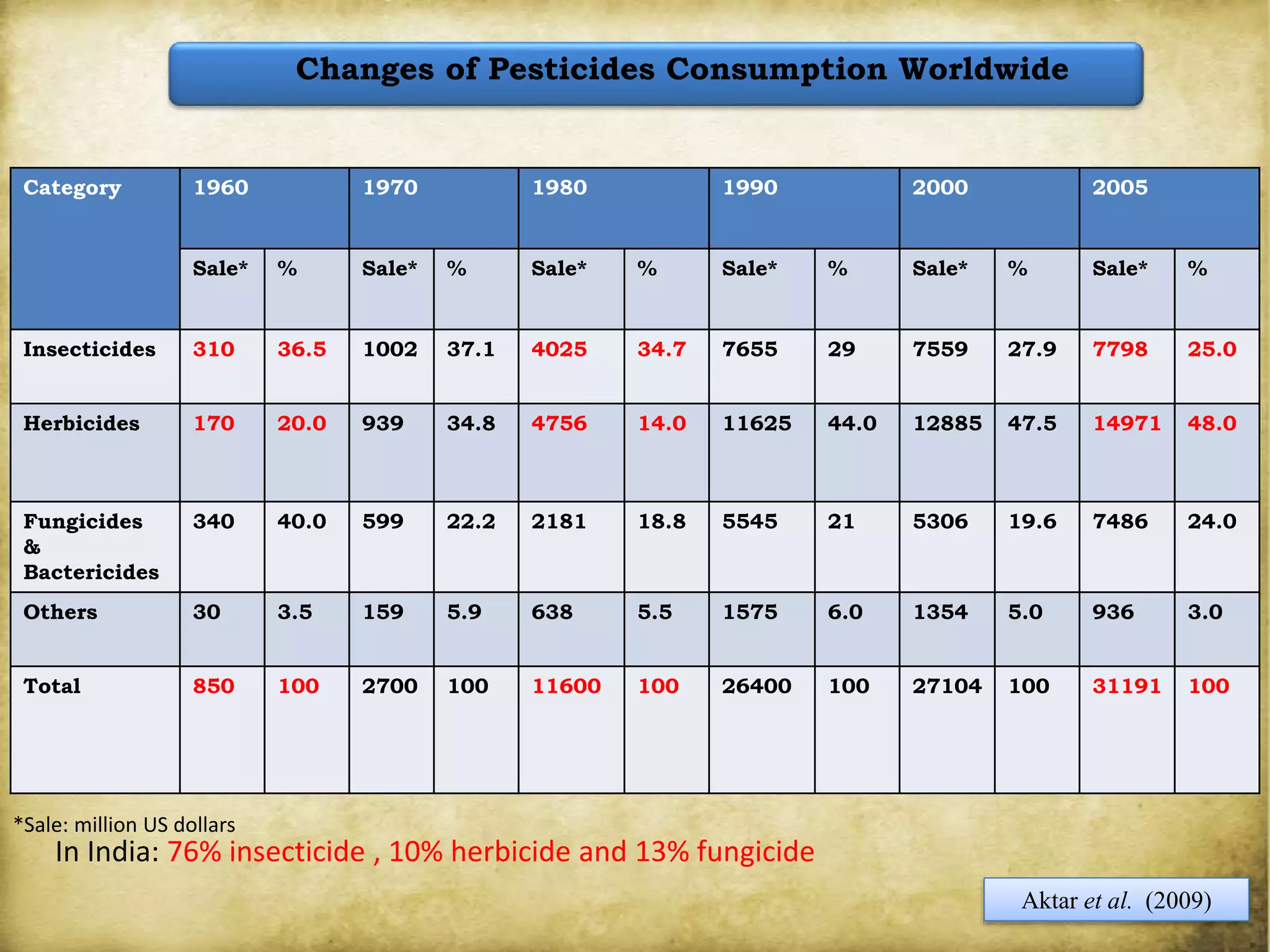
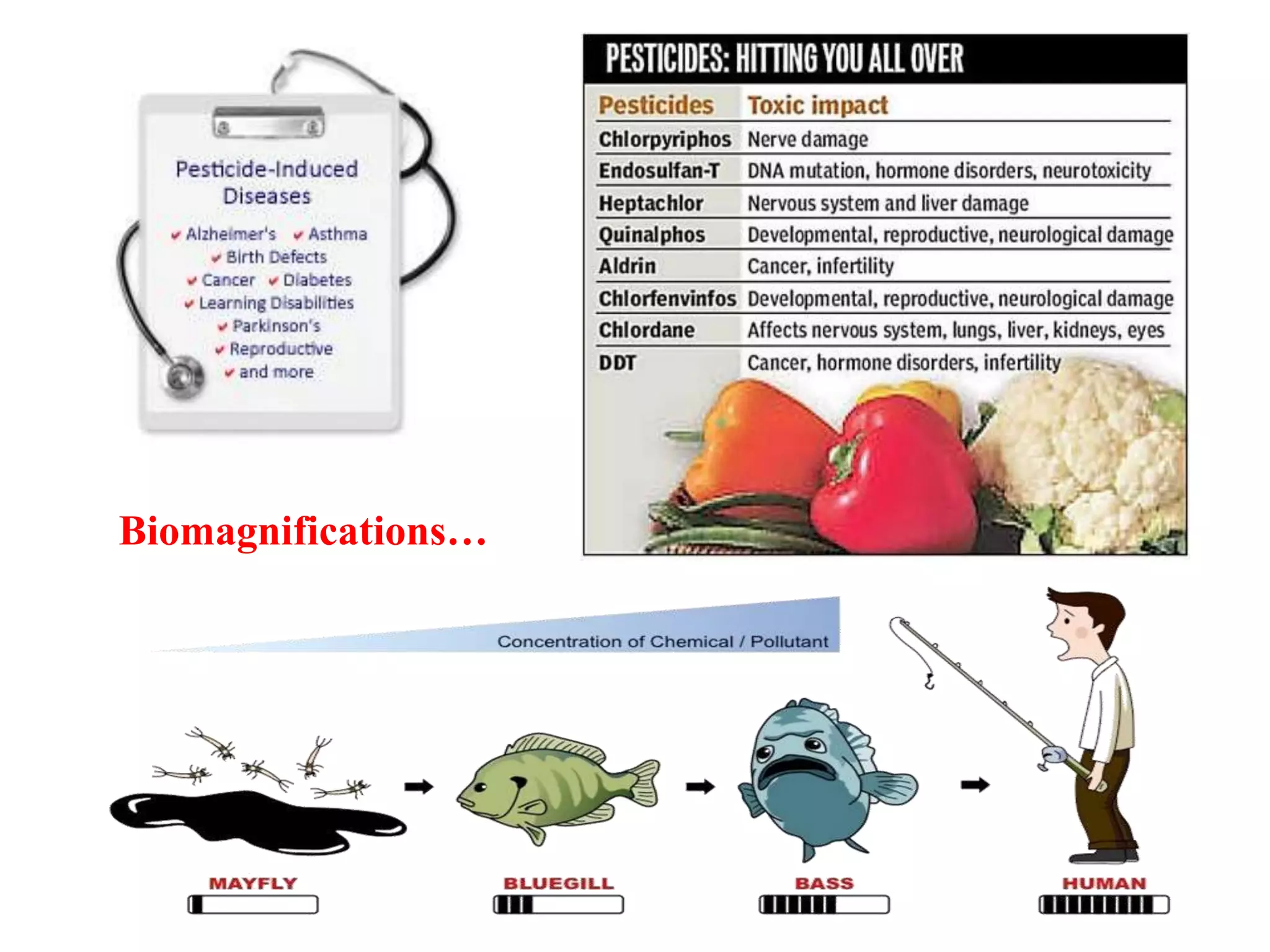
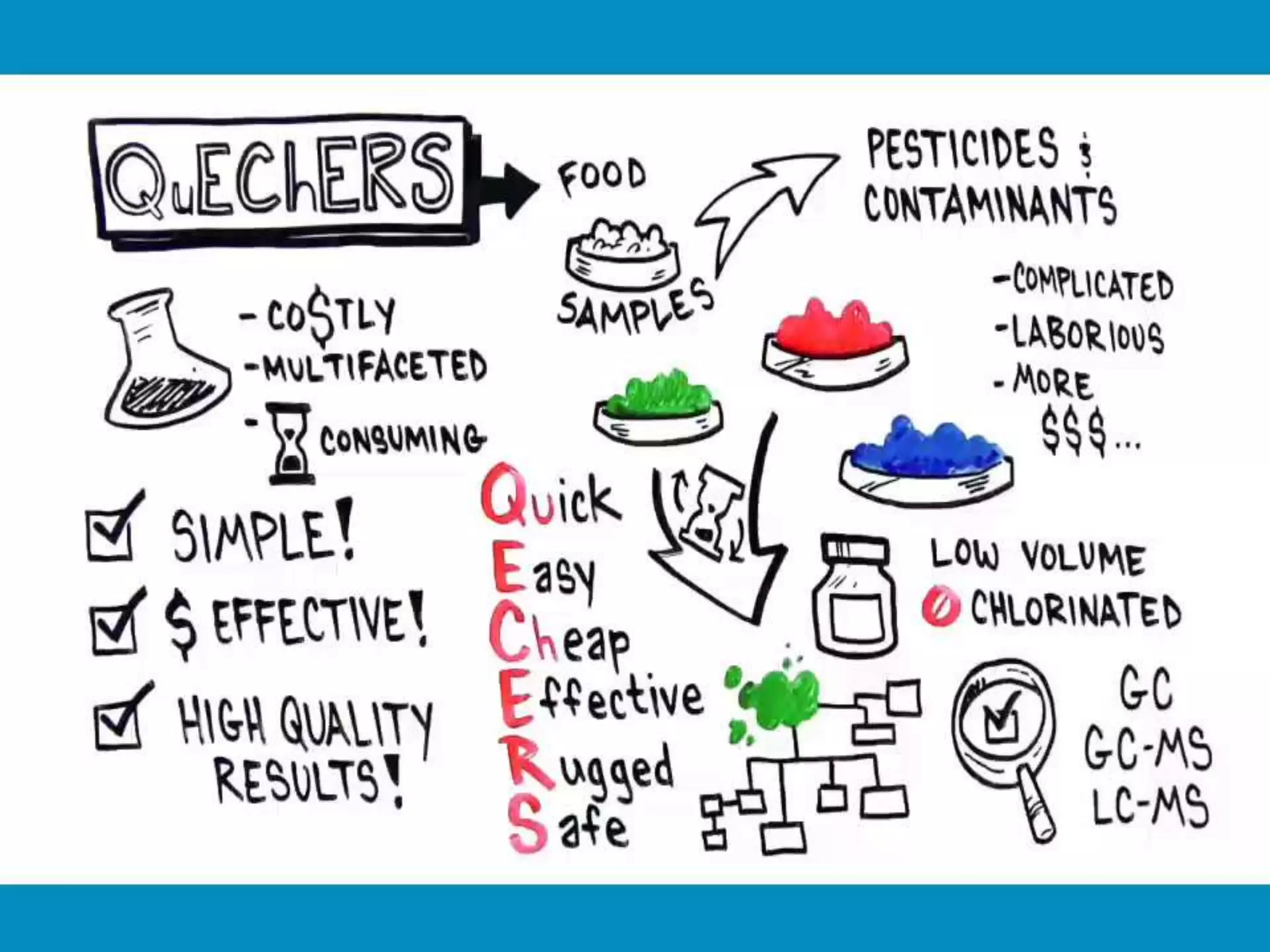
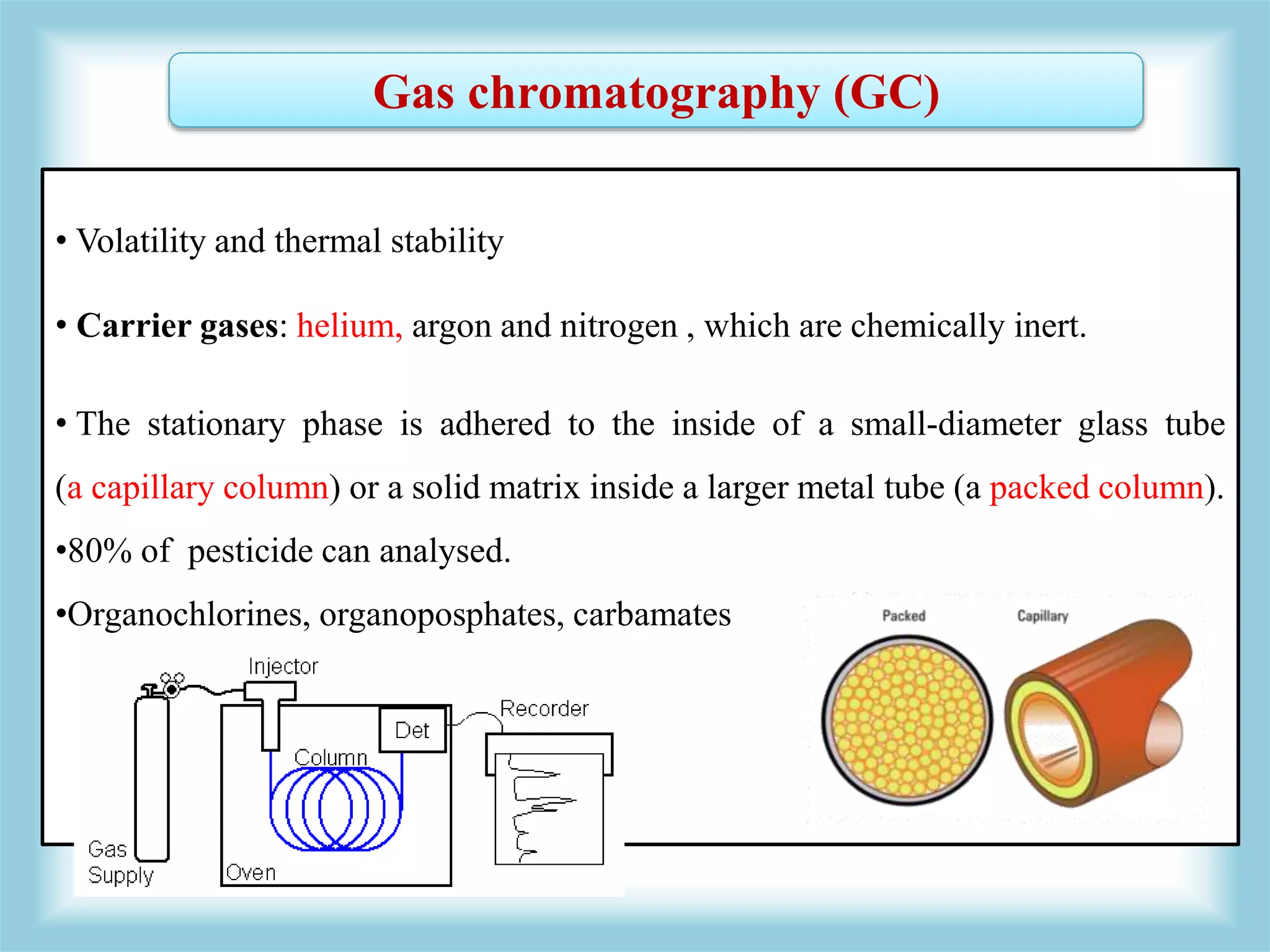
