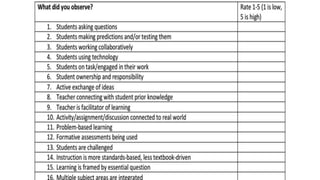
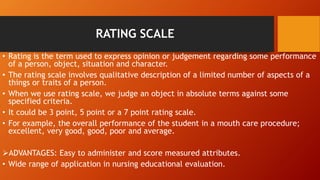
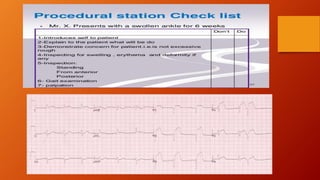
The document discusses various methods for clinical evaluation of students in nursing education. It describes formative and summative evaluation, as well as specific methods like case studies, practical exams, observational checklists, rating scales, oral exams, and OSCEs. Each method has advantages and disadvantages for objectively and reliably assessing students' clinical skills and competencies. An effective evaluation combines several methods to provide a holistic view of students' abilities.