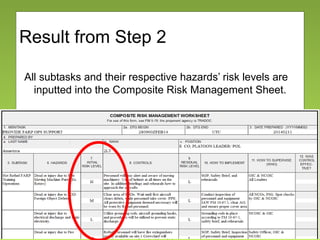
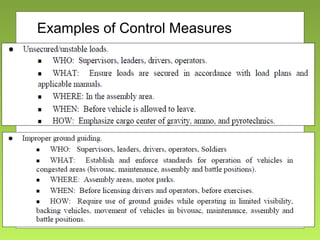
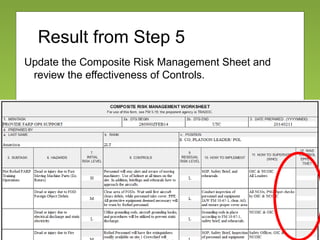
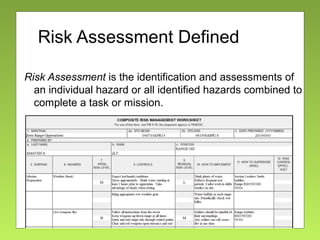
The document outlines the fundamentals and processes of risk management in military operations, emphasizing the need to integrate risk management into all tasks and missions. It describes a five-step risk management cycle: identify hazards, assess risks, develop controls, implement them, and supervise and evaluate the outcomes. The presentation also highlights various types of risks and hazards, along with tools and strategies for effective risk management.