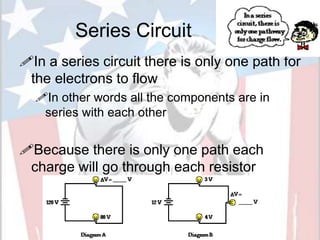
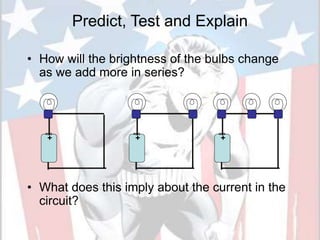
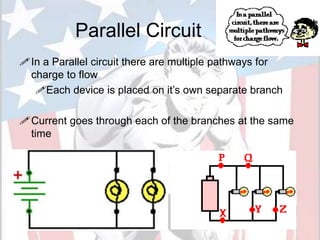
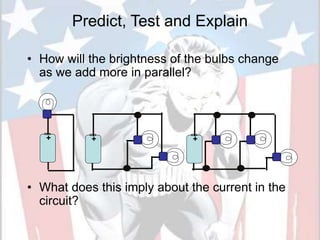
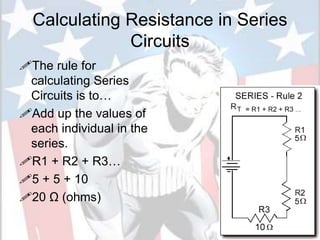
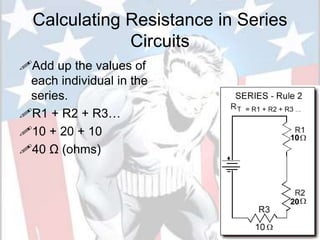
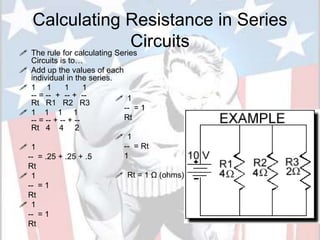
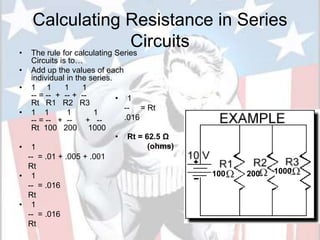
In a series circuit, there is only one path for electrons to flow through each component in the circuit. As more components are added in series, the total resistance increases and the current decreases. In a parallel circuit, there are multiple pathways for current to flow simultaneously through different branches. As more components are added in parallel, the total resistance decreases and the current remains the same. Components in series represent resistance like boulders in a stream, while parallel circuits provide alternative pathways like branches in a stream. The total resistance of components in series is calculated by adding the resistance of each individual component.