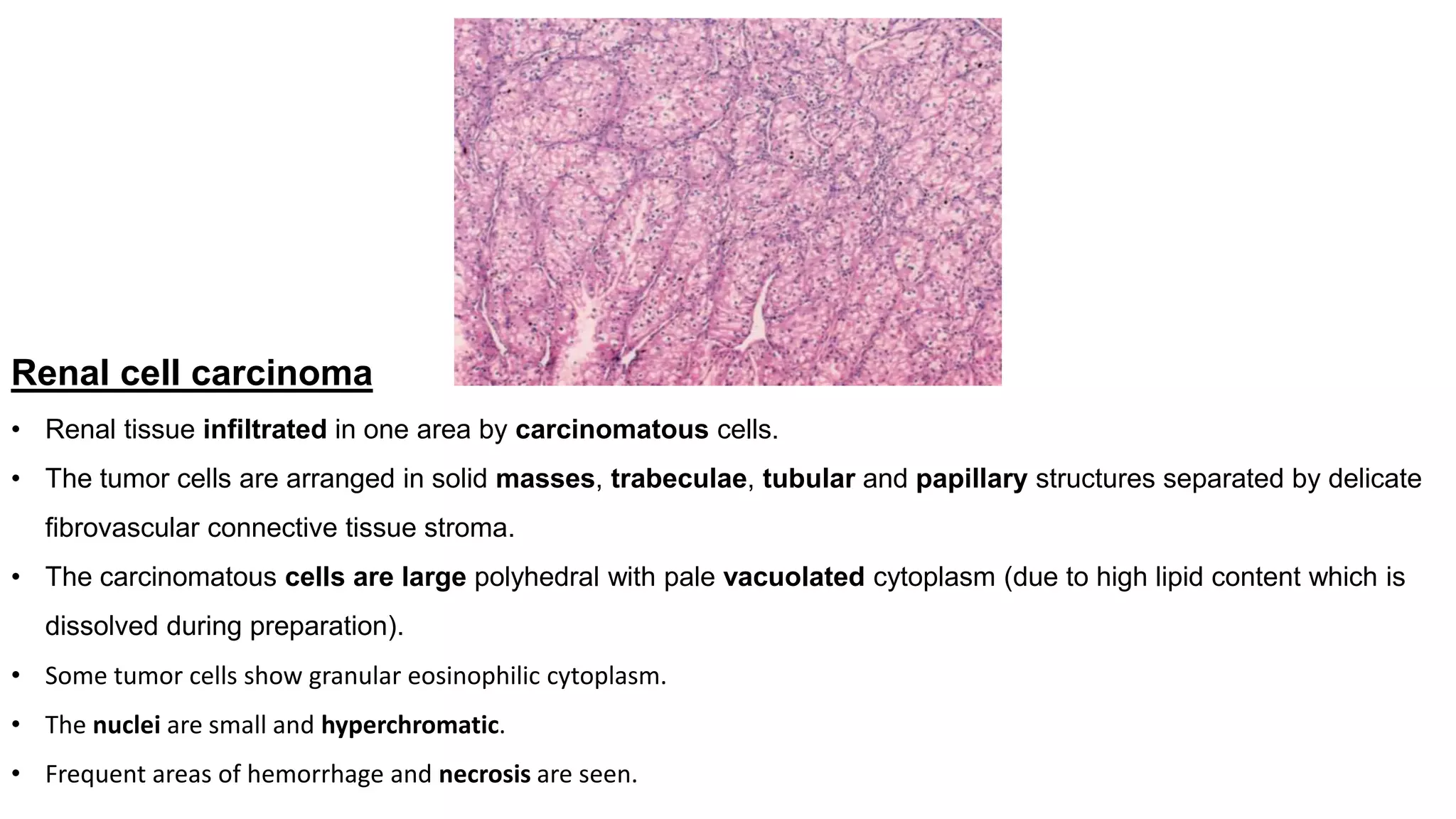
