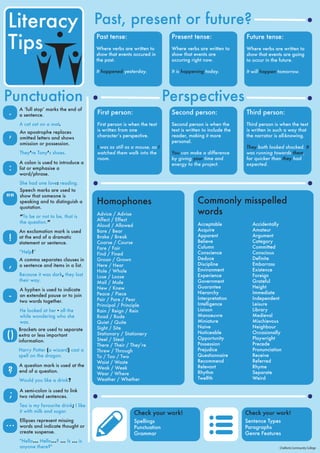
This document provides information about different perspectives, tenses, homophones, commonly misspelled words, and punctuation used in writing. It explains the differences between first, second, and third person perspectives. It also outlines the past, present, and future tenses and provides examples. Additionally, it lists many homophones and commonly confused words as well as the proper definitions and spellings. Finally, it identifies different punctuation marks and their appropriate uses in writing.