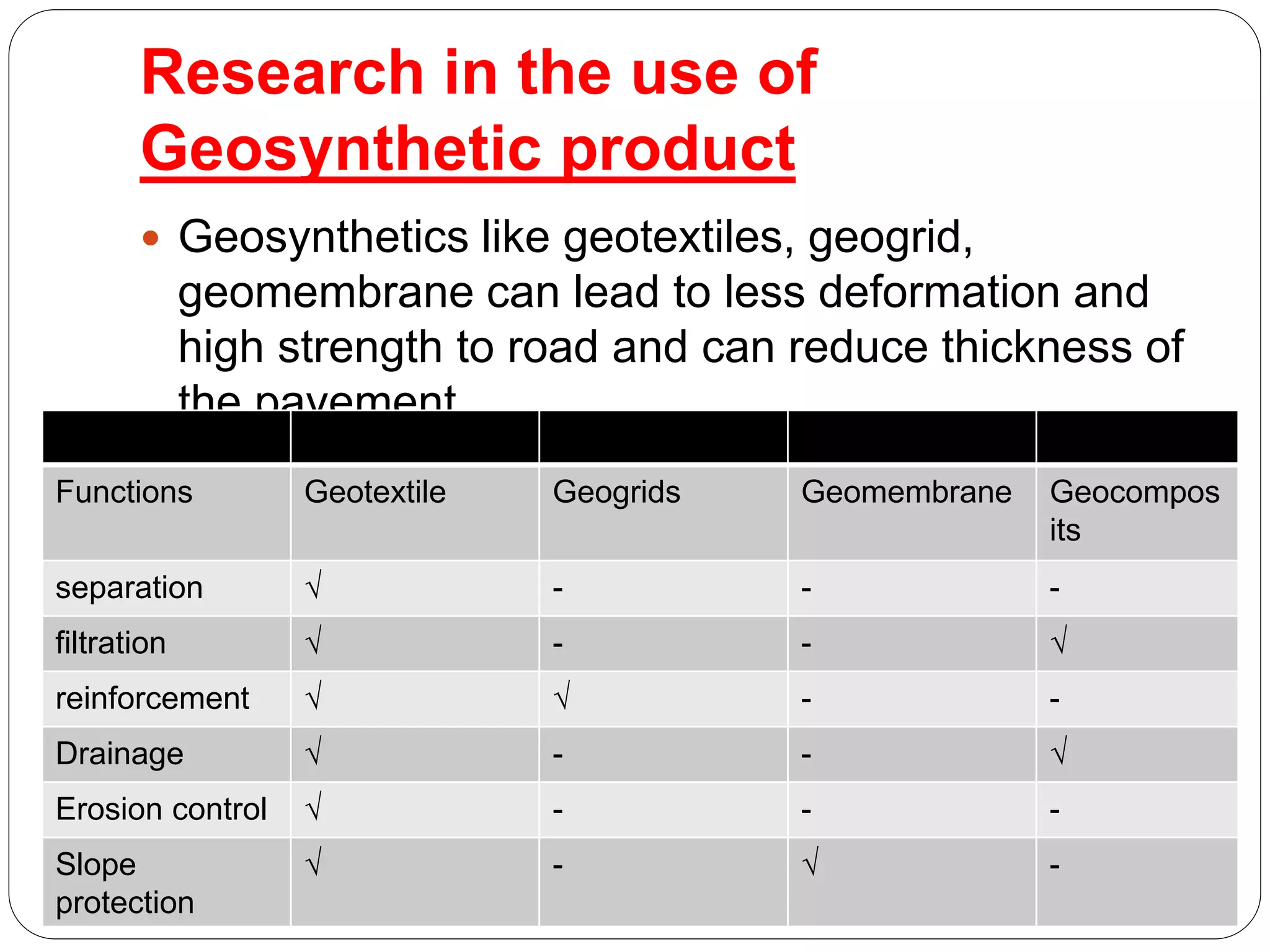
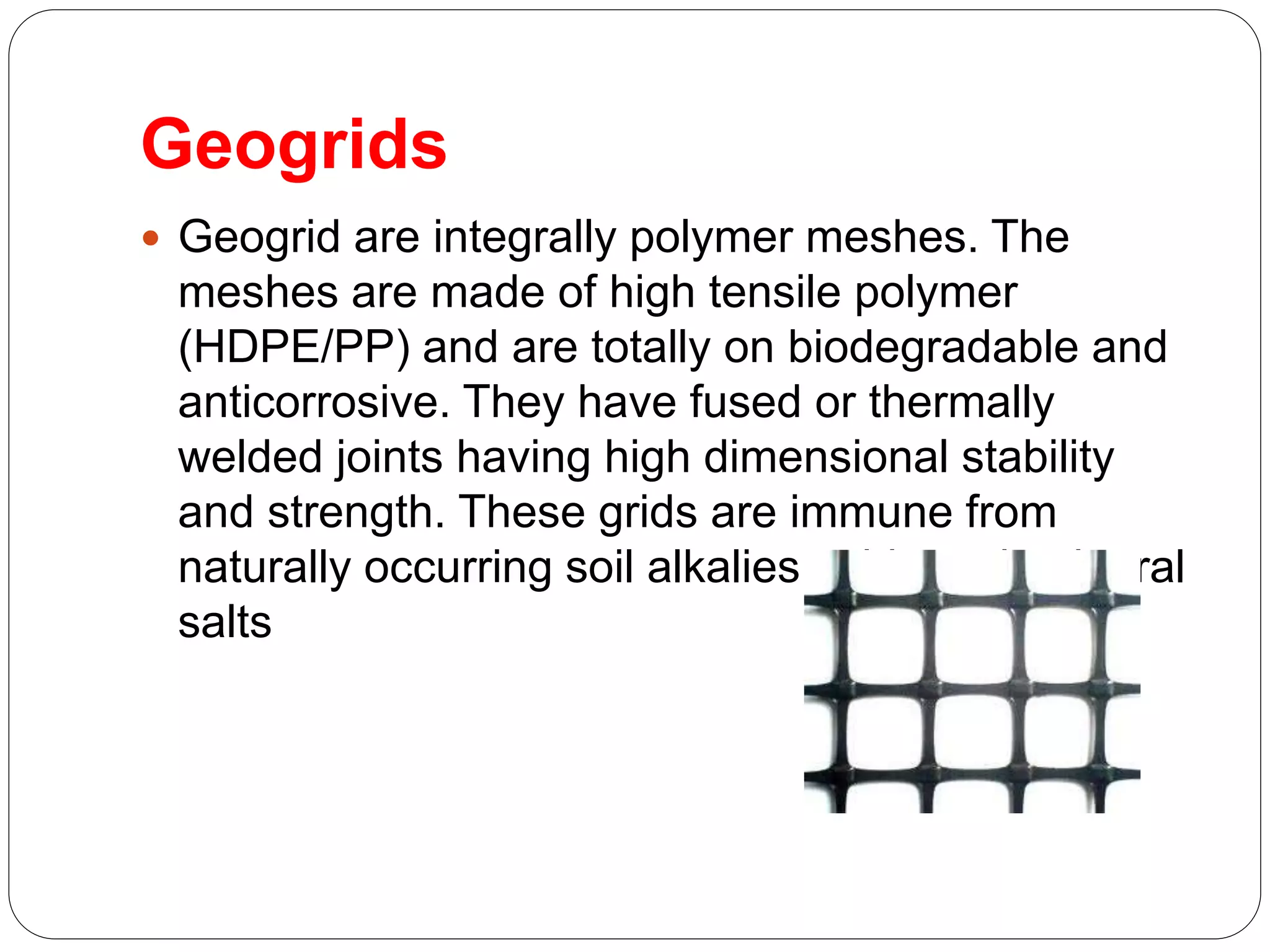
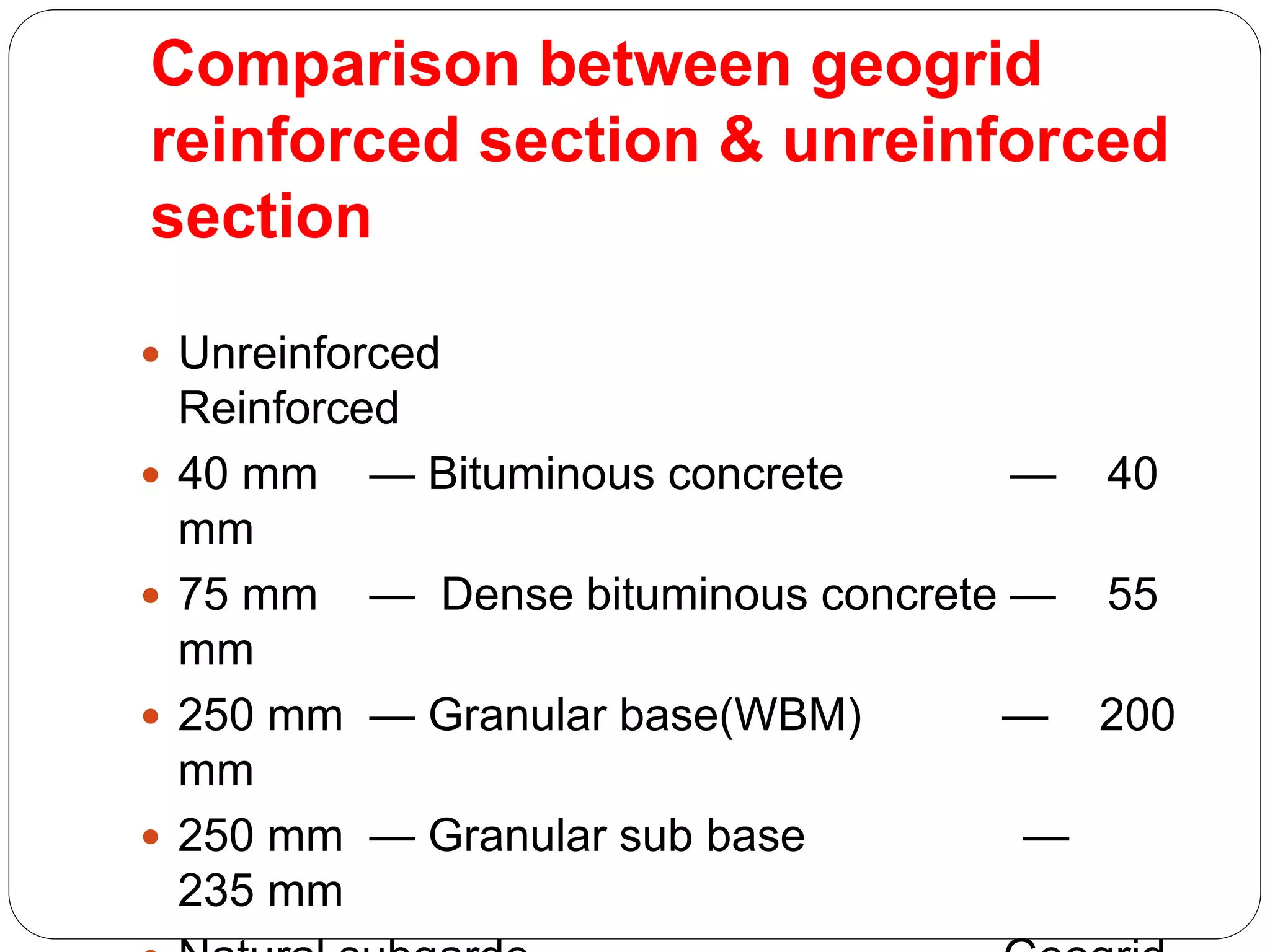
Ground improvement involves altering the properties of soil to better suit engineering project requirements rather than changing the design. This involves reducing settlement, increasing shear strength and bearing capacity, and improving liquefaction resistance. A simple demonstration showed how adding a cloth layer to a pile of sand reduced dispersion, analogous to how geosynthetics can improve soil. Geogrids are polymer meshes that reinforce soil through friction and adhesion. Geotextiles and geogrids can reduce required pavement thickness for roads by improving soil strength properties.