The document summarizes several major historical events and revolutions:
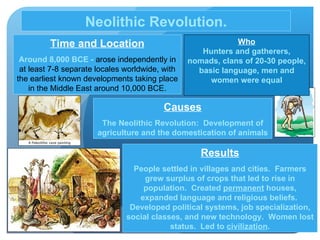
1) The Neolithic Revolution saw the development of agriculture and domestication of animals around 10,000 BCE, leading to settled villages and the rise of early civilizations.
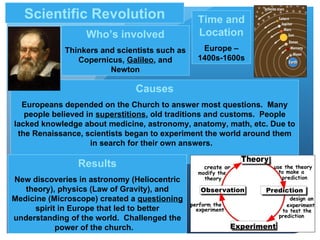
2) The Scientific Revolution in Europe from 1400-1600 CE challenged the power of the Church and led to new discoveries in astronomy, physics, and medicine through scientists like Copernicus, Galileo, and Newton.
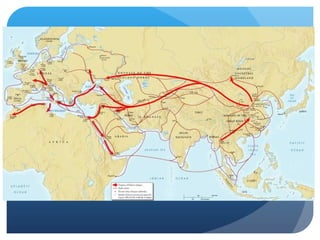
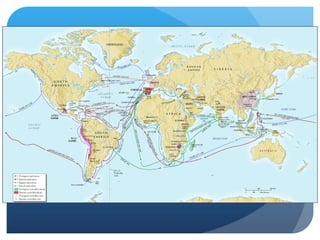
3) The French Revolution from 1789-1799 overturned the French absolute monarchy and feudal system, establishing a republic in France and influencing other revolutions with Enlightenment ideals.