Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times















This document provides guidance on reporting and controlling degradation products in new drug products. It describes degradation products as impurities that arise from reactions between the drug substance and excipients or container closure materials. The summary should include a scientific rationale for evaluating degradation pathways and laboratory studies to detect degradation products. It should also describe reporting results from relevant batches, including degradation product levels and analytical procedures used. The selection of degradation products for product specifications should be based on those observed in batches made by the proposed commercial process. Qualification of degradation products involves acquiring safety data to establish their biological safety at specified levels.
Introduction to the topic of impurities in drug products by Vinit Gohel, highlighting focus on pharmaceutical analysis.
Differentiation between Q3A(R2) and Q3B(R2) guidelines regarding impurities in drug substances and products.
Overview of various sources of impurities in APIs including organic/inorganic substances and environmental factors.
List of impurities and products not covered by guidelines, including excipients, contaminants, and biological products.
Justification for reporting and controlling degradation products arising from drug-excipient interactions.
Guidance on handling degradation products that are below identification thresholds yet might be potent or toxic.
Importance of documenting validated analytical procedures for detecting specified and unspecified degradation products.
Handling differences in analytical procedures, including use of reference standards and correction factors.
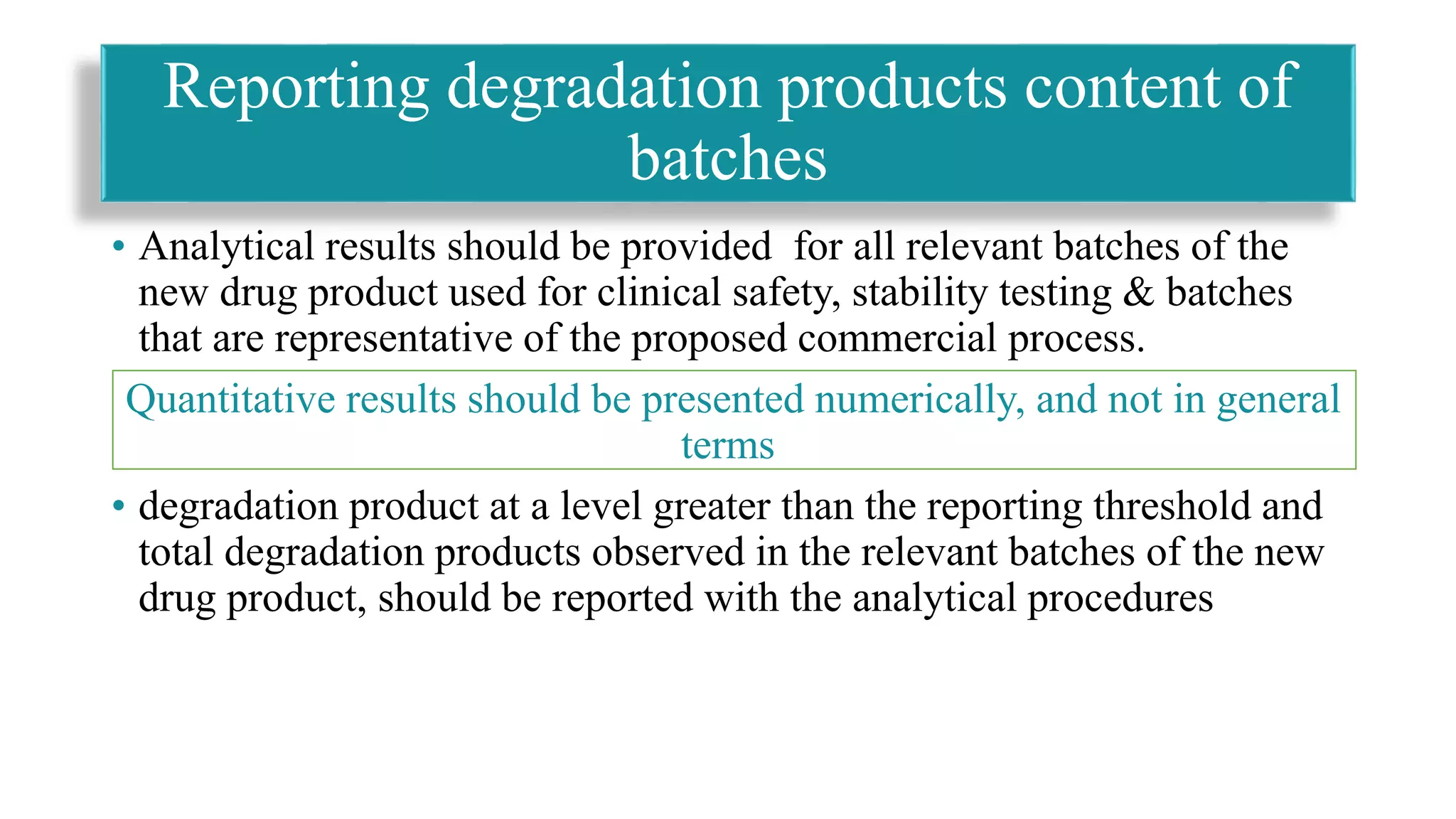
Requirements for reporting quantitative degradation product content in drug batches for safety and stability.
