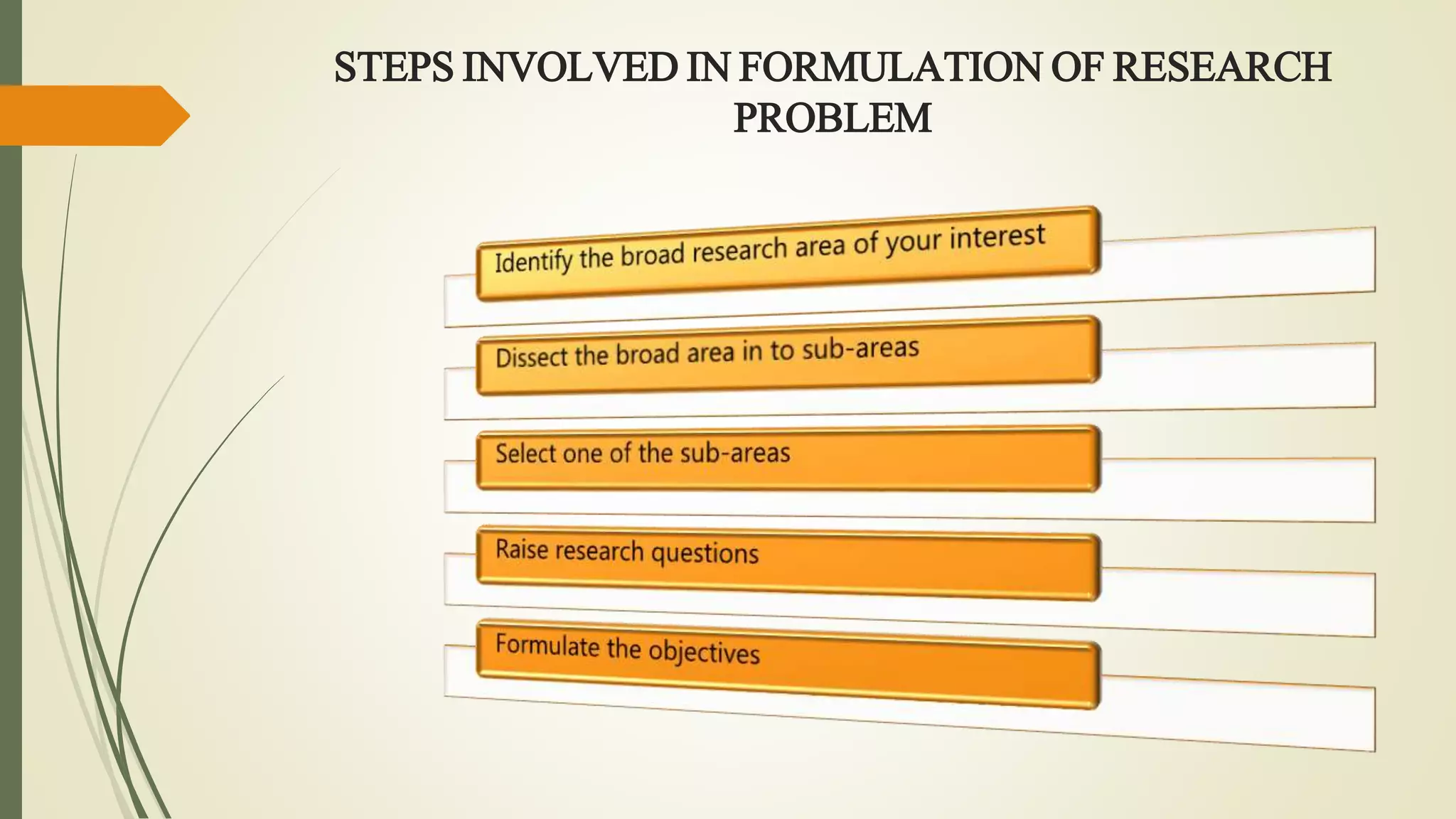
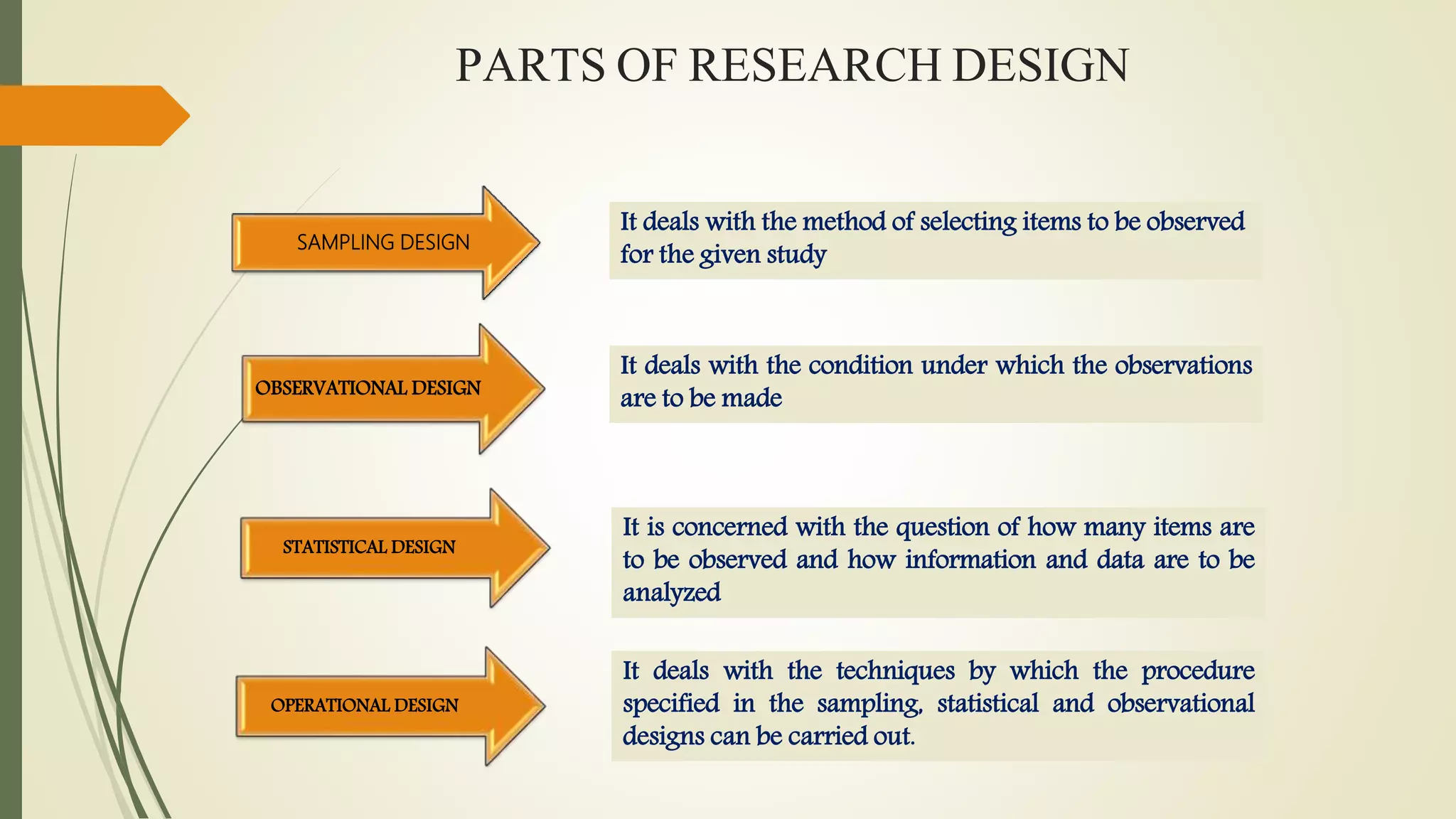
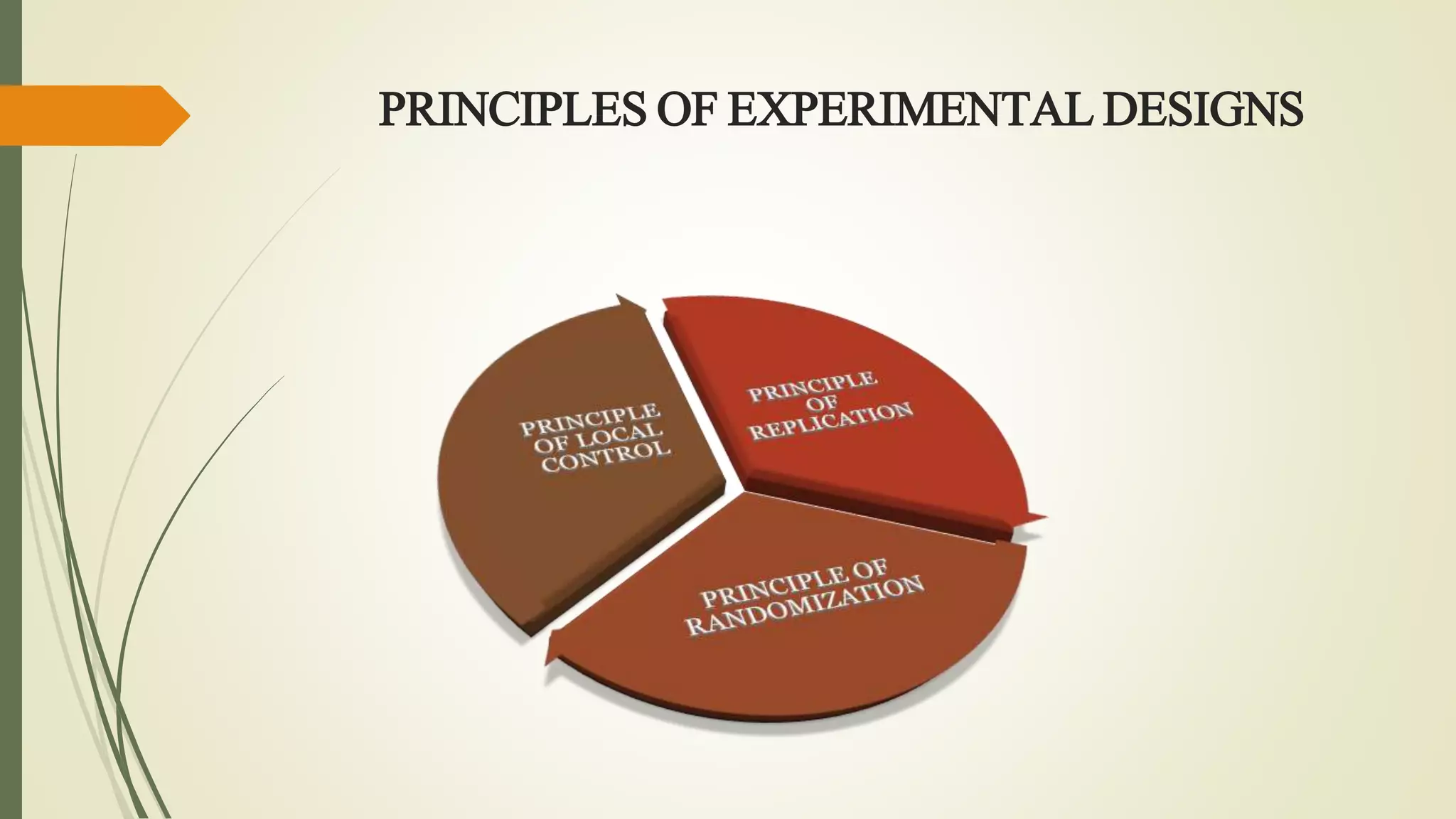
