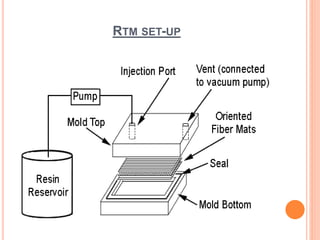
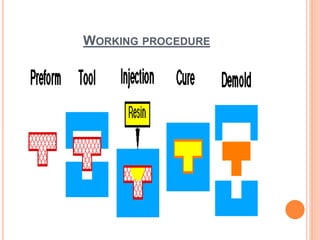
This document discusses resin transfer molding (RTM), which is a manufacturing process for composites. It involves injecting resin into a closed mold containing reinforcing fibers. RTM was originally developed for boat manufacturing in 1946. Common resins used include epoxy, polyester, and vinyl ester. Glass, carbon, and natural fibers are often used as reinforcements. The resin is injected into the mold containing the fibers, where it impregnates the fibers and hardens to form a composite part with good surface quality and complex shapes. Applications include truck panels, boat hulls, wind turbine blades, and various other industrial and consumer products.