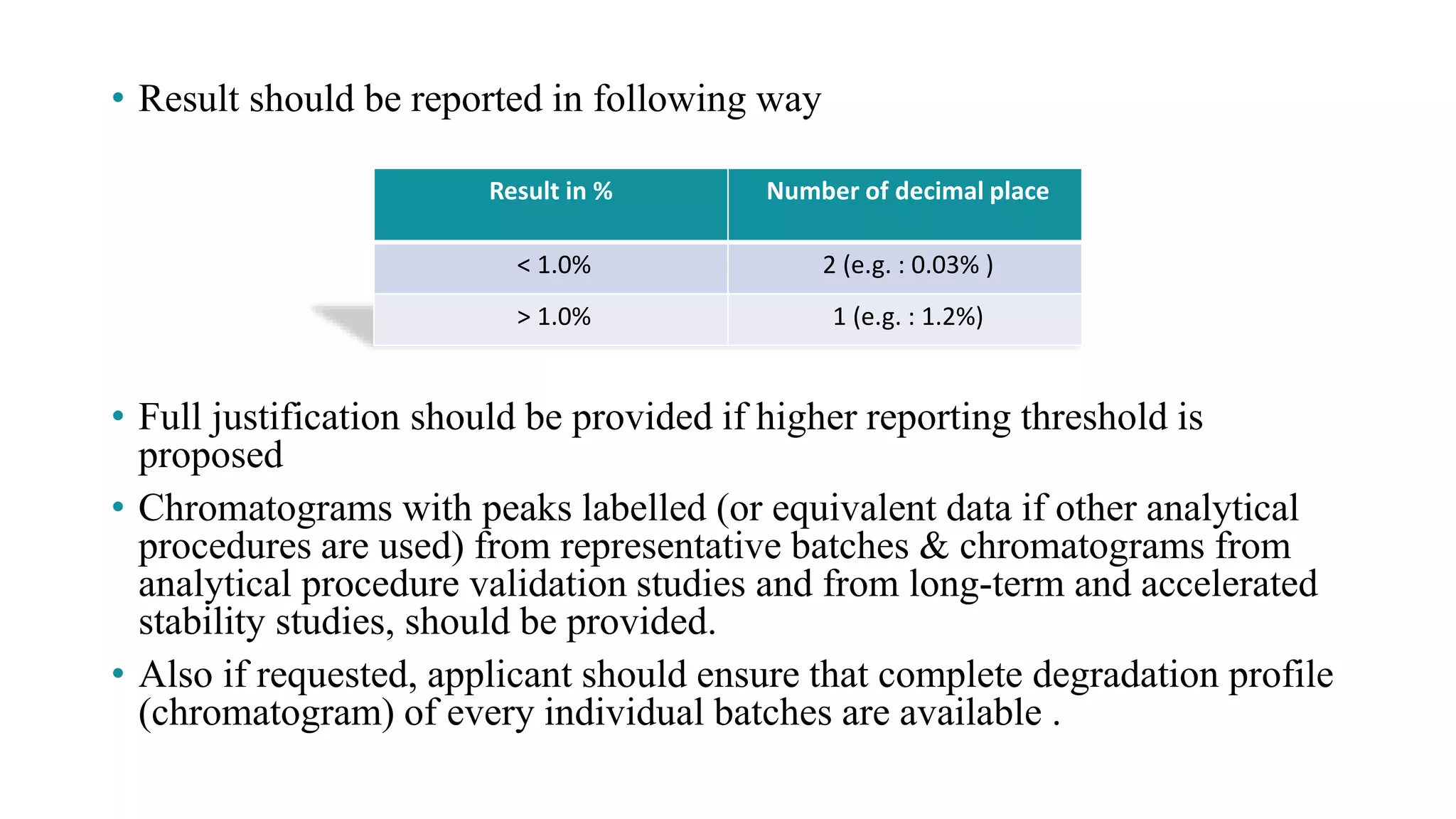
Format for reporting degradation product results and requirements for chromatogram submissions.