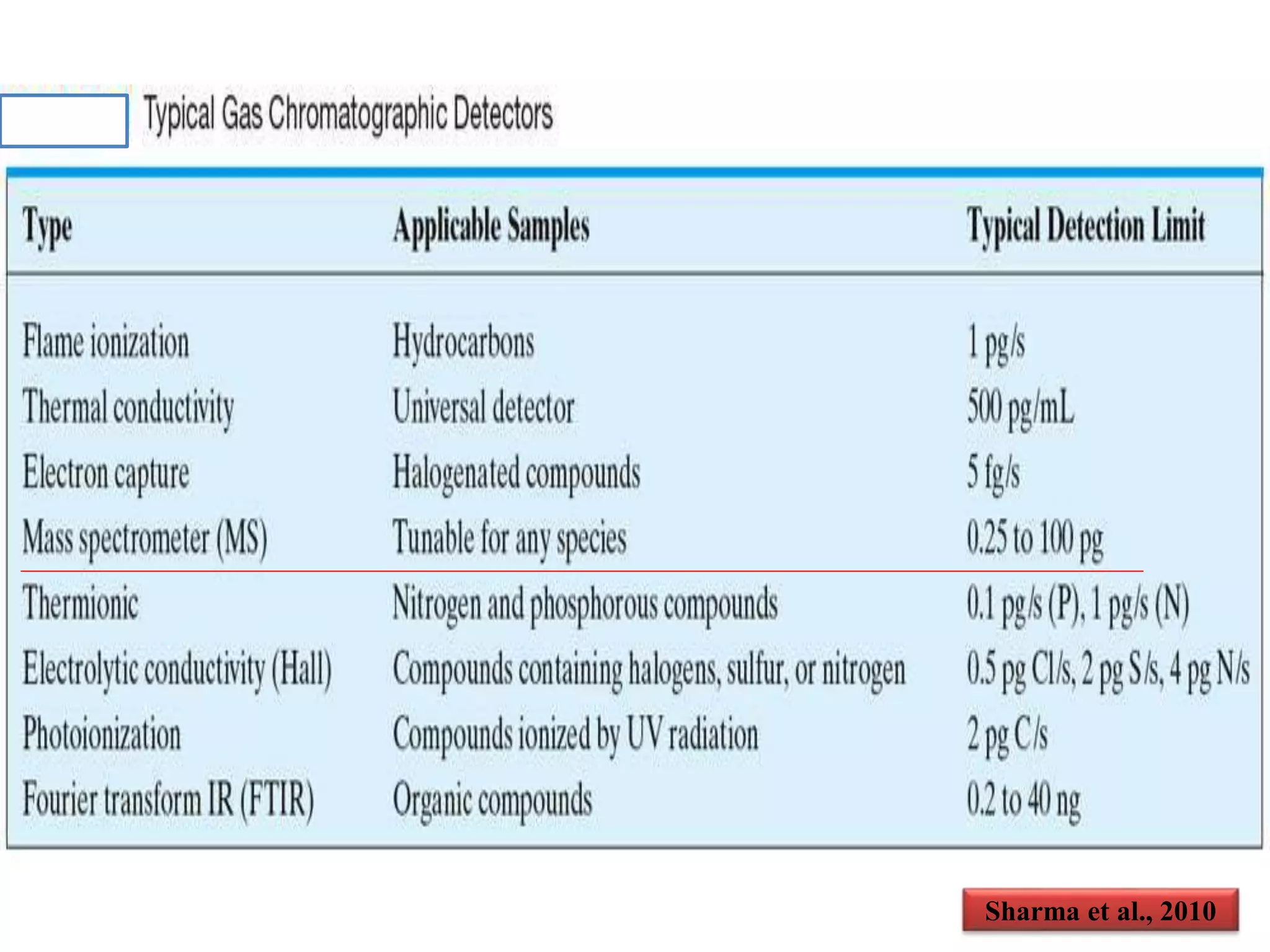
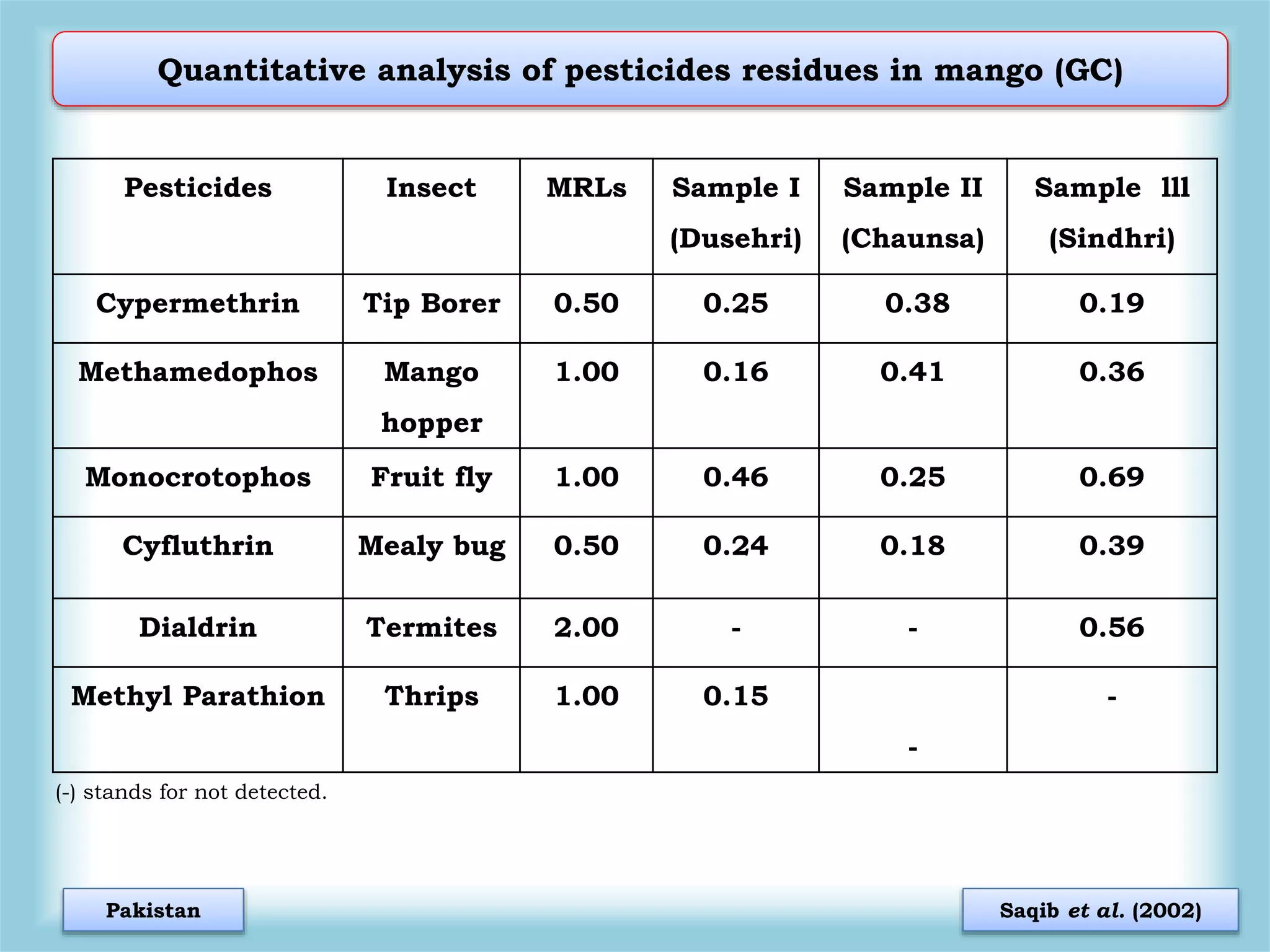
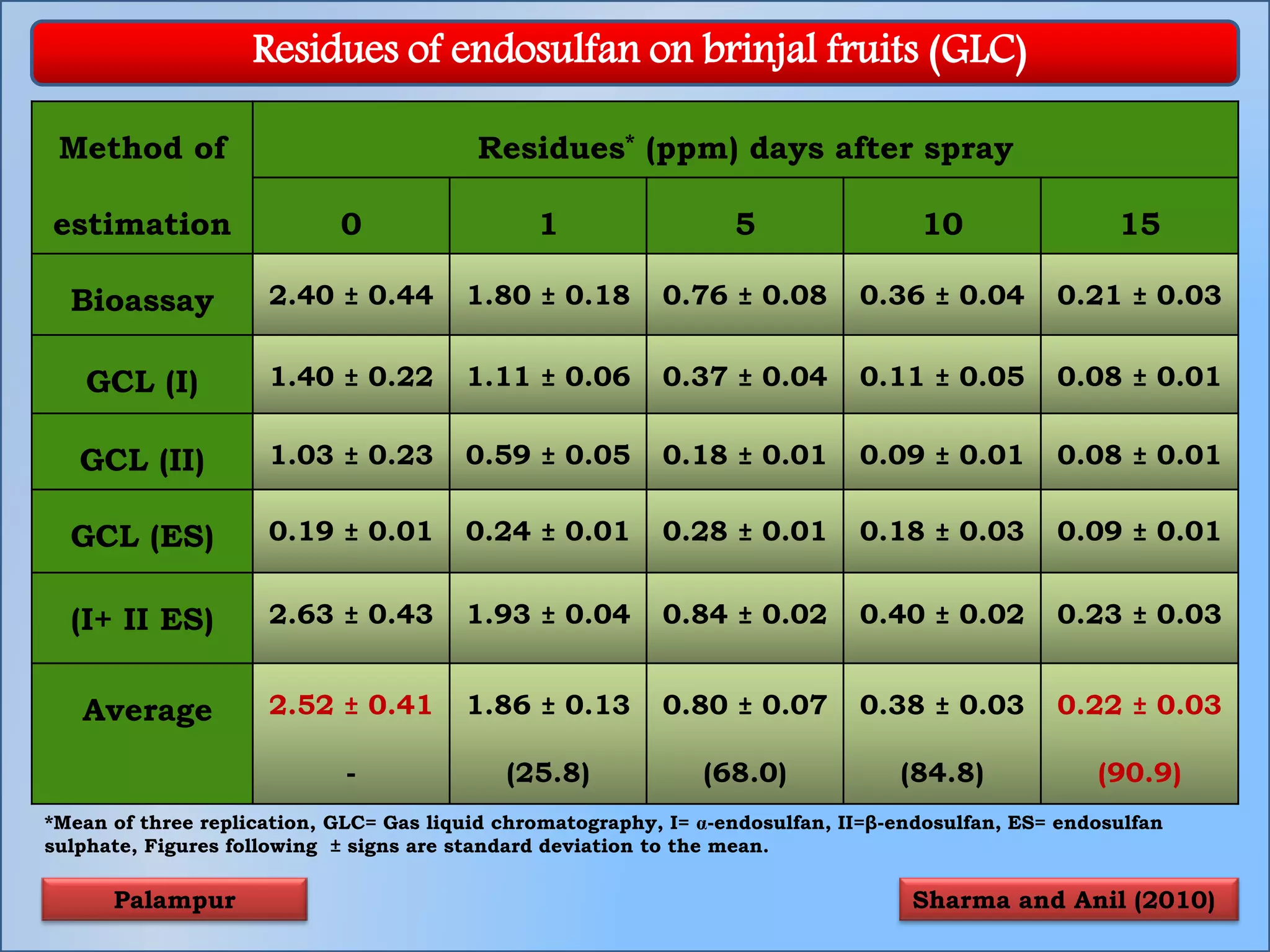
