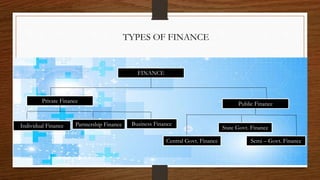
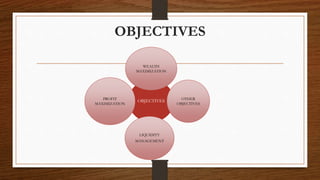
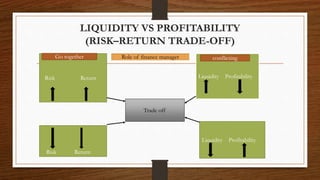
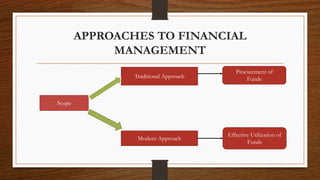
This document discusses key concepts in financial management. It begins by defining finance and its importance in economic activities. It then discusses different types of finance including private, public, individual, partnership and business finance. The main topics covered include financial management, its objectives like profit maximization and wealth maximization, liquidity management, approaches to financial management including traditional and modern approaches, and the main functions of finance like investment, financing, liquidity and dividend decisions. Criticisms of profit and wealth maximization objectives are also provided. The document provides an overview of fundamental concepts in the field of financial management.