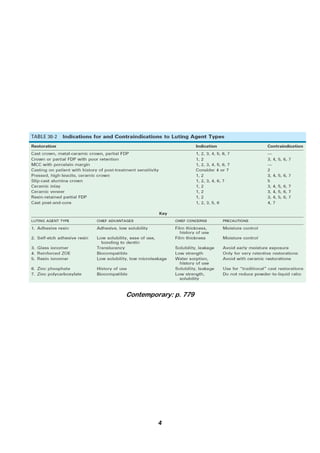
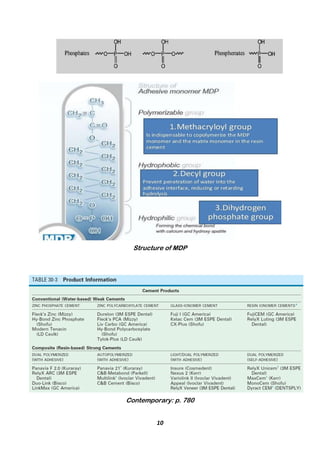
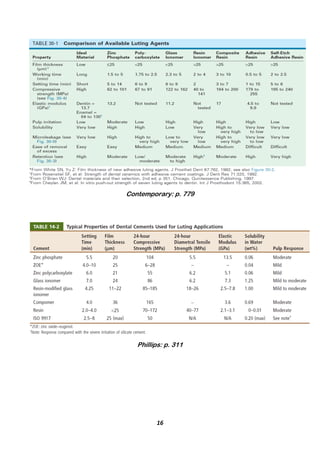
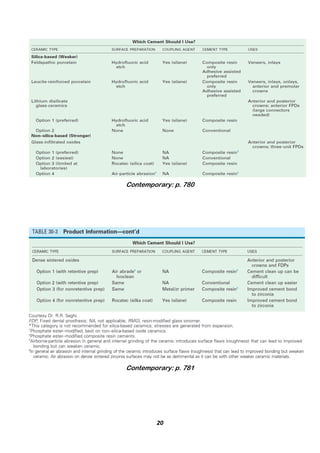
The document provides a comprehensive overview of resin luting cements, detailing their uses, types, compositions, and properties, including methods of activation such as light-cured, chemical-cured, and dual-cured variants. It emphasizes the importance of resin cements in the cementation of dental restorations, particularly for ceramics and dental applications, while discussing issues like mechanical properties, cytotoxicity, and bonding mechanisms. Additionally, it covers manipulation techniques and the influence of different resin types on bonding to tooth structures and ceramic materials.