Residual ridge resorption
- 2. Definitions Pathology classification Pathogenesis Epidemiology Etiology Prevention Treatment Conclusion
- 3. Residual alveolar ridge is the portion of the alveolar ridge and its soft tissue covering which remains following the removal of or loss of teeth. [GPT-8] INTRODUCTION
- 4. • The residual bony architecture of the maxilla and mandible undergoes a life-long catabolic remodeling. • The rate of reduction in size of the residual ridge is maximum in the first 3-6 months and then gradually tapers off. • However, bone resorption activity continues throughout life at a slower rate, resulting in loss of varying amount of jaw structure, ultimately leaving the patient a ‘dental cripple’.
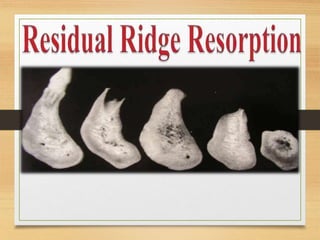
- 6. CLASSIFICATION BY ATWOOD’S • Order 1 : Pre-extraction • Order 2 : Post- extraction • Order 3 : High, well rounded • Order 4 : Knife-edge • Order 5 : Low, well rounded • Order 6 : Depressed Pre extraction Post ext High, well rounded Knife edge Low well rounded Depressed
- 8. • Immediately following the extraction (Order II), any sharp edges remaining are rounded off by external osteoclastic resorption leaving a high well rounded ridge (Order III). • As resorption continues from the labial and lingual aspects, the crest of the ridge becomes increasingly narrow, ultimately becoming knife edged (Order IV). • As the process continues, the knife-edge becomes shorter and eventually disappears leaving a low well- rounded or flat ridge (Order V). Eventually this too resorbs, leaving a depressed ridge (Order VI).
- 9. • Class I : Upto one third of the original vertical height lost. • Class II : From one third to two thirds of the vertical height lost. • Class III : Two third or more of the mandibular height lost. CLASSIFICATION BY WICAL AND SWOOPE
- 10. ACCORDING TO THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF PROSTHODONTISTS Based on Bone Height (Mandible only) • Type I: Residual bone height of 21 mm or greater measured at the least vertical height of the mandible • Type II: Residual bone height of 16 - 20 mm measured at least vertical height of the mandible. • Type III: Residual alveolar bone height of 1 1 - 1 5 mm measured at the least vertical height of the mandible. • Type IV : Residual vertical bone height of 10 mm or less measured at the least vertical height of the mandible.
- 11. PATHOGENESIS
- 12. • The pathogenesis of residual ridge resorption is not well understood. • Longitudinal studies of the form and weight of the edentulous residual ridge in wearers of complete dentures have demonstrated a continuous loss of bone tissue after tooth extraction and placement of complete dentures. • The reduction is a sequel of alveolar remodelling due to altered functional stimulus of the bone tissue. It follows a chronic progressive and irreversible course that often results in severe impairment of prosthetic restoration and oral function.
- 14. • Epithelial tissues begin its proliferation and migration within the first week and the disrupted tissue integrity is quickly restored. • Histologic evidence of active bone formation is seen as early as 2 weeks after the extraction and the socket is progressively filled with newly formed bone in about 6 months.. • The most striking feature of the extraction wound healing is that even after the healing of wounds, the residual ridge undergoes a lifelong catabolic remodeling.
- 15. • This unique phenomenon has been described as RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION(RRR). • The rate of RRR is different among persons and even at different sites in the same person.
- 16. According to Boucher, During the first year after tooth extraction, the reduction in residual ridge height in the midsagittal plane is 2-3 mm for maxilla 4-5 mm for mandible Annual rate of reduction in height 0.1-0.2 mm for mandible 4 times less in the maxilla AMOUNT AND RATE OF BONE RESORPTION
- 17. • Maxilla resorbs upward and inward to become progressively smaller because of the direction and inclination of the roots of the teeth and the alveolar process. • The opposite is true of the mandible, which inclines outward and becomes progressively wider. • This progressive change of the edentulous mandible and maxilla makes many patients appear prognathic. DIRECTION OF BONE RESORPTION
- 18. Thus, RRR is centripetal in maxilla and centrifugal in mandible.
- 19. • In the Mandible, large proportions of bone loss occurs in the labial side of anterior residual ridge, equally on the buccal and lingual side in premolar region and lingually in the posterior or molar region. • In the Maxilla bone loss primarily occurs on the labial or buccal aspect. PATTERNS OF BONE RESORPTION
- 20. • While teeth arrangement we should try to restore the natural position of the teeth before they were lost, Hence teeth in the maxillary arch are arranged slightly labially and buccally. • While in the mandible, teeth in the anterior region are arranged labially, on the centre of the ridge in the premolar region and slightly lingually in the molar region.
