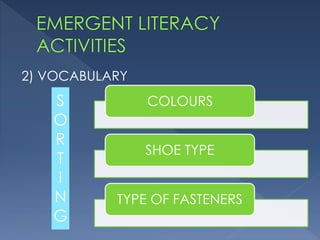
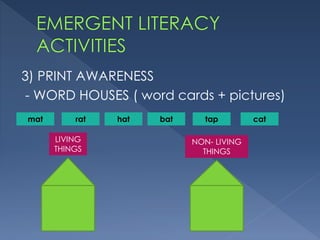
Emergent literacy refers to the early stages of literacy development from birth to when children enter formal schooling. It involves developing an understanding of how print works through exposure to books and writing. The document discusses that literacy skills begin developing from birth through activities with caregivers. It emphasizes the importance of starting early to build a strong foundation and prevent academic difficulties later on. Emergent literacy involves developing oral language, print awareness, phonological awareness, letter knowledge, and motivation to engage with books.