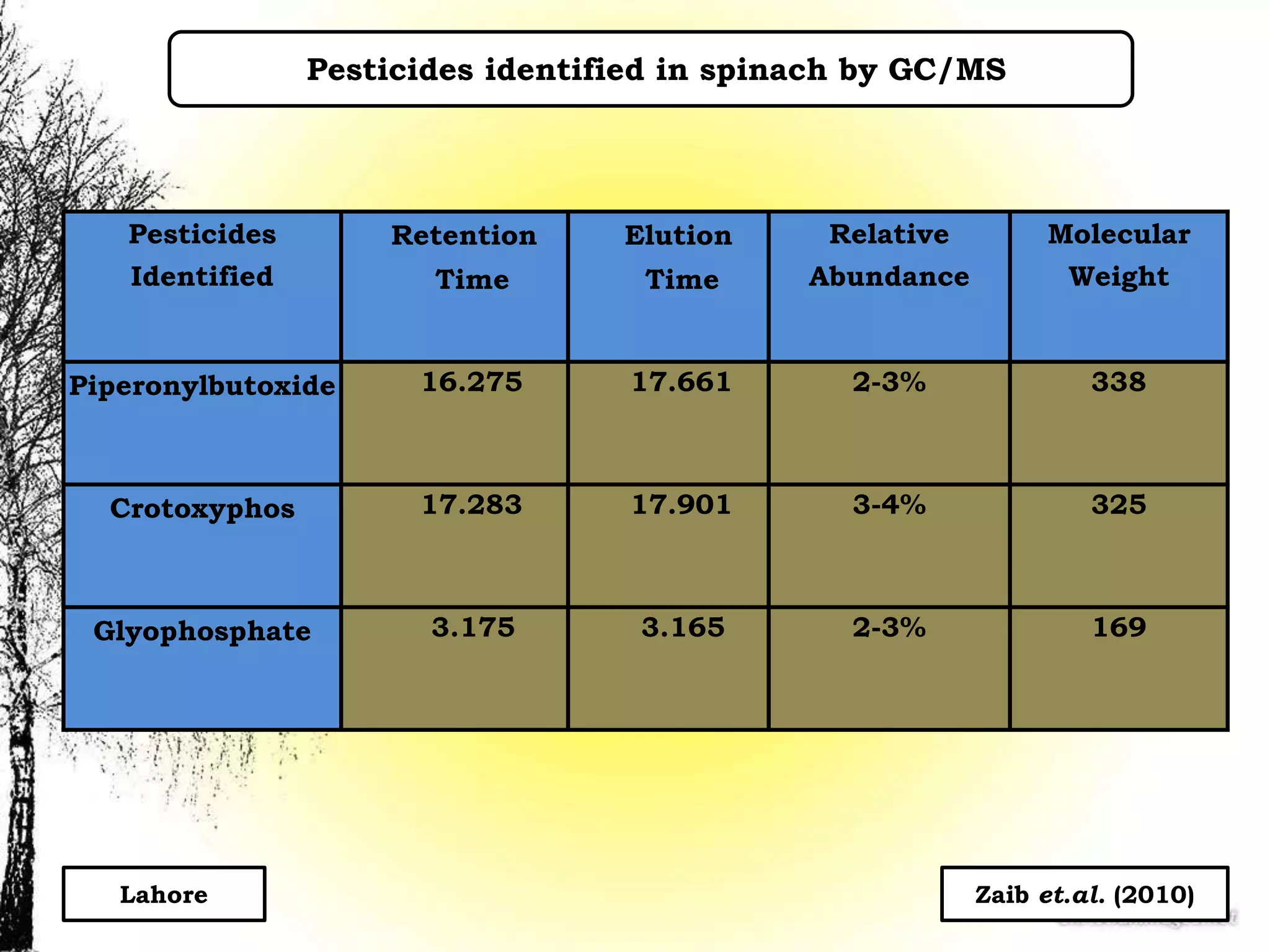
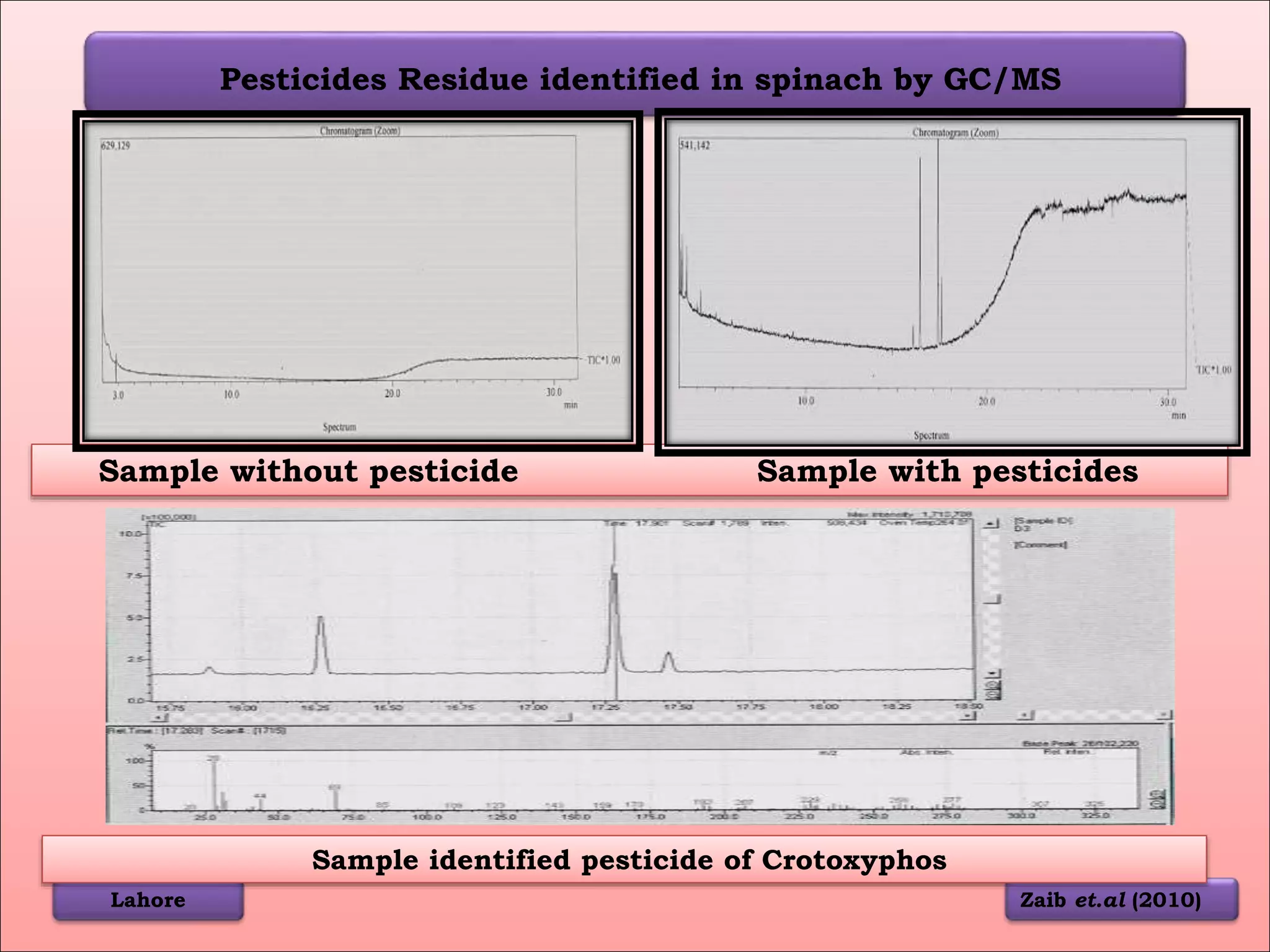
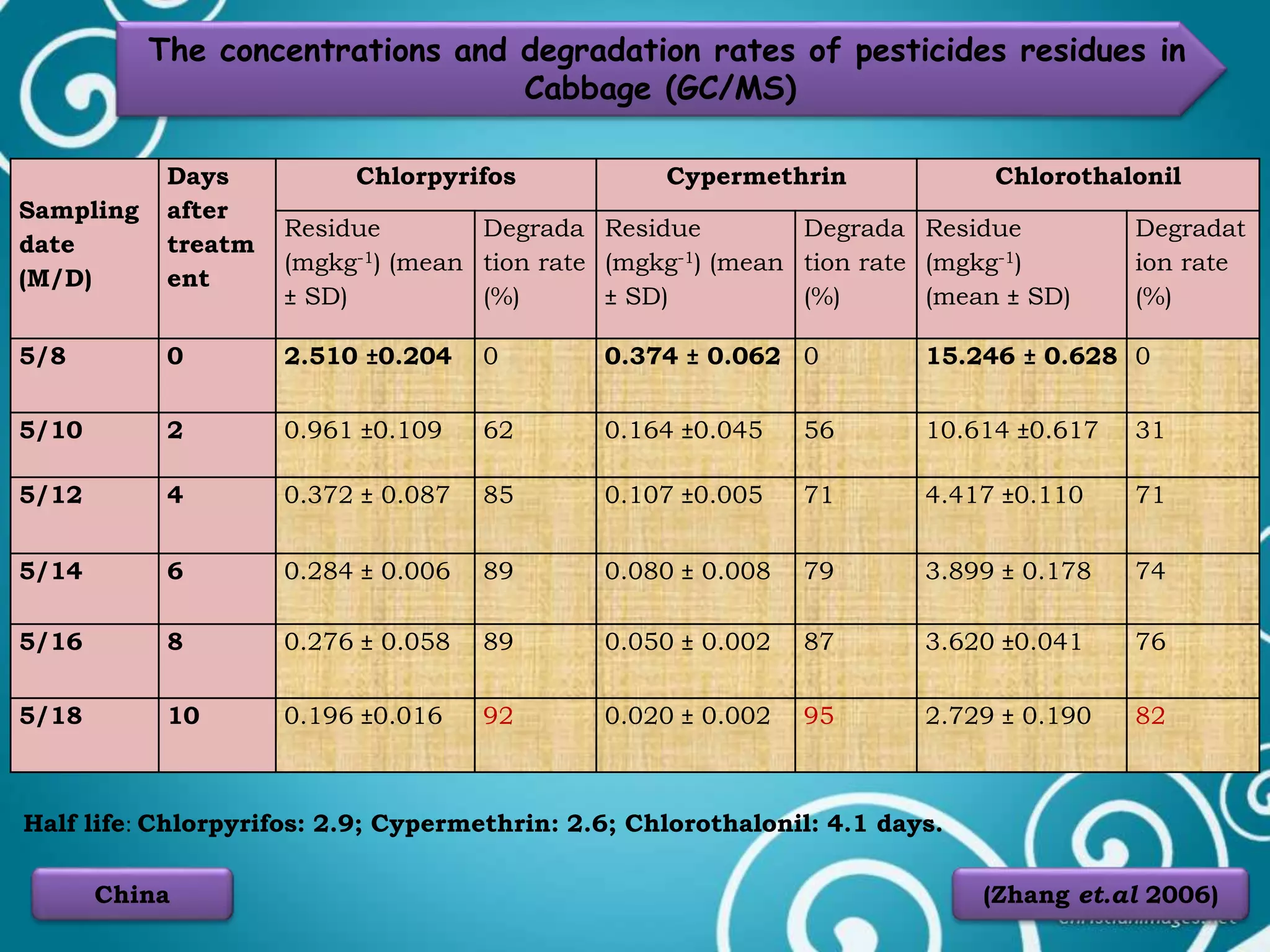
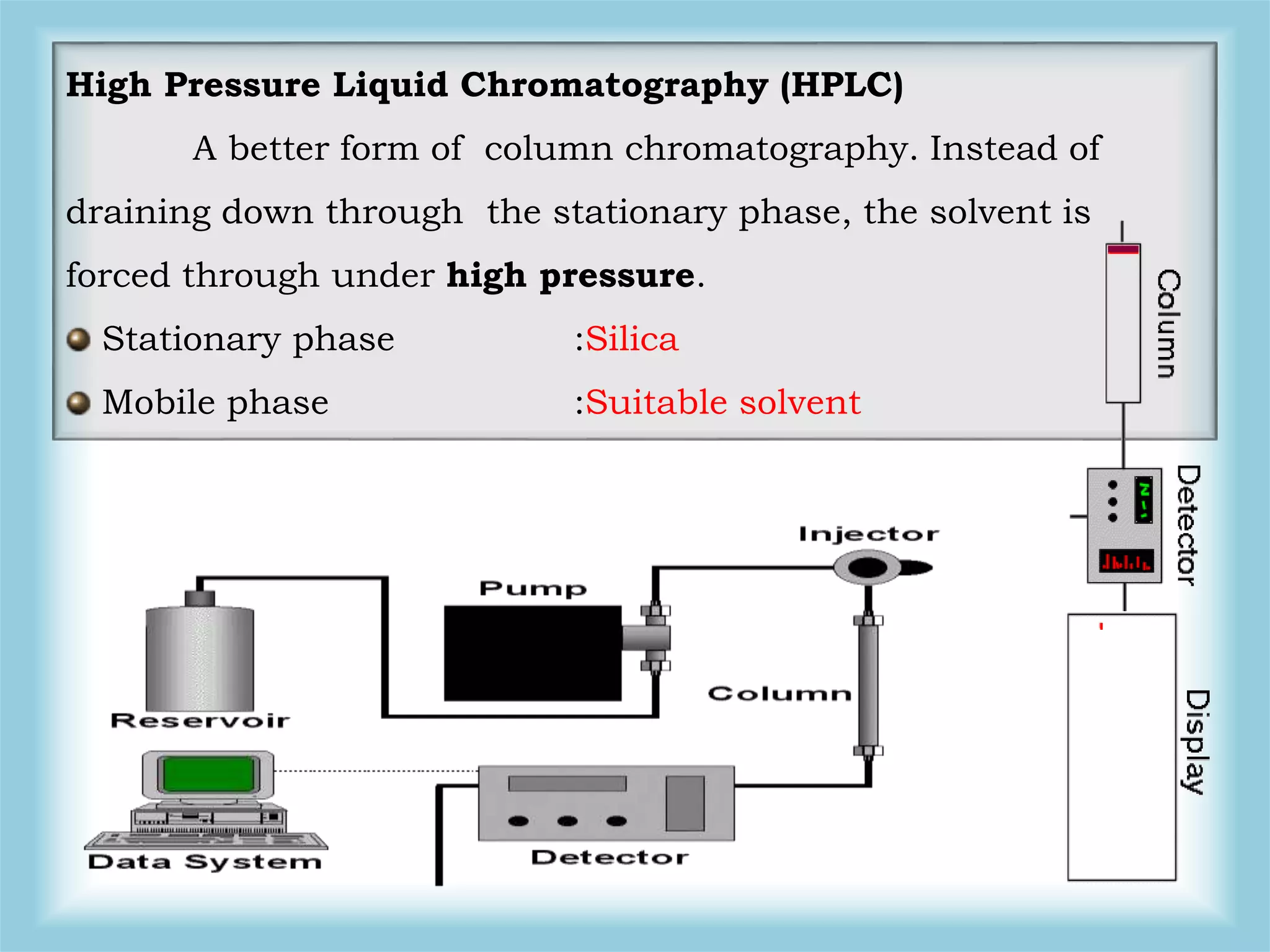