- 21. EPIDEMIOLOGY OF RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION • To date, it appears that RRR world-wide, occurs in males and females, young and old, sickness and in health, with and without dentures and is unrelated to the primary reason for the extraction of the teeth (Caries/periodontal disease).
- 22. AETIOLOGY
- 23. • RRR is a multifactorial biomechanical disease caused by a combination of ◦ ANATOMIC FACTORS ◦ MECHANICAL FACTORS ◦ METABOLIC FACTORS AETIOLOGY OF RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION
- 24. • It is postulated that RRR varies with the quantity and quality of the bone of residual ridges. RRR α Anatomic factors ie, the more bone there is, the more RRR will ultimately be. But this cannot be considered a good prognostic factor, because in some cases large ridges resorb rapidly and some knife-edge ridges may remain with little change for long periods of time. ANATOMIC FACTORS
- 25. ANATOMIC FACTORS These are more pronounced in mandible with the maxilla; associated more in patients with short and square with increased masticatory forces. Large well-rounded ridges and broad palates are favourable anatomic factors for residual ridge resorption.
- 26. ANATOMIC FACTORS Alveoplasty But this cannot be considered a good prognostic factor, because in some cases large ridges resorb rapidly and some knife-edge ridges may remain with little change for long periods of time.
- 27. • RRR varies directly with certain systemic or localized bone resorptive factors and inversely with certain bone formation factors. RRR BONE RESORPTION FACTORS BONE FORMATION FACTORS METABOLIC FACTORS
- 28. BONE RESORPTION FACTORS • Correct amount of circulating estrogen, thyroxine, growth hormone, calcium, phosphorus, • vitamin D , • Osteoporosis • Hypophosphetemia • Parathormone • Calcitonin LOCAL SYSTEMIC • Endotoxins from dental plaque • Osteoclast activating factor(OAF) • Prostaglandins • Human gingival bone resorption factor • Trauma due to ill fitting dentures which leads to increased or decreased vascularity and changes in oxygen tension.
- 29. Osteoporosis is defined by the WHO as bone mineral density (BMD) greater than 2.5 standard deviations below that of the young adult BMD. Osteoporosis is common in aging individuals, especially in post menopausal women when the estrogenic blood level is low. In elderly men and women, osteoporosis is caused by a variety of factors such as calcium loss, calcium deficiency, hormonal deficiency, change in protein nutrition and decreased physical activity. OSTEOPOROSIS
- 31. Residual ridge resorption of the jaws is also more rapid in increasing age group, depleted bone being prone to the injurious impact of mechanical forces.
- 32. MECHANICAL FACTORS Though residual ridge resorption may be inevitable due to ‘disuse atrophy’, it can also be caused due to excessive force transmitted through denture wearing and unstable occlusal conditions.
- 33. MECHANICAL FACTORS The mechanical factors (masticatory factors or parafunctional forces) transmitted by the denture or the tongue to the residual ridge are assumed to be important factors in the remodelling process. However, there is no scientific evidence that parafunctional forces are related to the degree of residual ridge reduction.
- 34. • Apparent loss of sulcus width and depth. • Displacement of muscle attachment close to the ridge. • Loss of vertical dimension of occlusion. • Reduction of the lower face height. • Anterior rotation of mandible and increase in relative prognathism. CONSEQUENCES OF RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION
- 35. CONSEQUENCES OF RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION • Mental foramen may come to lie at or near the level of upper border of the body of mandible. • The genial tubercles project above the upper border of the mandible in the symphysial region. • Flattening of the vault of the palate.
- 36. CONSEQUENCES OF RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION • Reduction in the height of both the maxillary and mandibular edentulous arches. While the maxillary arch resorbs buccally and labially with a concomitant reduction in perimeter or circumference of the arch, the mandibular arch resorbs in a labial and lingual direction resulting in widening of the arch posteriorly. This will lead to the confinement of maxillary arch within the mandibular arch in long-standing edentulous situations, giving a pseudo class III ridge relationship.
- 37. CONSEQUENCES OF RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION • Changes in inter alveolar relationship after progression of the residual ridge reduction, which is essentially centripetal in the maxilla and centrifugal in the mandible. • Morphological changes of the alveolar bone such as sharp, spiny uneven residual ridges. • Location of mental foramina close to the ridge crest.
