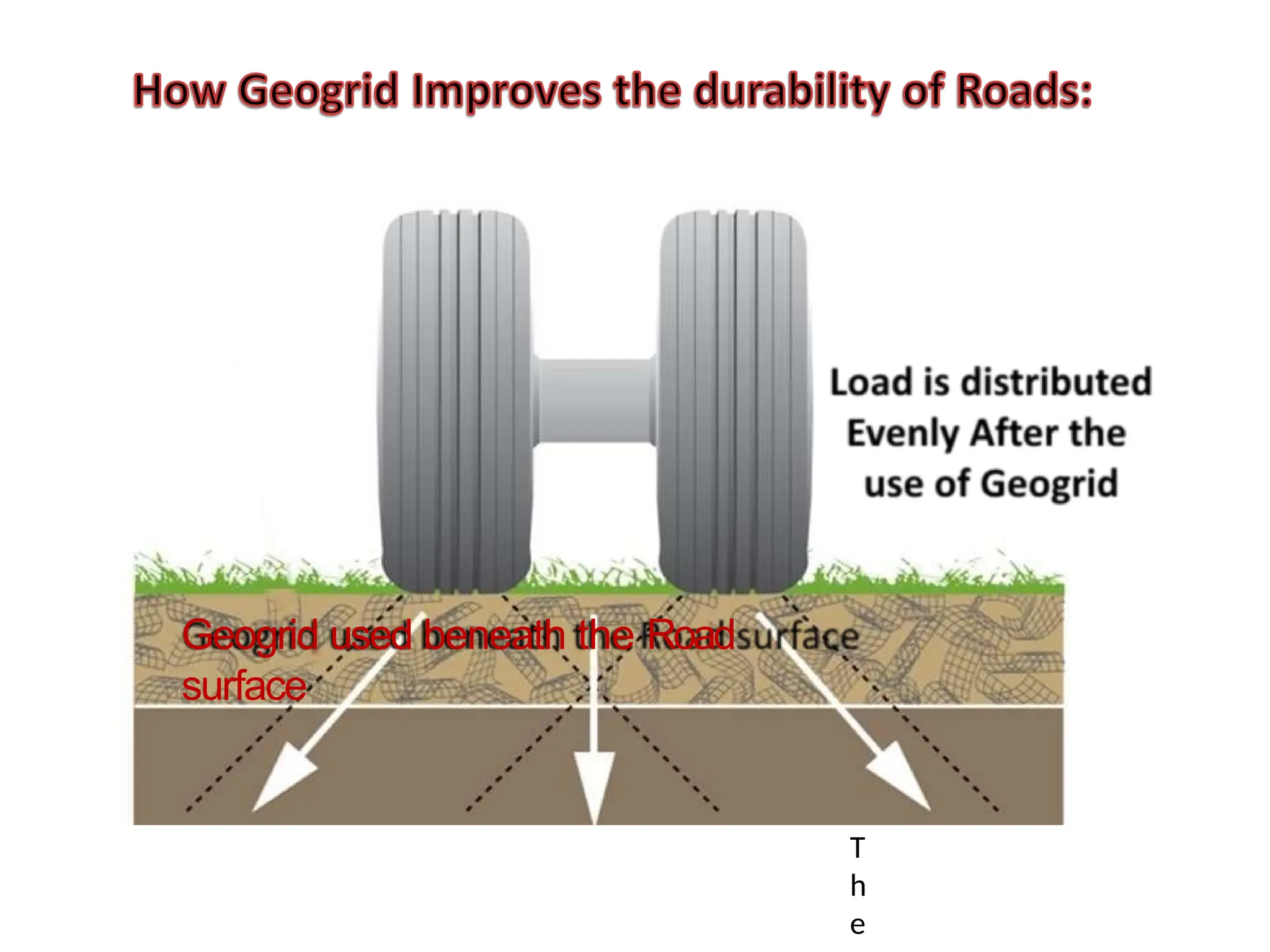
Geosynthetics are polymer-based materials used in civil engineering to enhance the behavior of geological materials such as soil and rock, with applications in various fields including transportation and erosion control. Different forms such as geotextiles, geogrids, and geomembranes serve specific functions like separation, reinforcement, and drainage. These materials provide advantages in ground stabilization, building foundations, and managing environmental conditions.