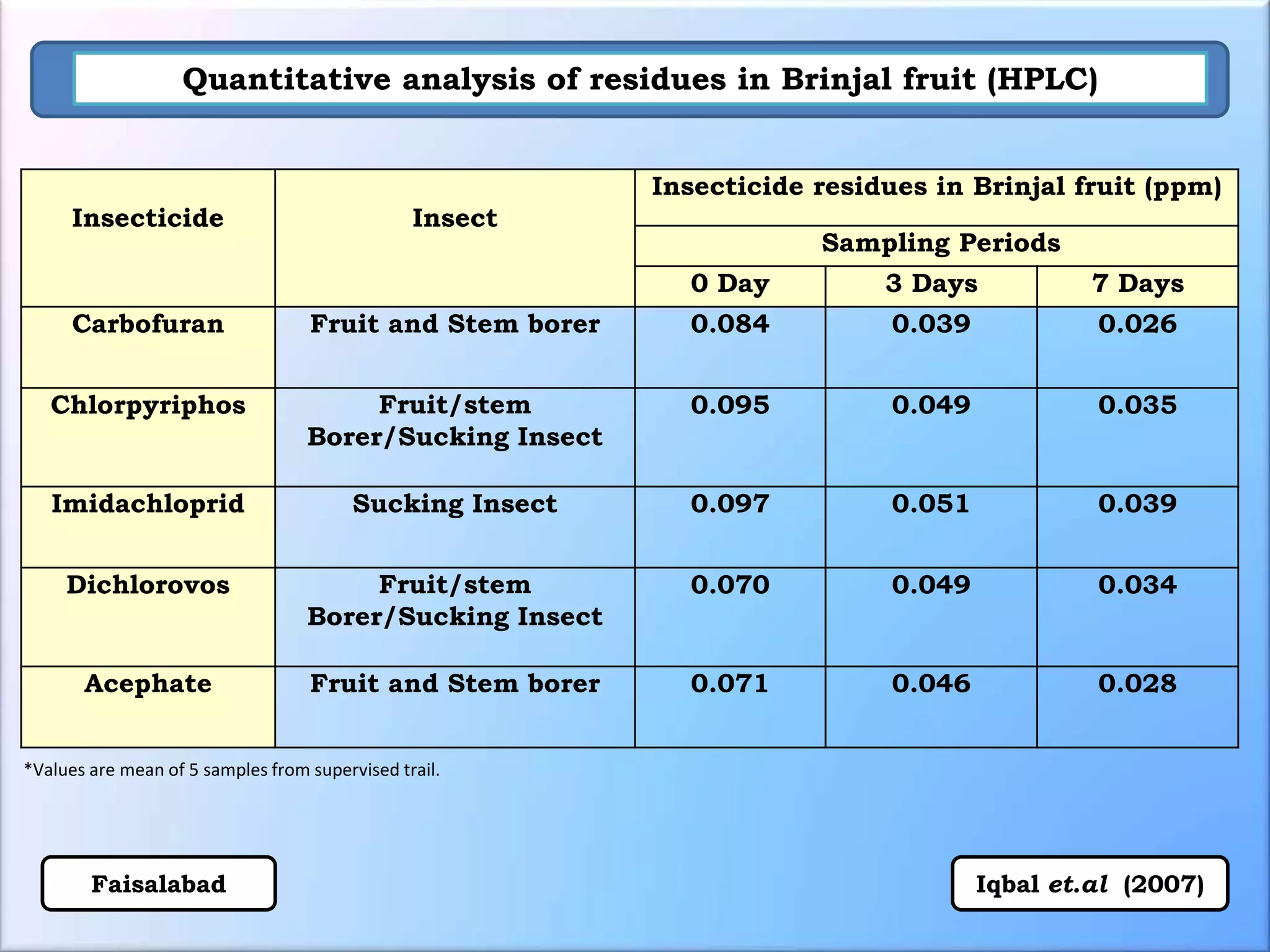
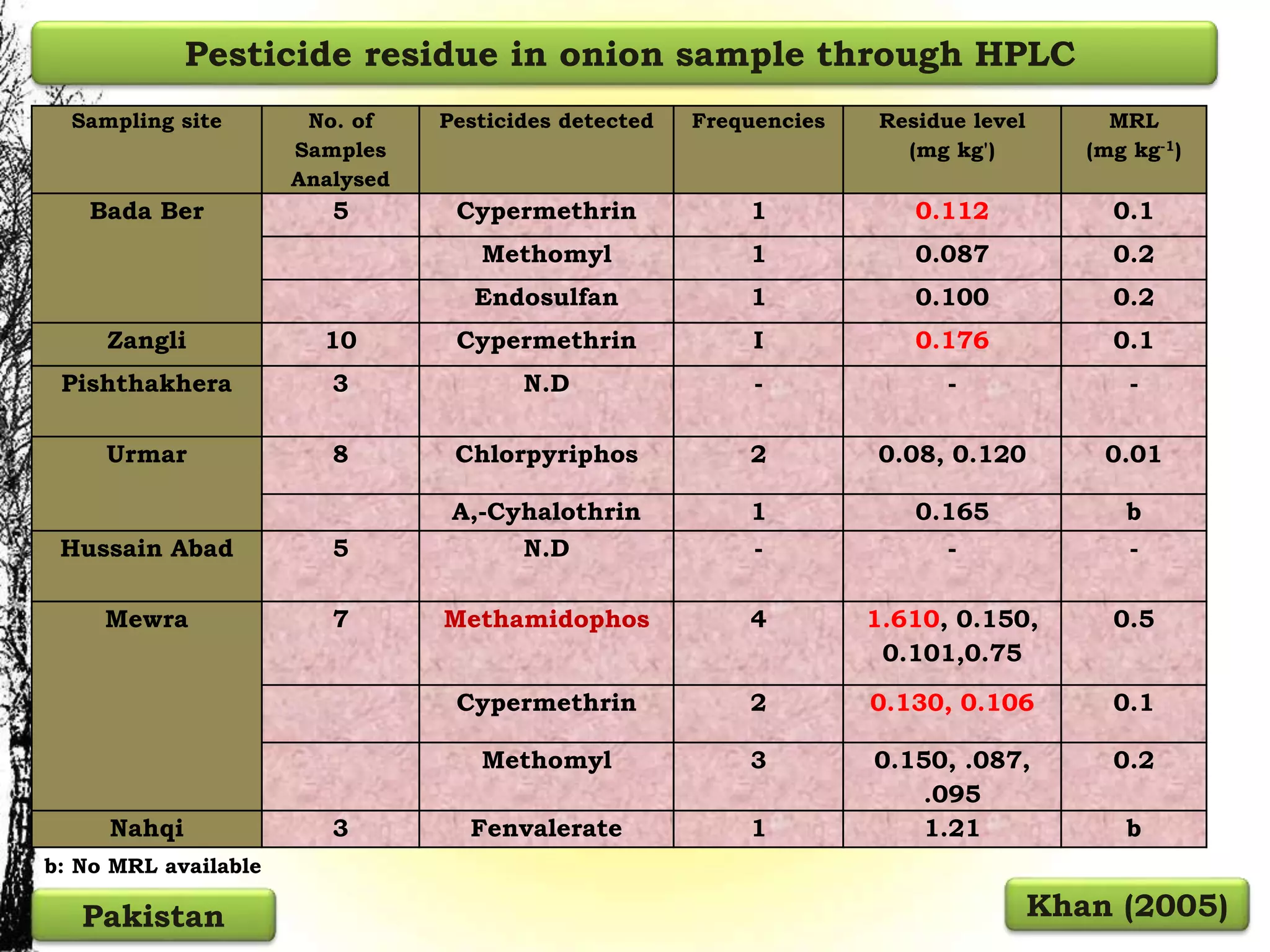
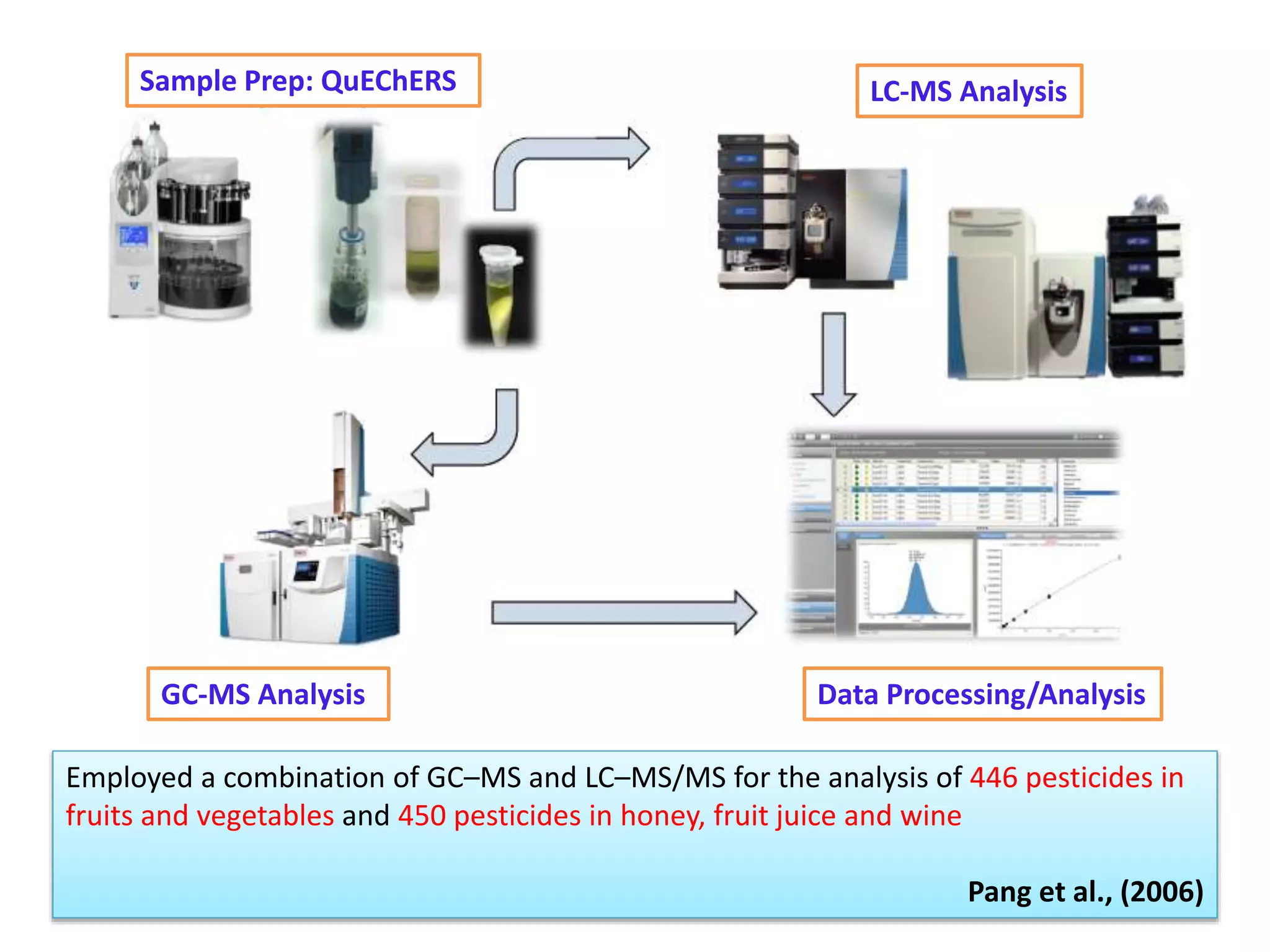
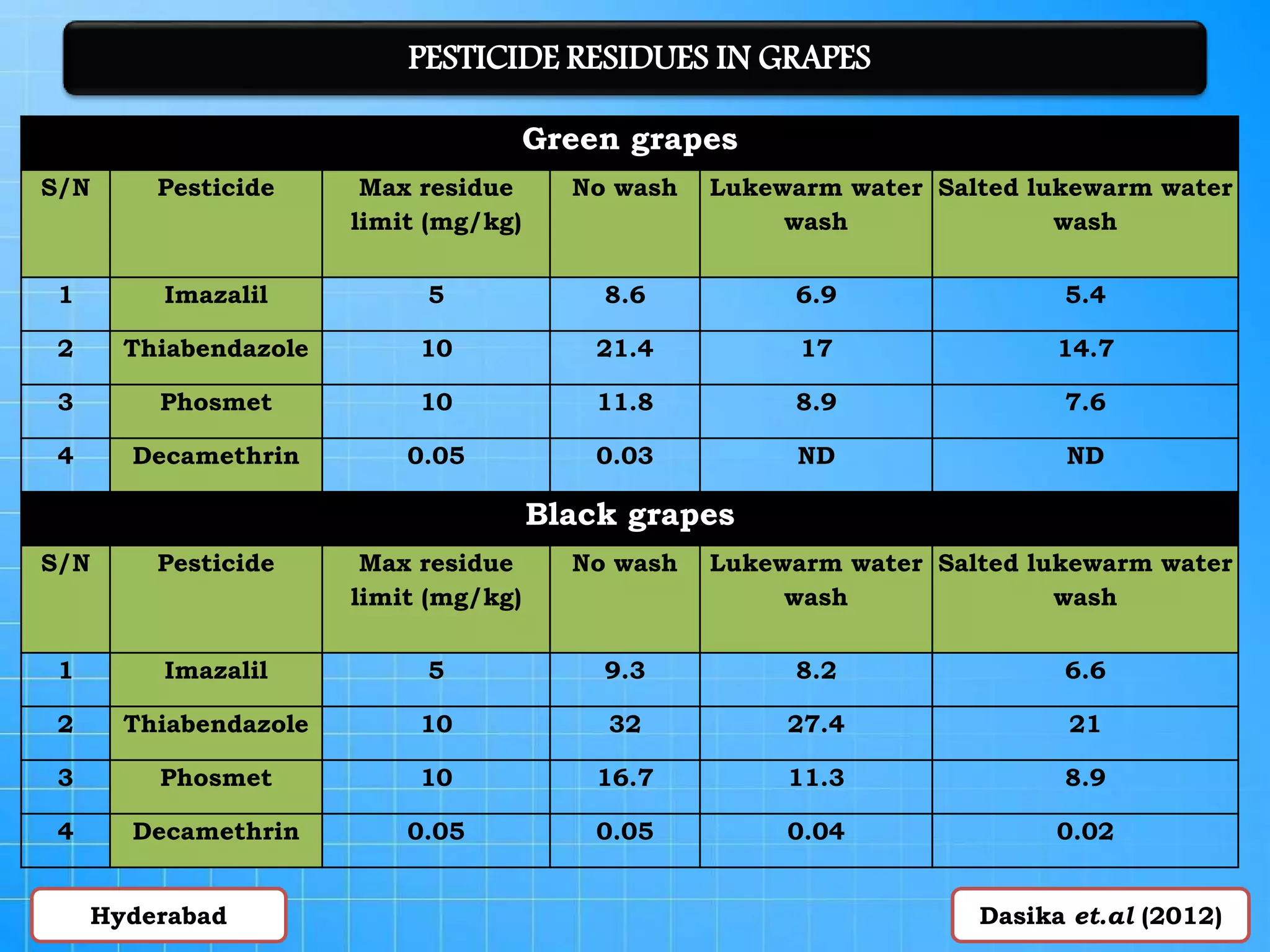
