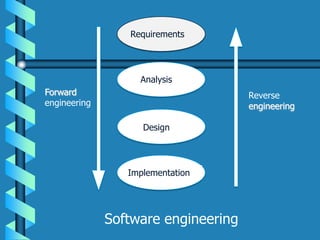
Reverse engineering is the process of analyzing a product or system to understand its design, functionality, and operation. It involves taking something apart and studying how it works. Reverse engineering can be used to retrieve lost source code, study how a program performs operations, improve performance, fix bugs, or identify malicious content. It is commonly used for security research, software development, product analysis, and understanding legacy software when documentation is lost. The key steps of reverse engineering involve collecting information, examining the structure and functionality, and documenting the recovered design. Common tools used include disassemblers, debuggers, and decompilers. While useful, the legality of reverse engineering varies depending on jurisdiction and software licenses.