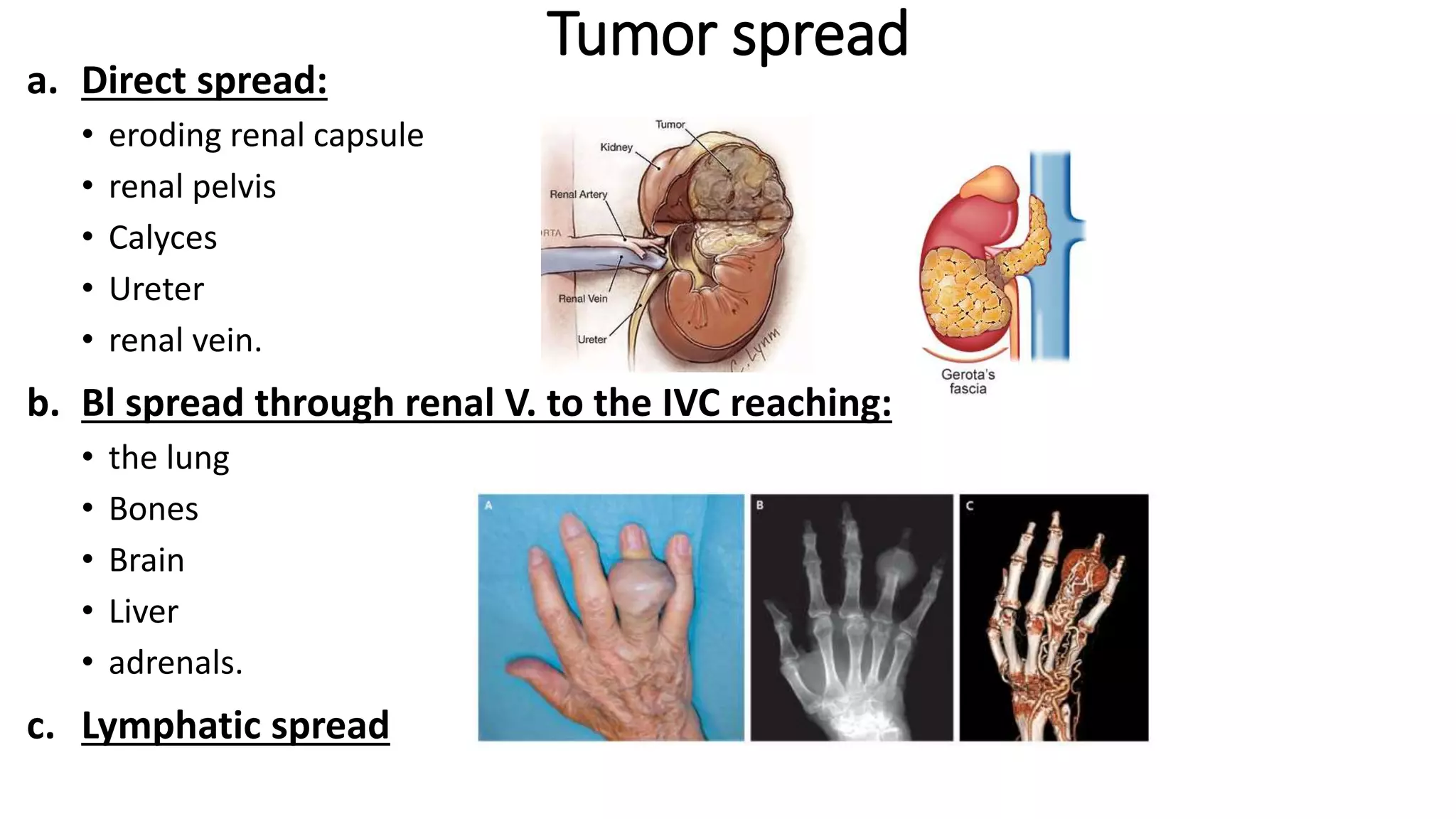
