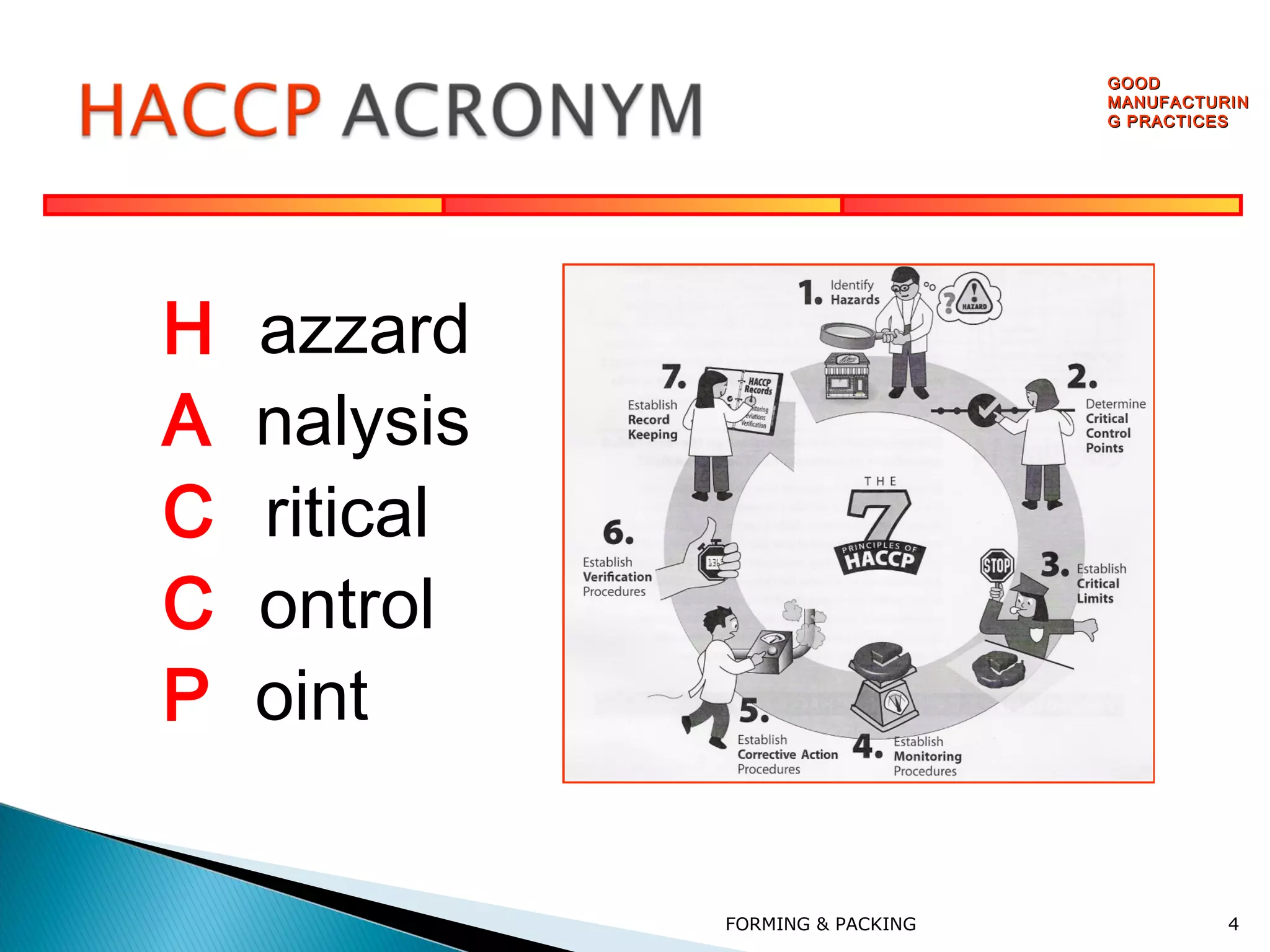
The document discusses Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP). It explains that GMPs and HACCP are important food safety systems used in the food industry. HACCP involves identifying potential hazards at critical control points in the manufacturing process and establishing procedures to monitor and control these hazards. The document provides details on the seven principles of HACCP and outlines critical control points in glass manufacturing as an example. It emphasizes that following GMPs and having standard operating procedures are important foundations for an effective HACCP program.