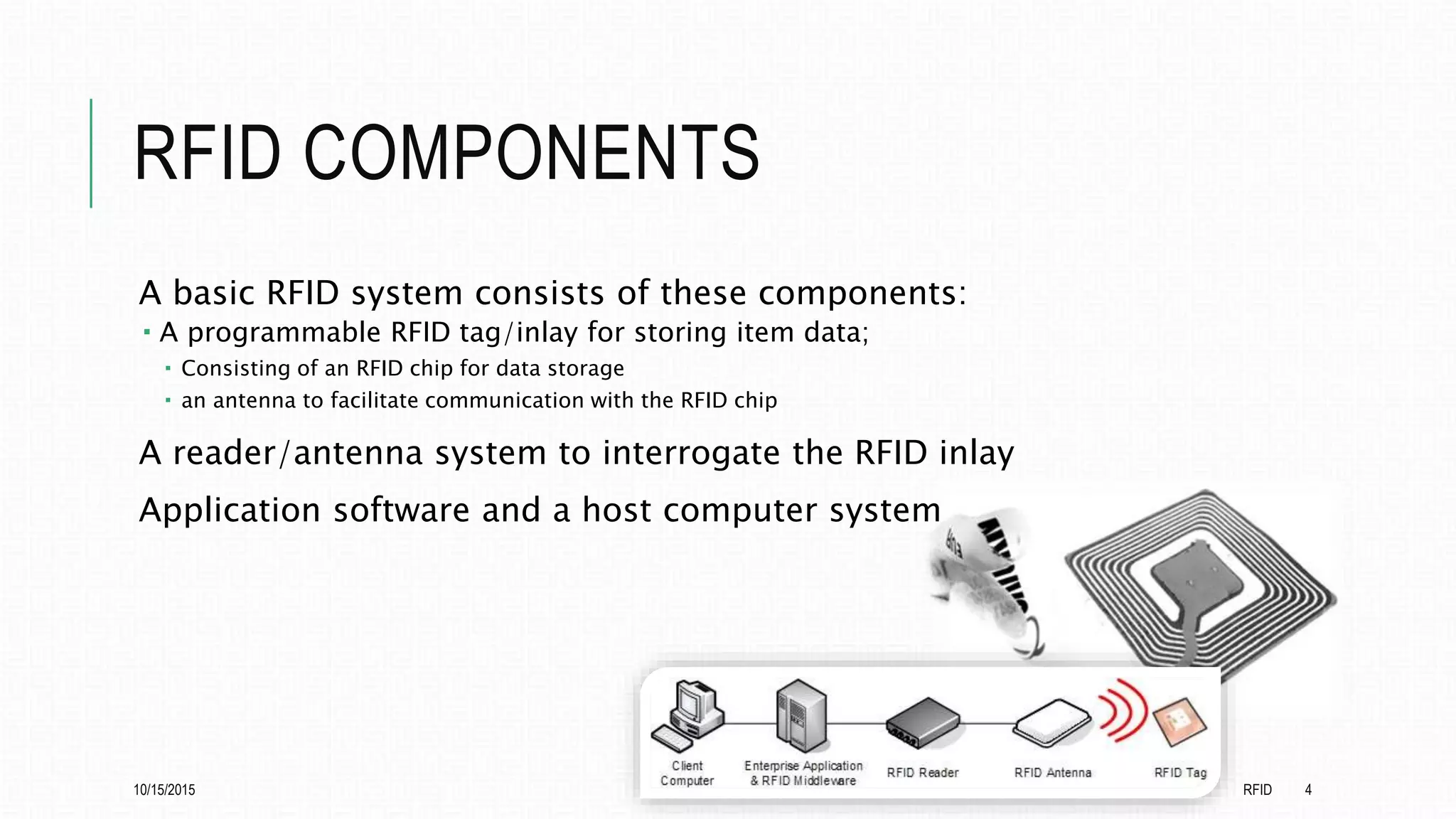
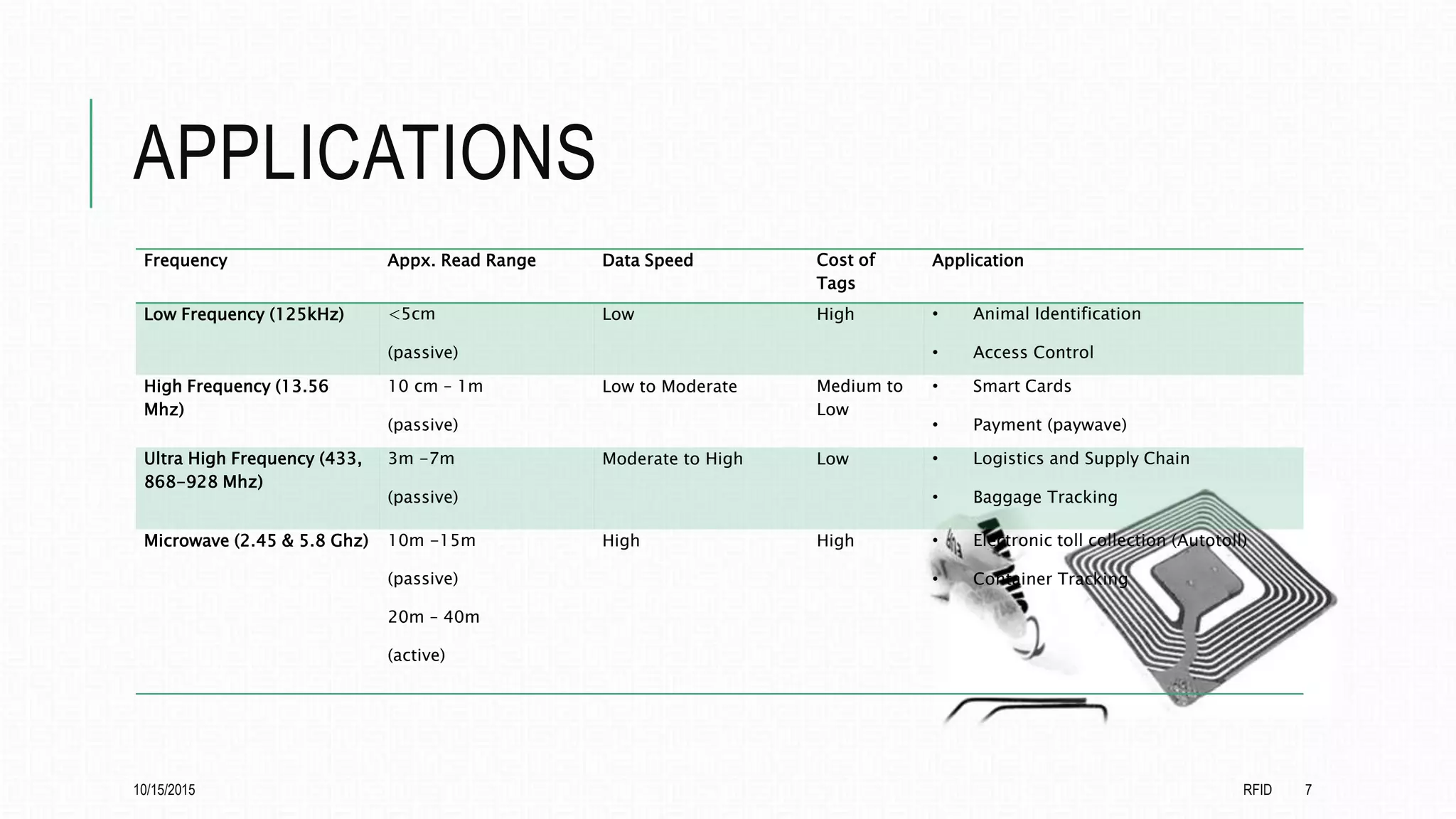
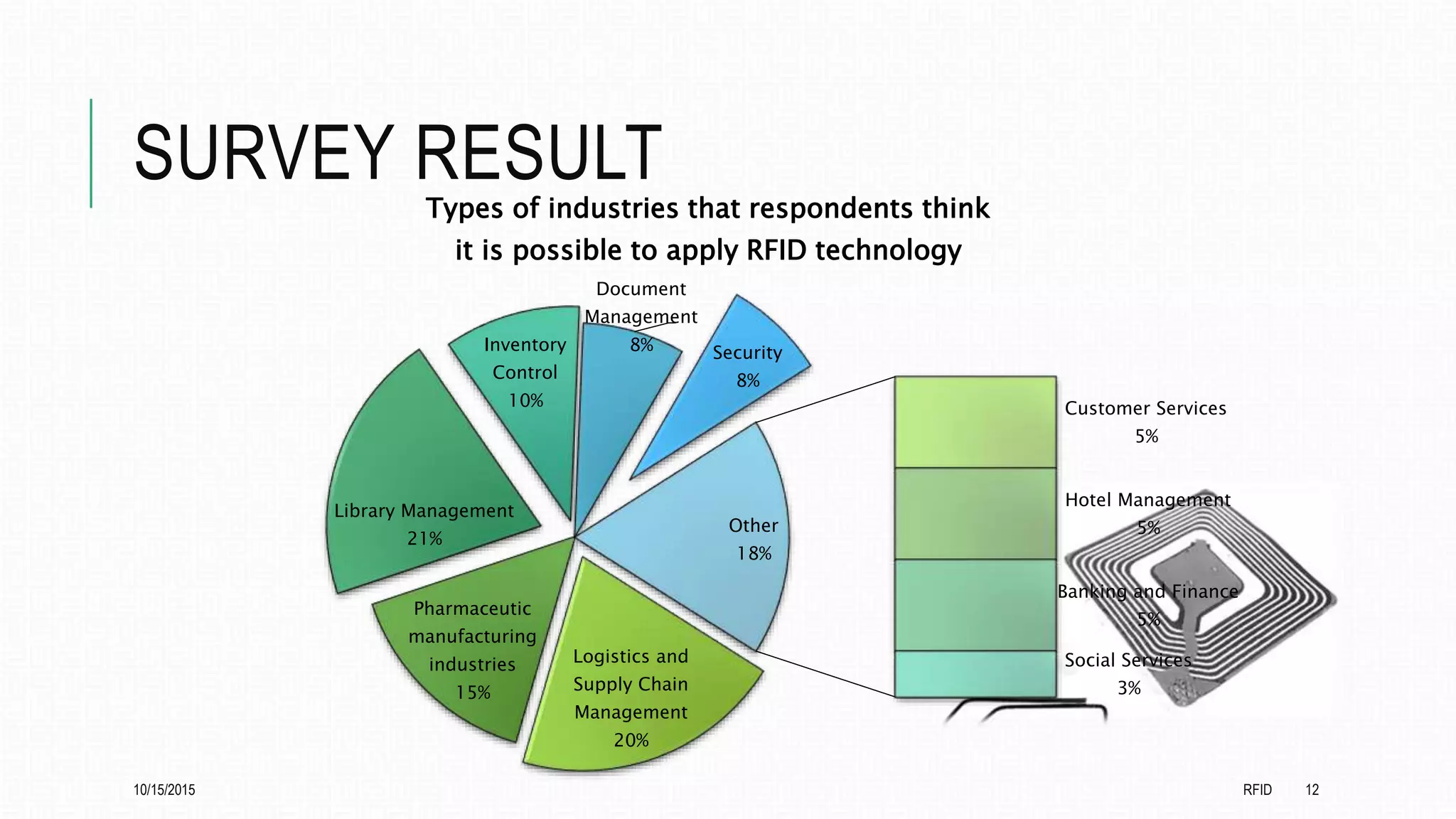
This document discusses radio frequency identification (RFID) and its applications. It begins with an introduction to RFID technology, describing how RFID tags transmit information to readers. It then outlines the basic components of an RFID system and describes the different types of RFID tags. The document provides examples of applications of RFID technology in various frequency ranges and industries. It presents the results of an online survey on opinions of RFID and its potential applications. It concludes with a discussion of further development opportunities for RFID in medical and library uses.