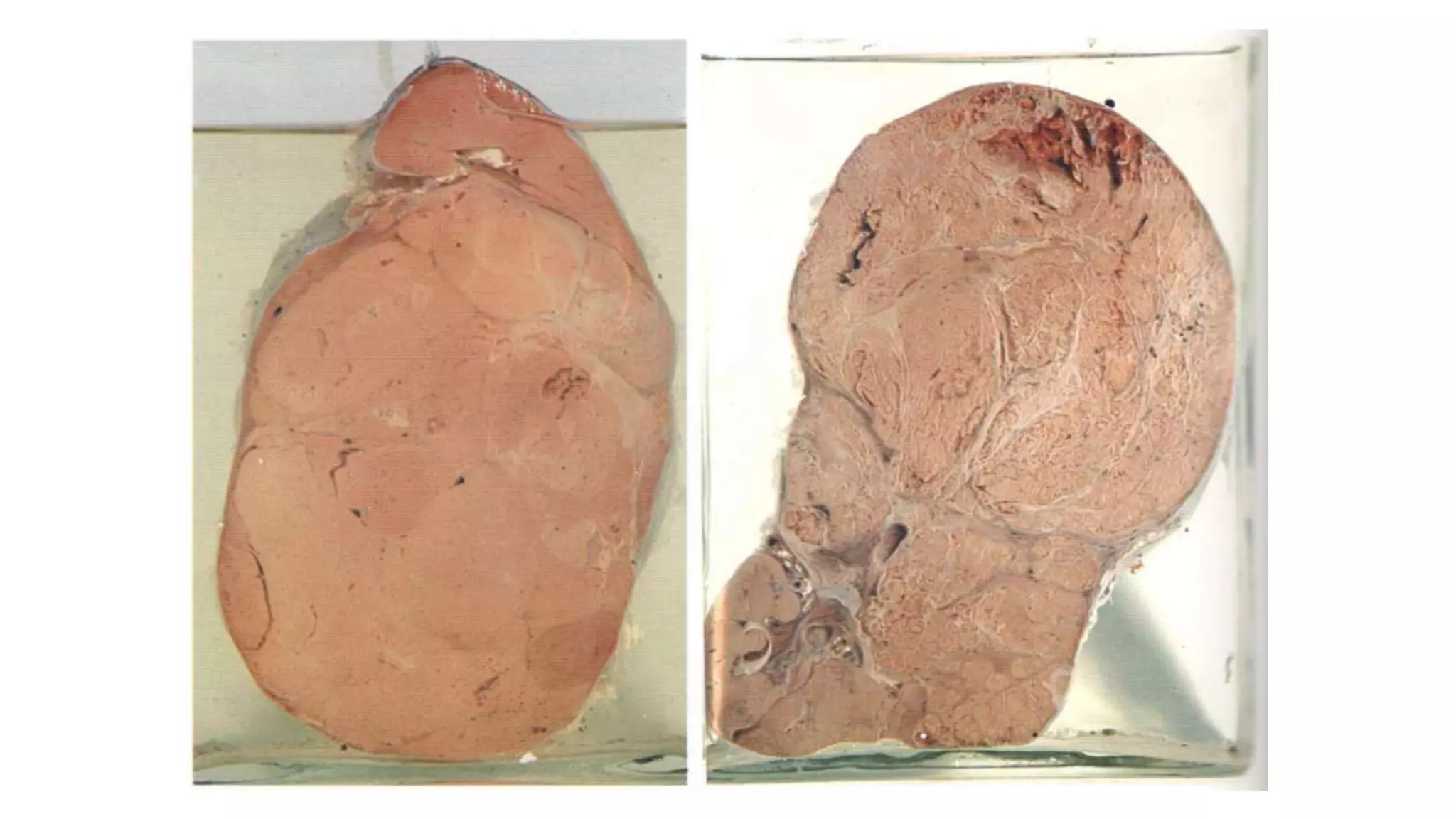
