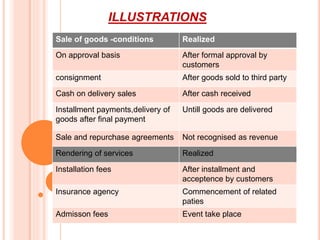
This document discusses accounting standard 9 regarding revenue recognition. It defines revenue as the gross inflow of cash or receivables from the sale of goods, rendering of services, or use of enterprise resources by others. Revenue is recognized when it is earned and realizable, following the revenue recognition and matching principles. The standard provides criteria for revenue recognition such as evidence of an arrangement, delivery, fixed pricing, and collectability. It also discusses types of revenue recognition for different transactions and the effect of uncertainties.