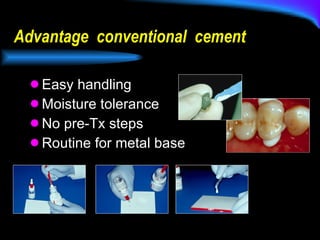
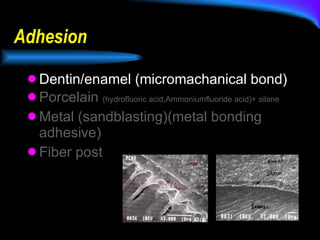
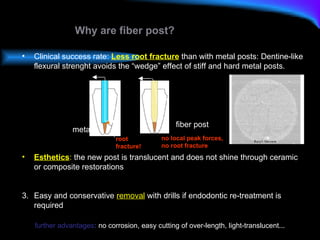
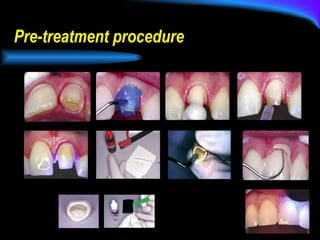
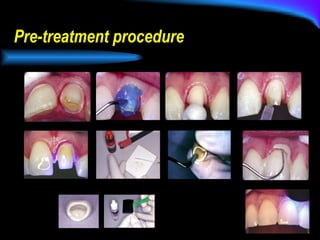
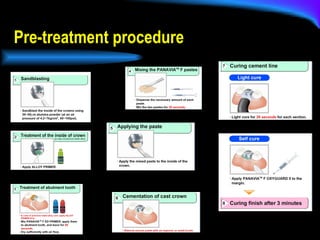
The document discusses different types of dental luting cements including zinc phosphate, polycarboxylate, glass ionomer, resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI), and resin cement. Resin cement provides superior bond strength compared to other cements, bonds well to various restorative materials, and has low solubility resulting in reduced microleakage. Proper preparation and application techniques are required when using resin cement to ensure optimal adhesion.