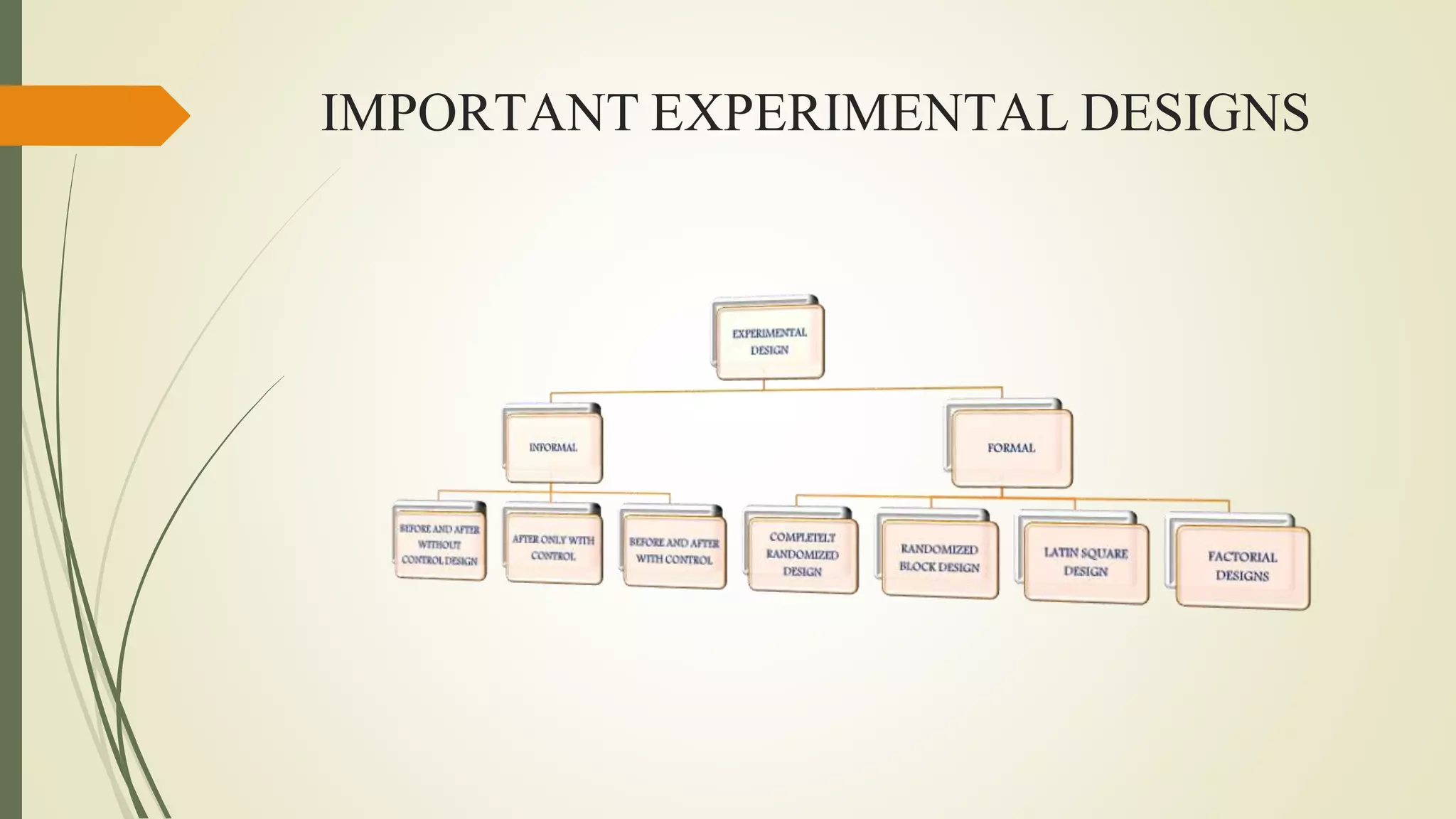
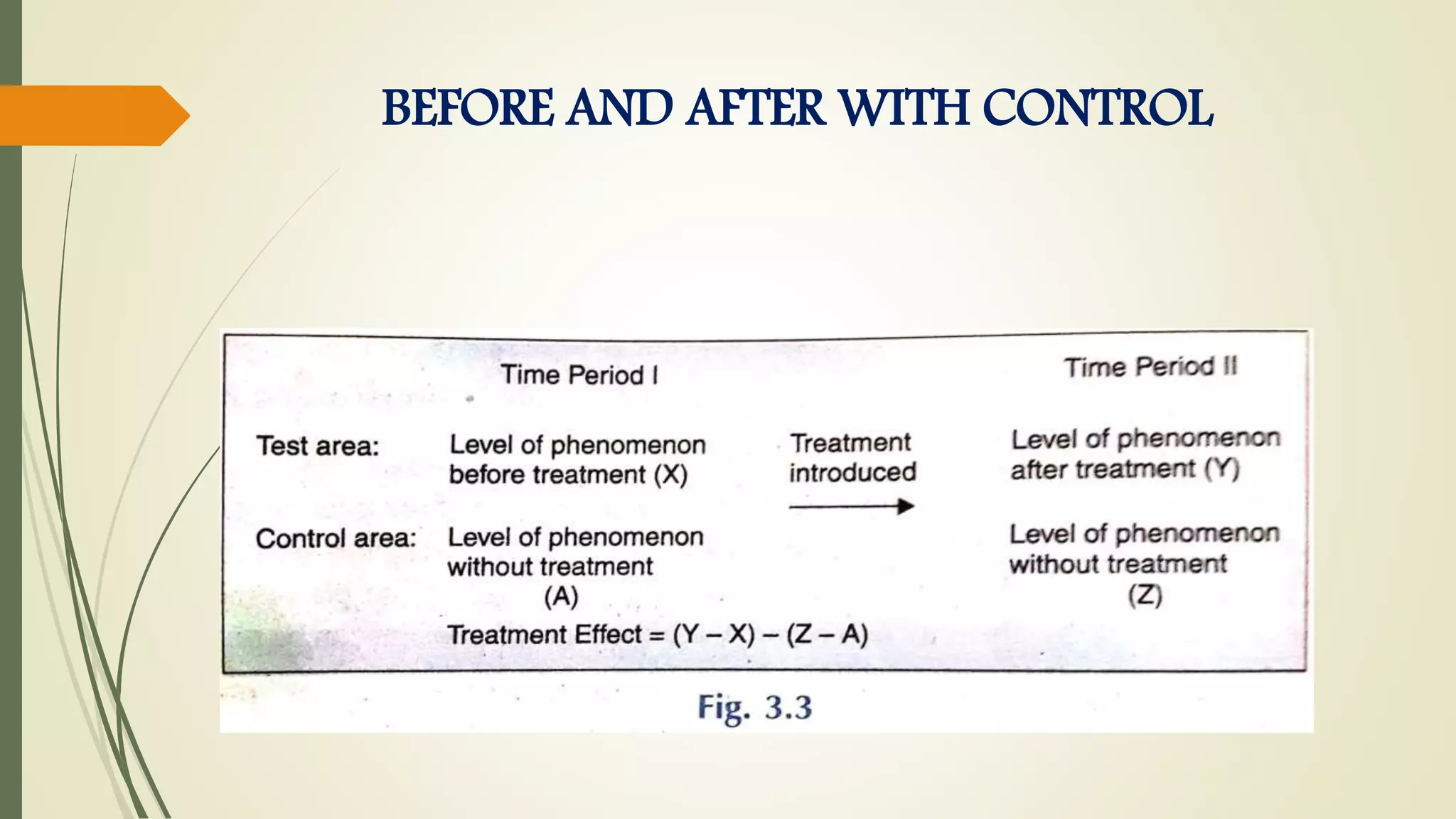
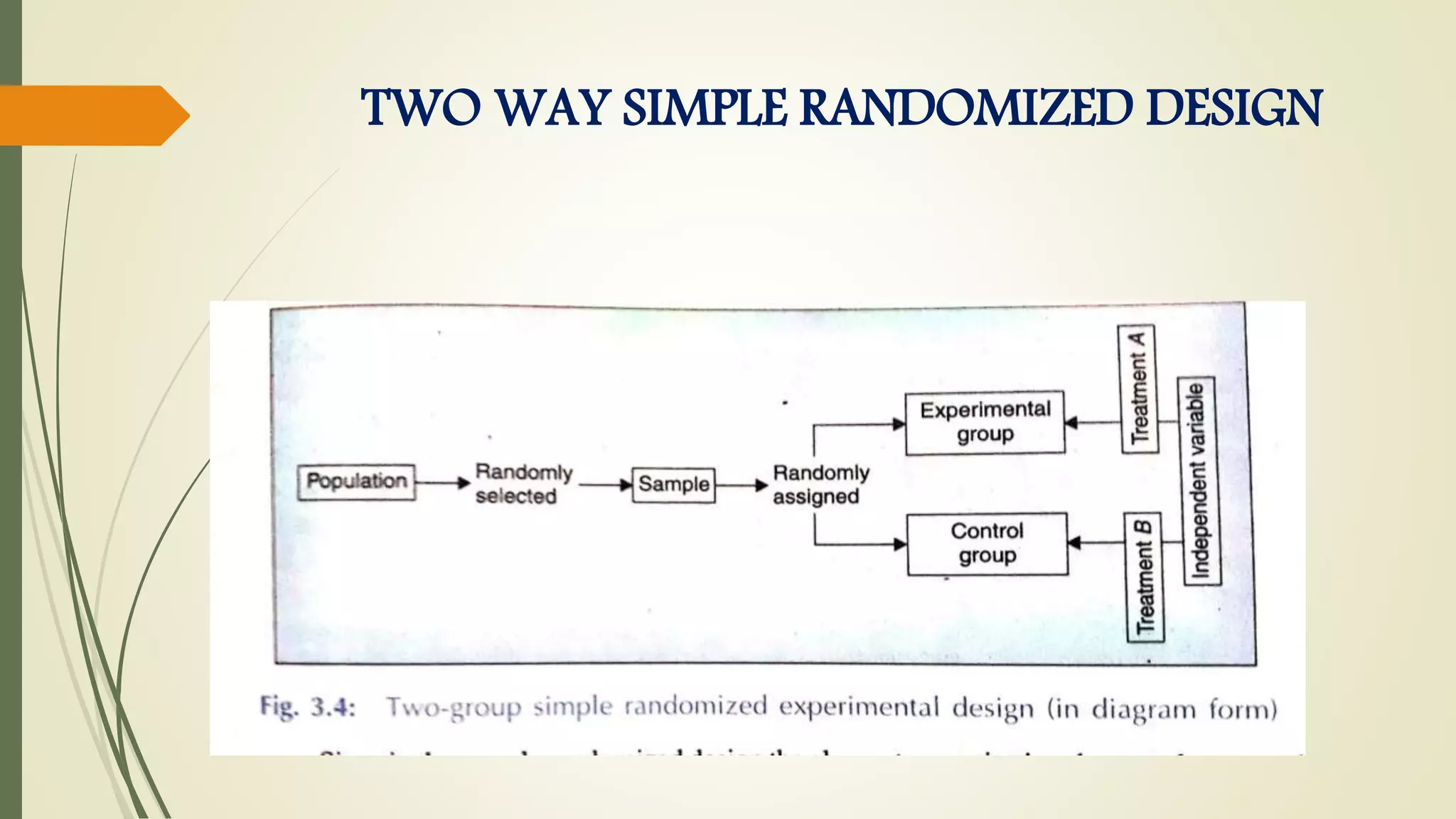
