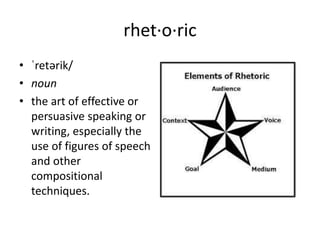
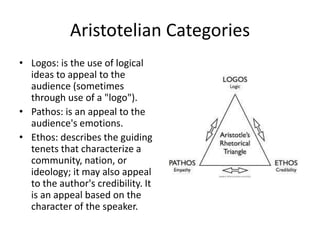
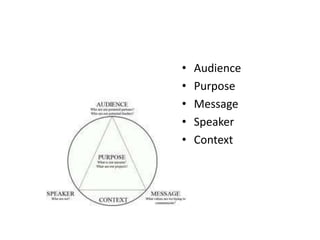
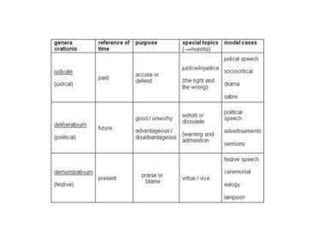
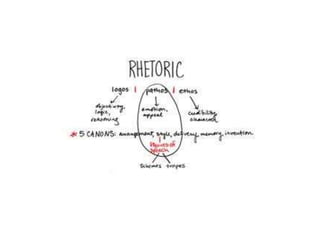
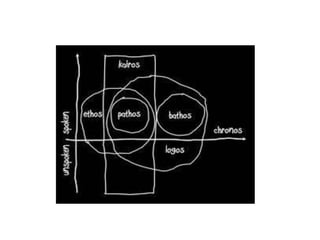
The document explains the concept of rhetorical devices, highlighting their importance in effective speaking and writing. It categorizes these devices into figures of speech, sonic devices, and Aristotelian appeals, detailing examples such as metaphors, alliteration, and pathos. The text also emphasizes the use of sound and emotional appeal as essential components of rhetoric.