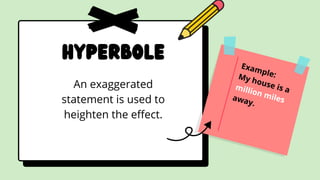
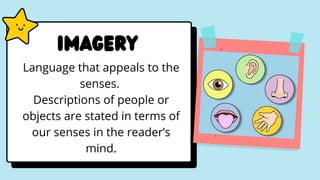
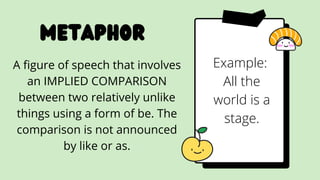
This document provides definitions and examples of various figurative language devices used in literature. It defines hyperbole, imagery, symbolism, allegory, idiom, irony, cliche, oxymoron, euphemism, paradox, pun, and various sound devices like alliteration, assonance, anaphora, and onomatopoeia. It also discusses poetic devices that use comparisons such as simile, metaphor, and personification. The document is intended as a guide to understanding these figurative language techniques.