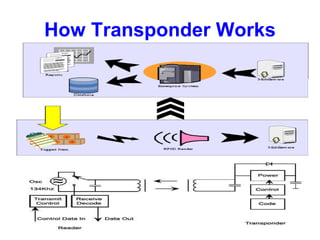
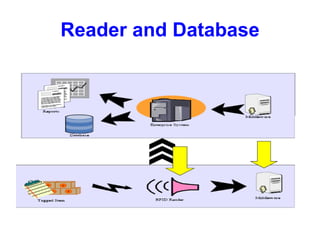
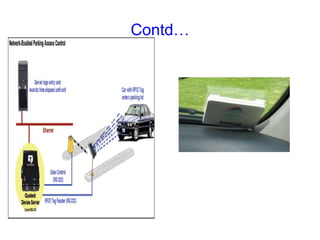
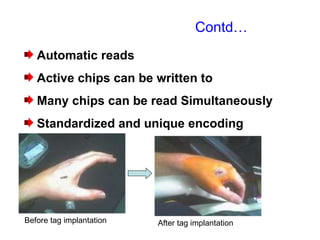
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is an automatic data capture technology that uses radio waves to electronically identify objects. RFID systems consist of RFID tags attached to objects, RFID readers to interrogate the tags, and a host computer system to process the data collected. RFID tags can be either passive, active, or semi-passive. Passive tags have no internal power source and must derive power from the reader, while active tags have an internal power source to transmit signals to the reader. RFID is used for applications such as tracking inventory and assets, cashless payments, and electronic access control because it allows for contactless identification of multiple tags simultaneously.