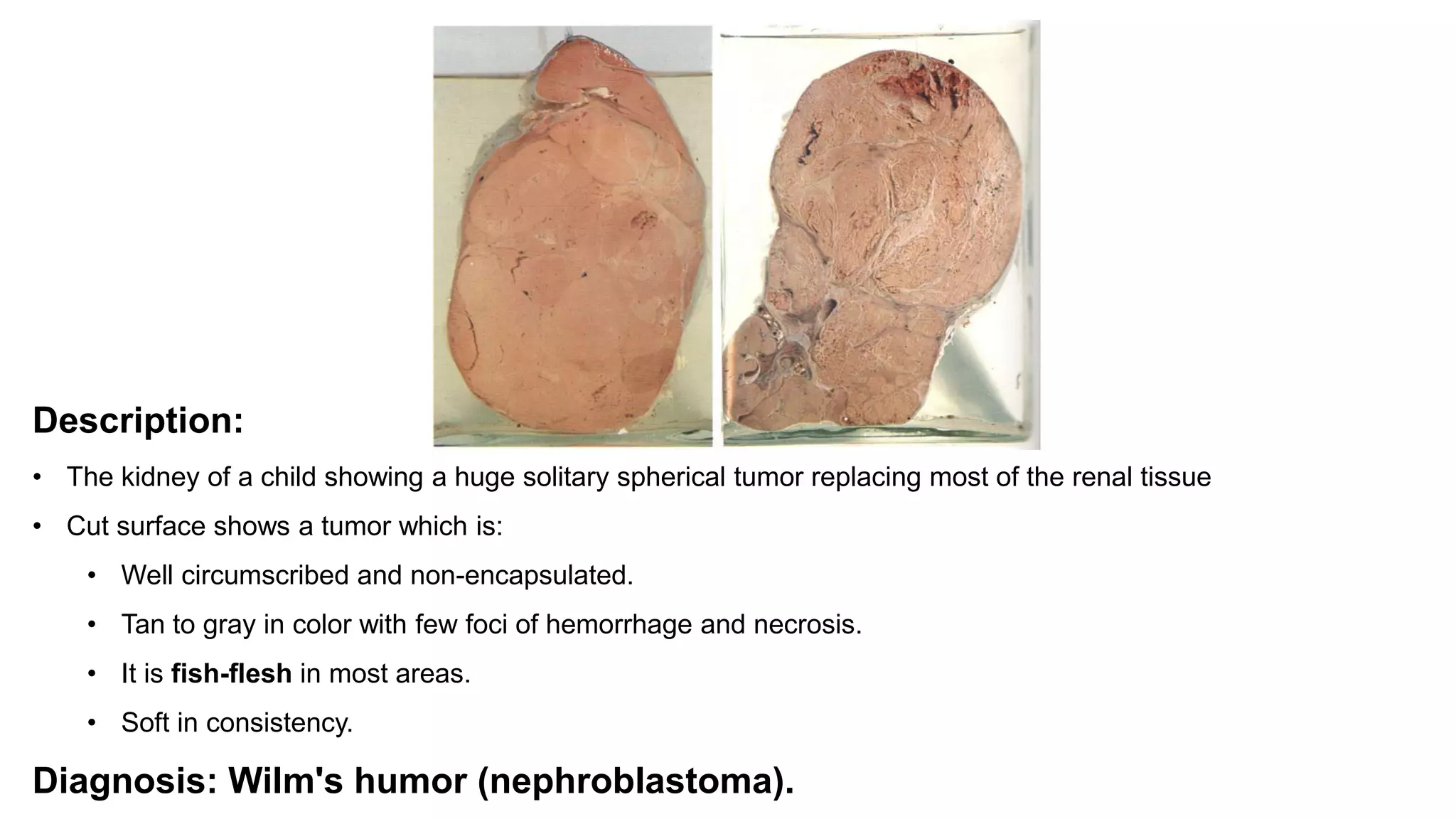
