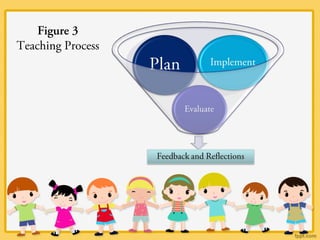
The document discusses the relationship between teaching-learning processes and curriculum development, emphasizing that curriculum encompasses the total learning experience. It outlines key phases of teaching—planning, implementation, and evaluation—while highlighting the goal-oriented nature of teaching and the need for feedback and reflection. The document also explores various methods of teaching and learning, underscoring the importance of how students learn in relation to curriculum effectiveness.