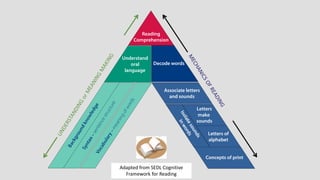
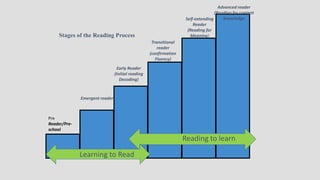
The document outlines the stages of reading development, from pre-reader to advanced reader, detailing characteristics and learning outcomes at each stage. It emphasizes the cognitive processes involved in reading, including phonemic awareness, fluency, comprehension, and the ability to analyze texts. Additionally, it establishes connections to educational curriculum standards for Urdu and Sindhi languages, illustrating how reading skills evolve through various educational milestones.











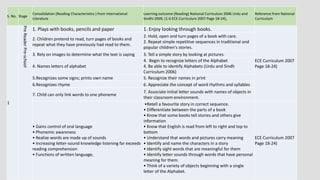
![S.
No
Stage
Consolidation (Reading Characteristics ) from
International Literature
Learning outcome (Reading) National Curriculum 2006
Urdu and Sindh 2009, (1-6 ECE Curriculum 2007 Page 18-
24),
Reference from
National
Curriculum
2
EmergentReader
1. Child is more comfortable with the alphabet 1. Be able to recognize letters of the Alphabet
Learning out
come Grade 1
National
Curriculum(Urdu
(2006) sindhi
(2009) Page 17-
18 Urdu, 13-14
Sindhi.
2. Become aware of vowels and vowel sounds.
2. Be able to read consonants and vowels alphabets
sounds.
3. Child learns relation between letters and sounds
and between printed and spoken words
3. To get fimilar with relationship with human sounds
[spoken] words and alphabet.
5. Realize letter combinations represent sounds.
6. Can combine graphemes to make longer phonemes
E.g. ‘th’
7. Increasing letter-pattern knowledge and phonemic
awareness
8. Grows aware of sound/symbol relationships; focuses
on printed symbols; attempts to break code of print;
uses decoding to figure out words
4.Be able to combine alphabet to make syllable and
combine syllable to make words and read them
9. Child is able to read simple text containing high
frequency words and phonically regular words
5. Be able to read simple sentences and comprehend
them.
• Uses skill and insight to “sound out” new one
syllable words](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readingdevelopmentstages-180612143220/85/Reading-development-stages-15-320.jpg)