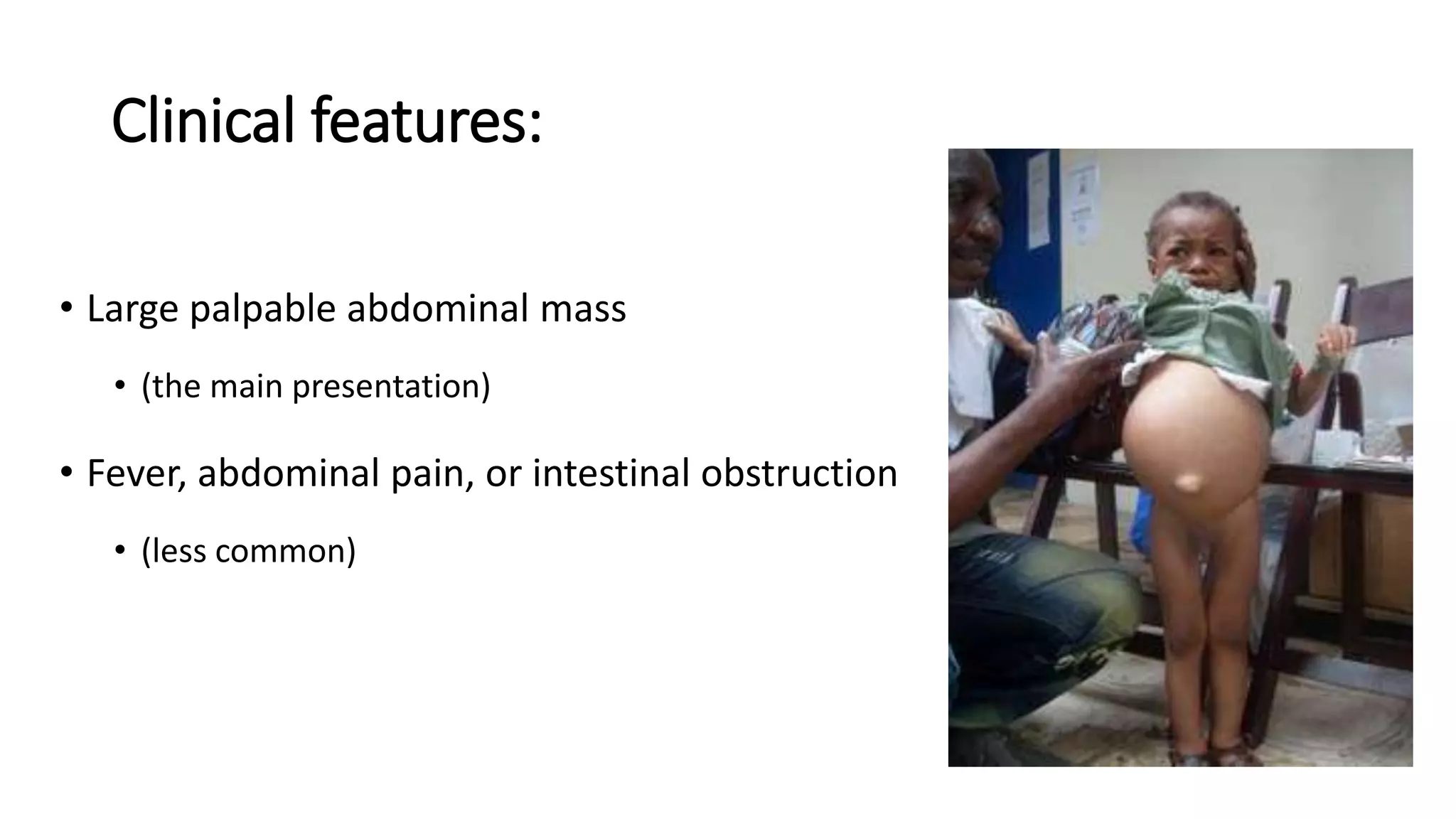
