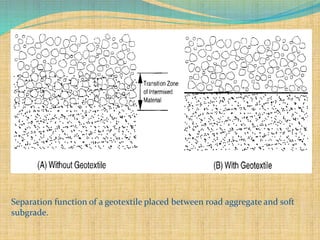
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on geosynthetics. Geosynthetics are synthetic materials used with soil in civil engineering projects to improve properties. They have various forms and are used in applications like roads, dams, and landfills. The presentation discusses why geosynthetics are used for ground stabilization, pavements, erosion control, retaining walls, and foundations. It then classifies and describes different types of geosynthetics - geotextiles, geogrids, geomembranes, geosynthetic clay liners, geofoam, and geocomposites. Examples of geosynthetic usage in India are presented. The conclusion advocates for mandatory geosynthetic use in India for