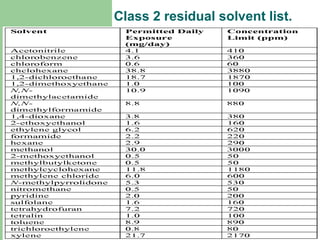
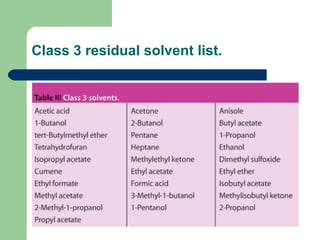
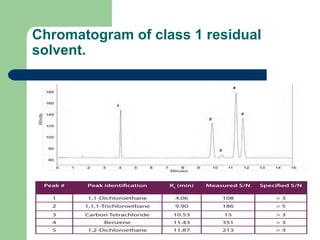
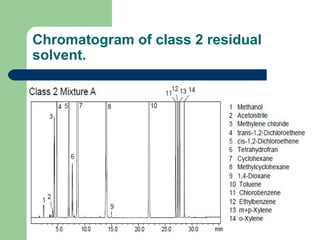
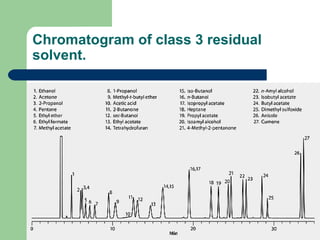
This document summarizes the determination of residual solvents in pharmaceuticals by gas chromatography according to ICH guidelines. Residual solvents are organic chemicals used in manufacturing that are not fully removed and may pose health risks. They are classified into Class 1, 2, or 3 based on toxicity, with Class 1 solvents prohibited. Gas chromatography with headspace injection and flame ionization detection is the primary analytical method. It involves using capillary columns, temperature programs, and identifies solvents by comparing retention times to standards. The document outlines accepted chromatographic conditions and procedures A, B, and C described in pharmacopeias.

![INTRODUCTION
“Residual solvents in pharmaceuticals are defined
as organic volatile chemicals that are used or
produced in the manufacture of drug substances
or excipients, or in the preparation of drug
products.” (ICH, USP, EP)
[Note: residual solvents´ refers to the amount not
removed during the purification of the product´]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/residualsolventppt-150426111354-conversion-gate01/85/Residual-solvent-2-320.jpg)