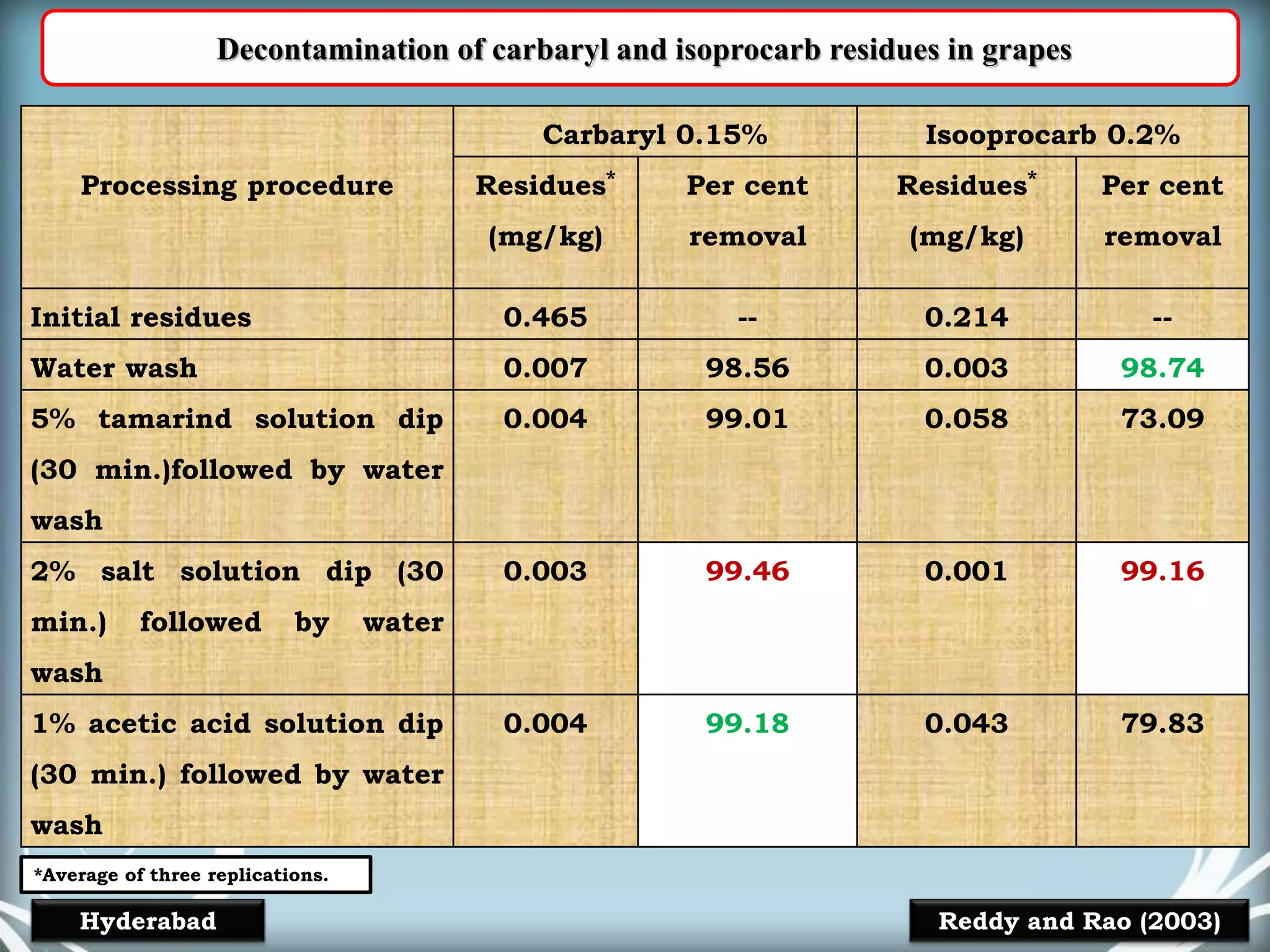
The document discusses various methods for analyzing pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables, including extraction techniques and chromatographic methods like gas and liquid chromatography. It highlights the growing concern over pesticide usage, the importance of monitoring residue levels, and legal limits such as maximum residue levels (MRL). The document also emphasizes the need for careful sampling and preparation, alongside guidelines for reducing exposure to pesticides through washing and cooking produce.