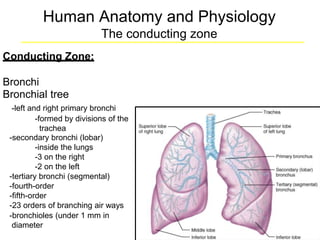
The respiratory system consists of a conducting zone and respiratory zone. The conducting zone includes the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi which are responsible for conducting air to the respiratory zone. The respiratory zone includes bronchioles, alveolar ducts and 300 million alveoli which are the primary sites of gas exchange between air and blood.