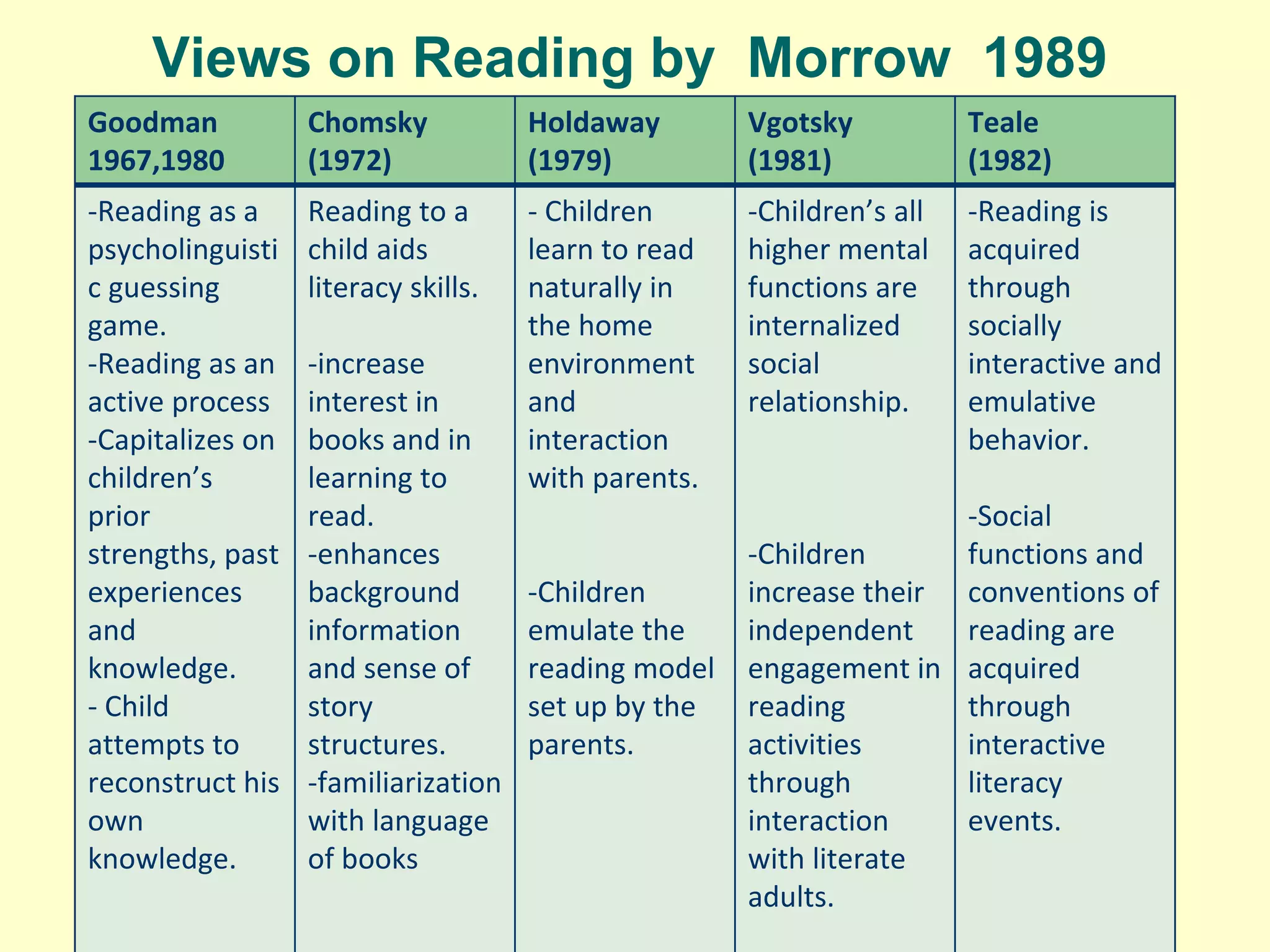
The document discusses the Constructivist Model of teaching literacy. It asserts that learners need to interact and engage in meaningful activities to develop literacy skills. Constructivism views learning as a process of actively constructing knowledge based on experience. The model has distinct advantages including literacy instruction embedded in meaningful social contexts, student-centered exploration of literacy functions, and recognition of diverse experiences and perspectives. The document also reviews several views on reading, including it as a psycholinguistic process, the importance of prior knowledge and social interaction, and acquiring literacy through emulation of literate role models.