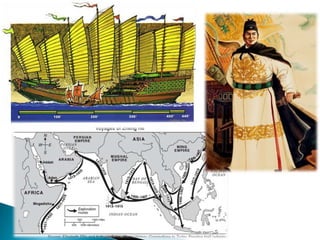
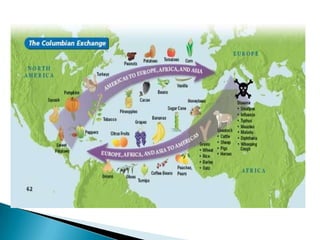
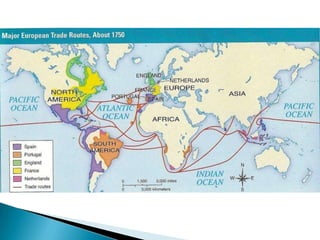
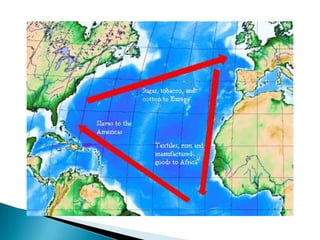
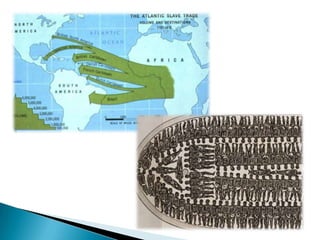
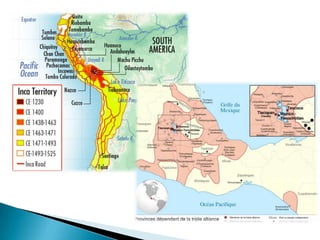
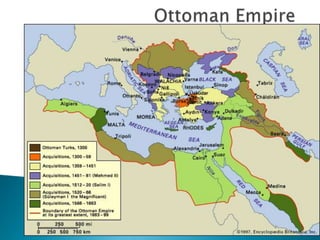
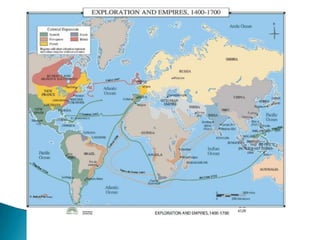
The Age of Exploration began in the 15th century and was driven by factors such as the Renaissance, desire for trade and profits, spreading Christianity, and new sailing technologies. Major European powers launched expeditions, resulting in the Columbian Exchange between the Old and New Worlds and the beginning of colonization in the Americas. This led to profound political, economic, and cultural changes globally, including the rise of capitalism and mercantilism in Europe. Indigenous populations, including the Aztec and Inca empires, suffered greatly from European conquest and disease.