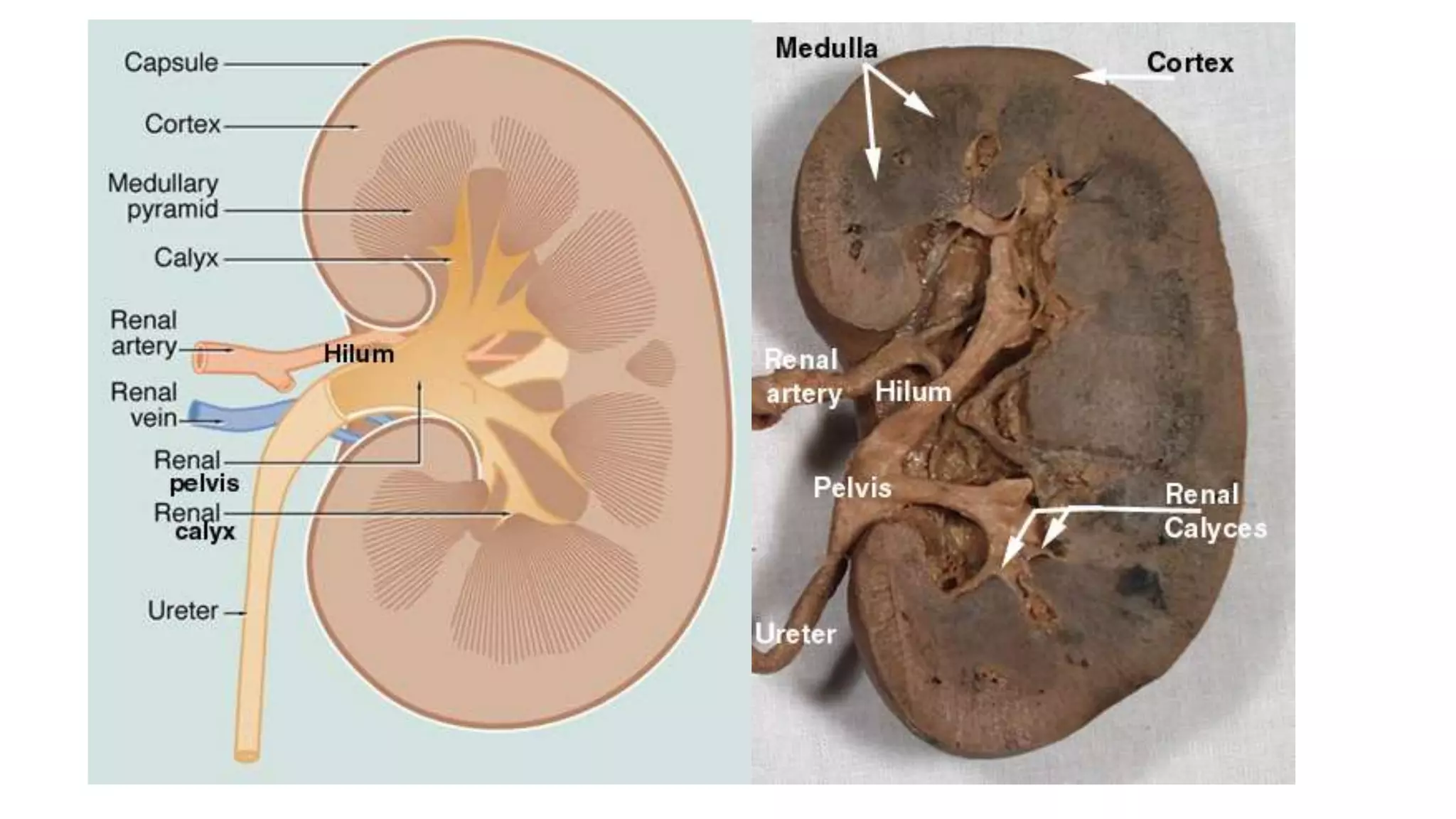