- 38. PREVENTION OF RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION a. Prevention of loss of natural teeth: • Alveolar bone supporting natural teeth receives tensile loads through a large area of periodontal ligament. • While the edentulous residual ridge receives vertical, diagonal and horizontal loads applied by a denture with a surface area much smaller than the total area of the periodontal ligament of all the natural teeth that had been present.
- 39. Optimal tissue health prior to making impression. Impression procedures • Minimal pressure impression technique. • Selective pressure impression technique: places stress on those areas that best resist functional forces • Adequate relief of non stress bearing areas eg. Crest of mandibular ridge.
- 40. • Avoidance of inclined planes to minimize dislodgment of dentures and shear forces. • Centralization of occlusal contacts to increase stability and maximize compressive forces. • Provision of adequate tongue room to improve stability of denture in speech and mastication.
- 41. • Adequate interocclusal distance during jaw rest to decrease the frequency and duration of tooth contact. • Occlusal table should be narrow • The concept and arrangement of teeth in neutral zone helps the teeth to occupy a space determined by the functional balance of the oro- facial and tongue musculature.
- 42. • It has been seen that one of the cofactor in RRR is low calcium and vitamin D metabolism. • Diet counseling for prosthodontic patients is necessary to correct imbalances in nutrient intake. • Denture patients with excessive RRR report lower calcium intake and poorer calcium phosphorus ratio, along with less vitamin D.
- 43. • Nutritionally deficient denture-bearing tissues will be uncomfortable for the denture, it is essential to improve the nutritional status of the elderly patients through proper counselling and nutritional supplements, for prosthodontic treatment to be successful.
- 44. TREATMENT OF RESIDUAL RIDGE • A close correlation between a patient’s satisfaction with dentures and the anatomical conditions of the residual ridge is not always present. • However, in long-term complete denture wearers, the morphological changes and the reduction of the residual ridges present serious clinical management challenges on how to provide adequate support, stability, and the retention of new dentures. These problems are approaches by various preprosthetic surgical initiatives.
- 45. PREPROSTHETIC SURGERY • Excessive residual ridge resorption leads to loss of sulcus width and depth with displacement of muscle attachment more to the crest of residual ridge. • Osseous reconstruction surgeries, removal of high frenal attachments, ridge augmentation procedures, vestibuloplasties with skin or mucosal grafts etc may be required to correct these conditions.
- 46. Inferior Border AugmentationSuperior Border Augmentation Interpositional Grafts RIDGE AUGMENTATION PROCEDURES
- 47. OVERDENTURES • Overdentures help in minimizing ridge resorption contribute towards enhanced retention, stability, support of prosthesis along with preservation of proprioception. Clinicians must try to retain residual roots whenever possible.
- 48. OVERDENTURES The advantages of overdentures over conventional dentures are: • The denture bearing mucosa of the residual ridges are spared abuse. • Maintenance of the alveolar bone. • Sensory feedback. • Tactile sensitivity discrimination. • Masticatory performance.
- 49. OSSEOINTEGRATION AND IMPLANT SUPPORTED STRUCTURES • The introduction of osseointegrated implants has eclipsed traditional preprosthetic surgical techniques. The use of implant-supported overdentures resembles the same clinical situation of teeth supported overdentures. These are cost-effective treatment option for the completely edentulous individual.
- 50. ADVANTAGES OVER COMPLETE DENTURES: • Better retention, stability and speech • Improved chewing and speech • Reduced prosthesis size • Reduced anterior bone loss
- 51. Metal based denture with soft liner is advocated in patients with severely atrophic residual ridges. Metal base provides- ◦ Weight necessary to facilitate retention ◦ MaintainAdequate strength with modest extensions The soft liner accomodates ridge irregularities and changes. METAL BASED DENTURES
- 52. IMMEDIATE DENTURES Some authors claim that extraction followed by immediate dentures reduces the ridge resorption.
- 53. • The ultimate aim of a successful prosthesis is stability in function and excellent esthetics. • The expectations of edentulous patients are highly variable therefore the outcome of patient treatment varies significantly. • Patients should be educated regarding the type and extent of treatment that is ideal for them, the prognosis of the treatment outcomes with various types of removable or fixed prostheses and the alternatives that are available. CONCLUSION
- 54. REFERENCES • Prosthodontic treatment for edentulous patients (12th Edition) – Zarb – Bolender • Textbook of prosthodontics (2nd Edition) – V. Rangarajan