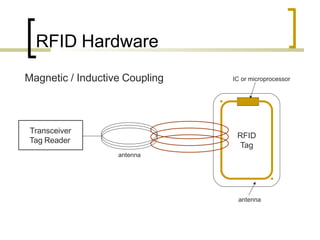
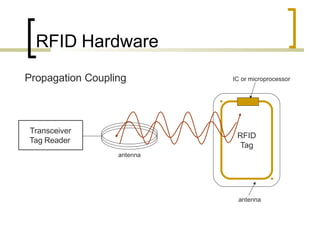
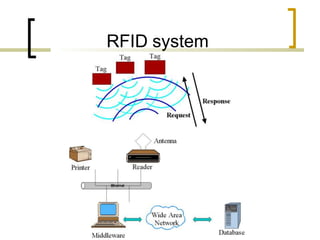
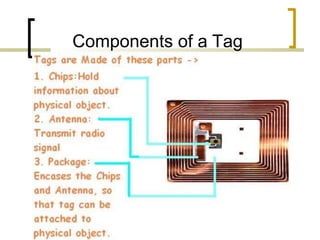
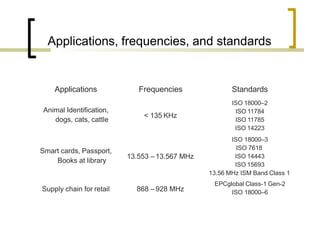
This presentation introduces radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. It discusses what RFID is, how it works using three main components (transceiver, transponder, and antenna), and provides examples of RFID hardware including tags, readers, and different frequency ranges. It also outlines several common applications of RFID technology in various industries like retail, transportation, security, and more.