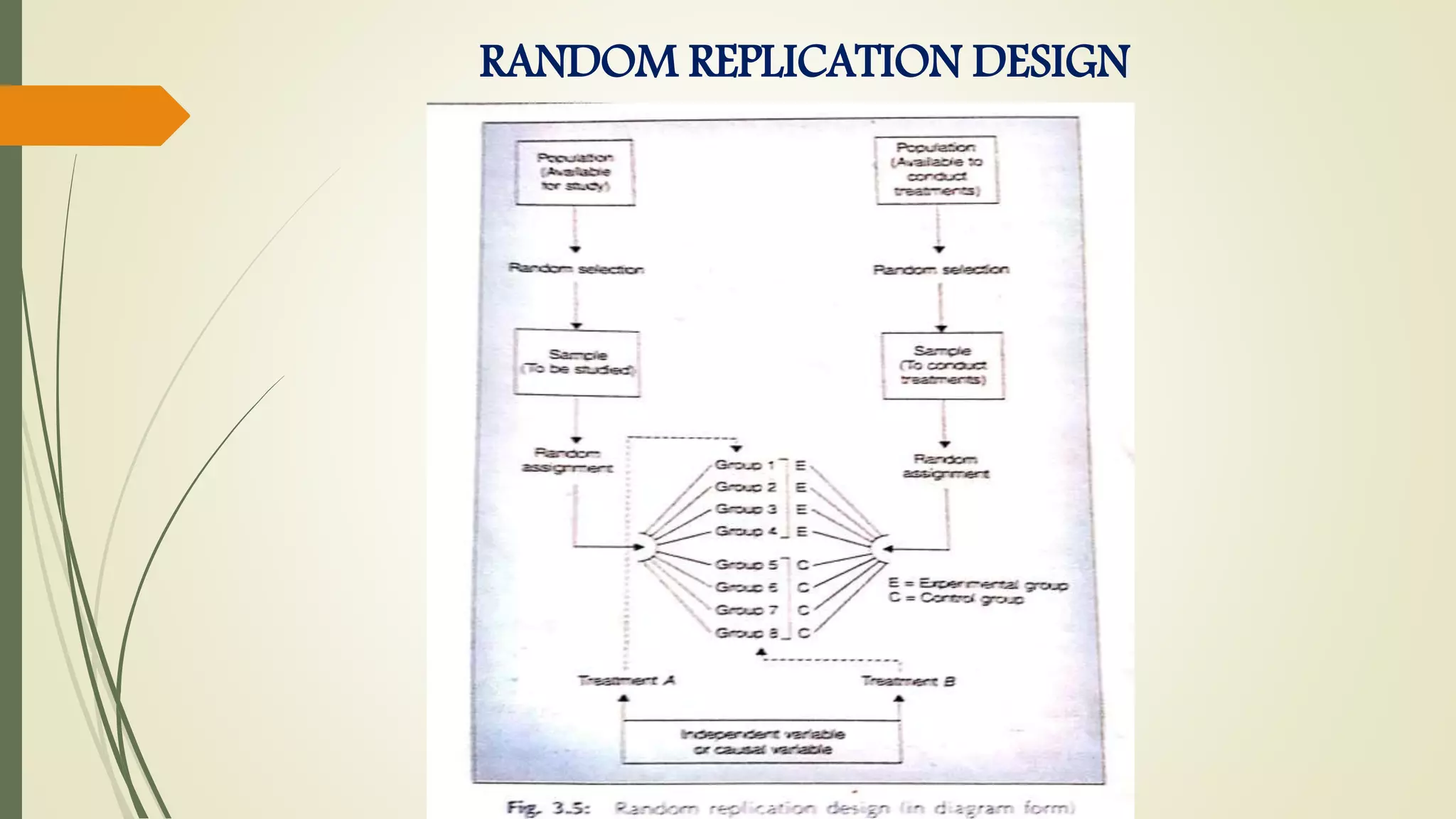
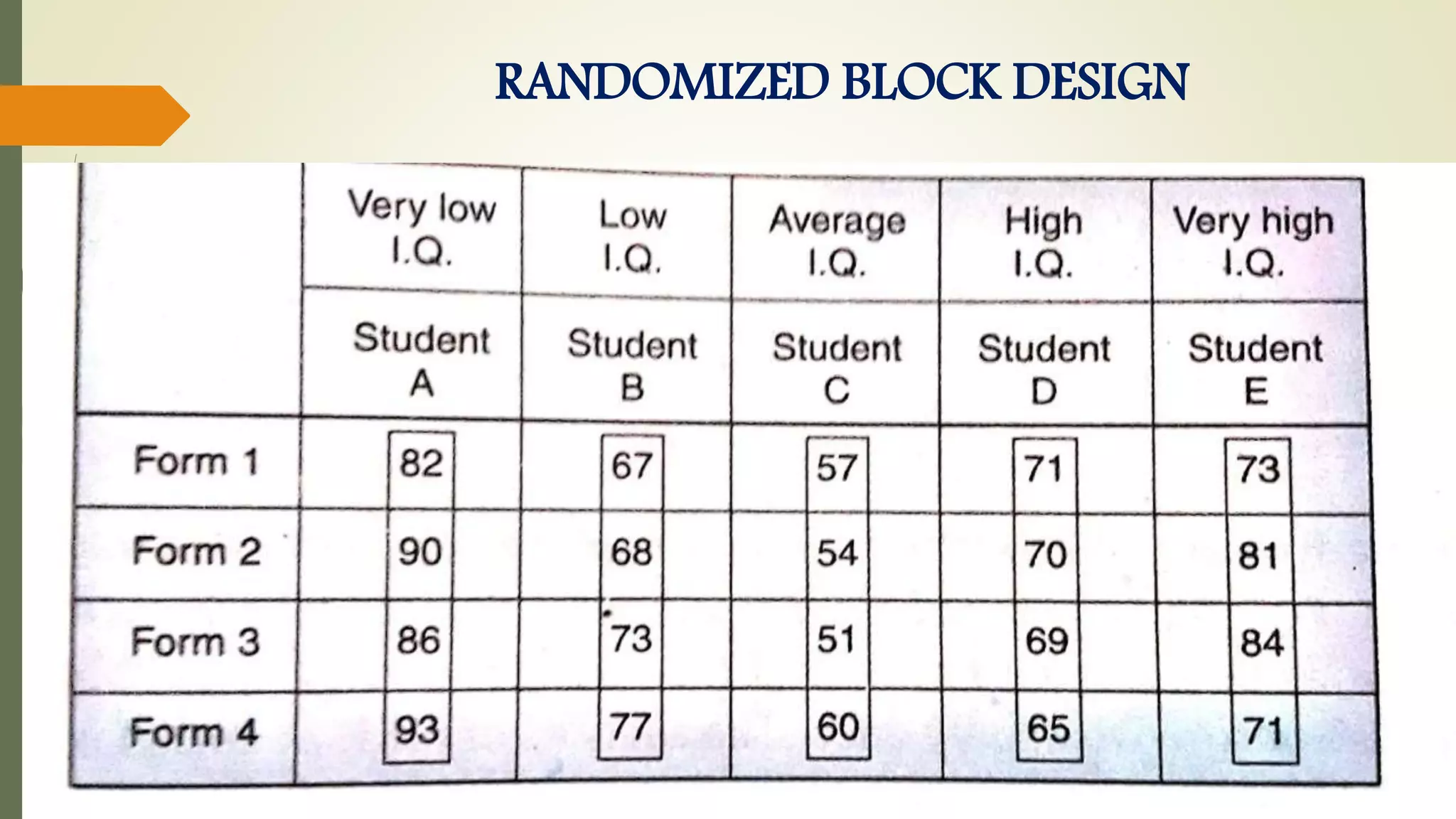
This document discusses research problems and research design. It begins by defining a research problem as some difficulty a researcher wants to solve, either theoretically or practically. Key components of a research problem include the individuals involved, objectives, environment, and possible outcomes. Properly identifying and formulating a research problem is important. The document then discusses research design, defining it as the conceptual framework for a research study. Key parts of research design include sampling, observation, statistics, and operational aspects. A good research design provides structure and limits errors.