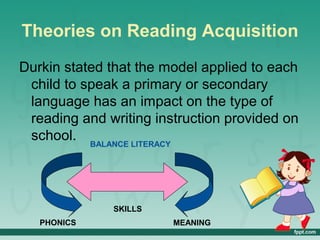
The document discusses various theories of emergent literacy and early literacy development. It defines key terms like learning, literacy, and emergent literacy. It outlines the perspectives of theorists like Clay, Teale, and Sulzby on emergent literacy. It also summarizes learning theories from theorists like Rousseau, Montessori, Dewey, Piaget, Froebel, Pestalozzi, and Vygotsky that support early literacy development. Finally, it discusses theories on reading and writing acquisition in early childhood.