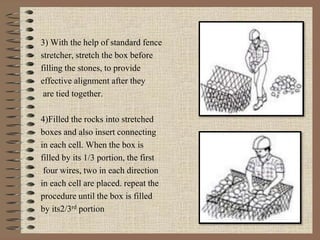
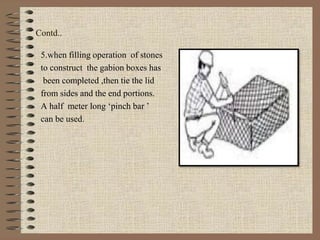
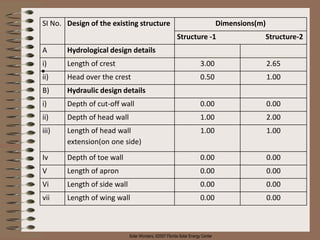
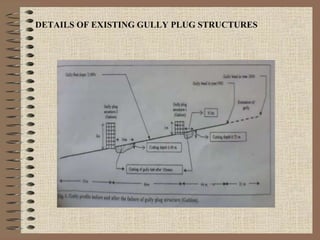
The document provides a comprehensive overview of gabion structures, detailing their definition, characteristics, uses, advantages, construction procedures, and cost computation methods. It also includes case studies on the effectiveness of gabions in controlling soil erosion and sediment retention in various environments. Gabions are highlighted as economical, flexible, and permanent solutions for civil engineering applications like gully control and riverbank protection.