Essential batch information needed in registration applications for new drug products, including identity and manufacturing details.
Guidance on listing degradation products expected during manufacturing and outlining acceptance criteria.
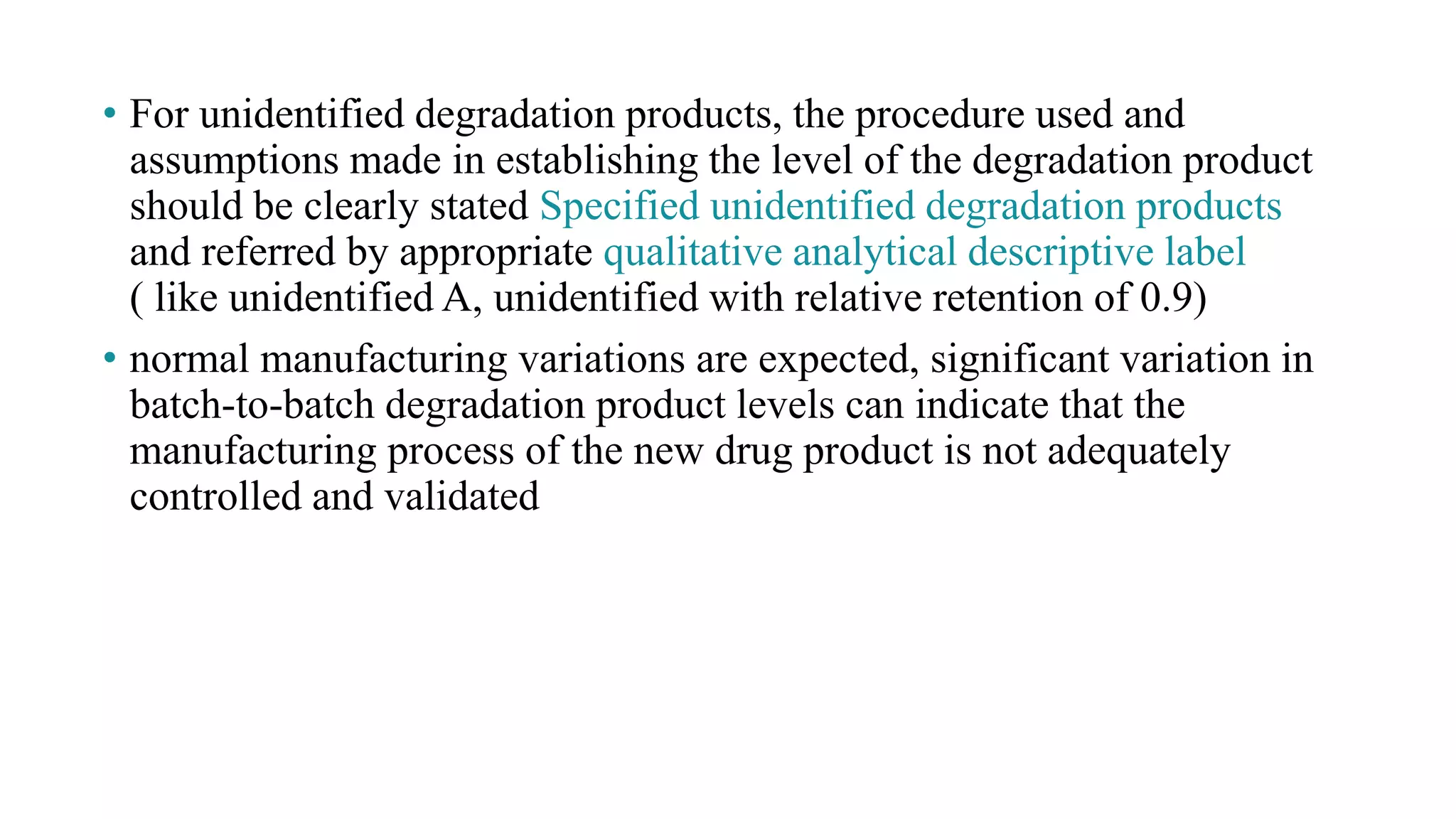
Procedures regarding unidentified degradation products and implications of variation in degradation levels.
Process of qualifying degradation products to ensure biological safety based on clinical study data.
Alternatives to maintaining degradation product levels, including container closure adjustments and literature reference.
Testing safety of drug products with degradation products relative to previously qualified materials.
List of references for guidelines on impurities in drug substances and products, linking to related documents.

















