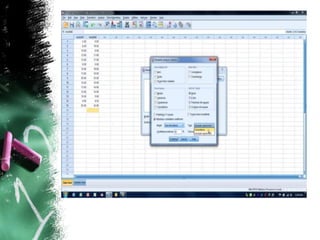
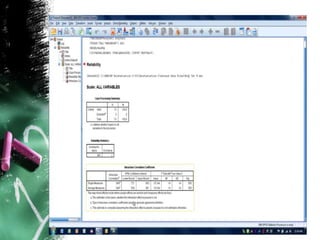
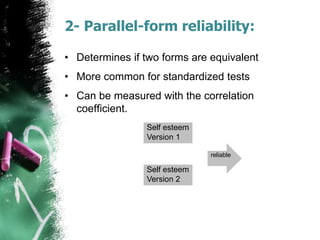
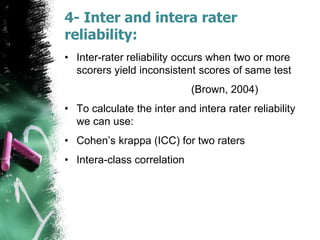
This document discusses the concept of reliability in testing. It defines reliability as the consistency of a test in measuring what it intends to measure. There are different types of reliability: test-retest reliability measures consistency over time; parallel-forms reliability compares equivalent tests; and internal consistency examines reliability between parts of a single test using methods like split-half, Cronbach's alpha, and inter-rater reliability. Factors like standardized administration, clear scoring criteria, and minimizing errors can improve a test's reliability. Reliability is a necessary but not sufficient condition for validity - a test must demonstrate reliability before its validity can be established.