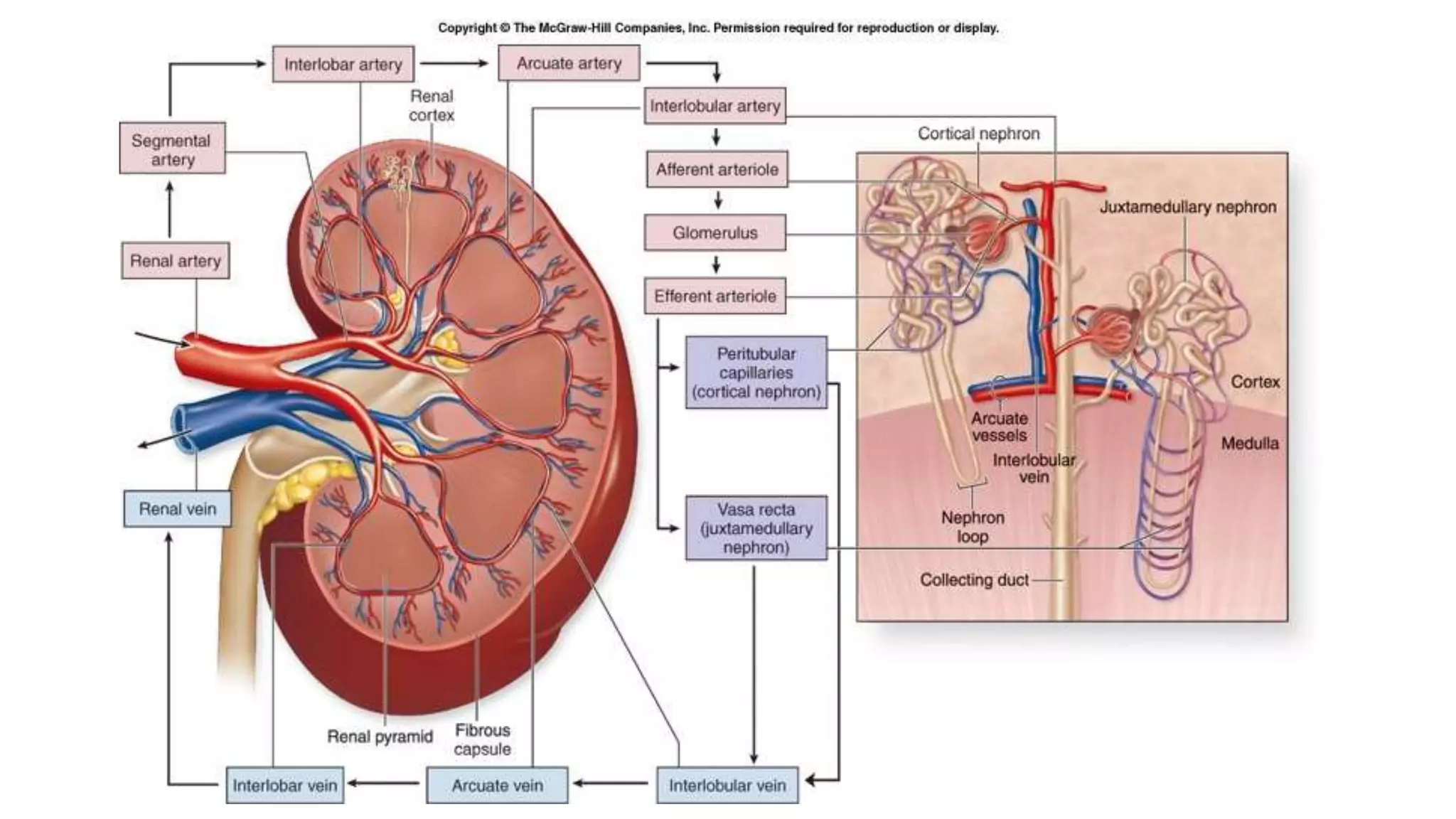
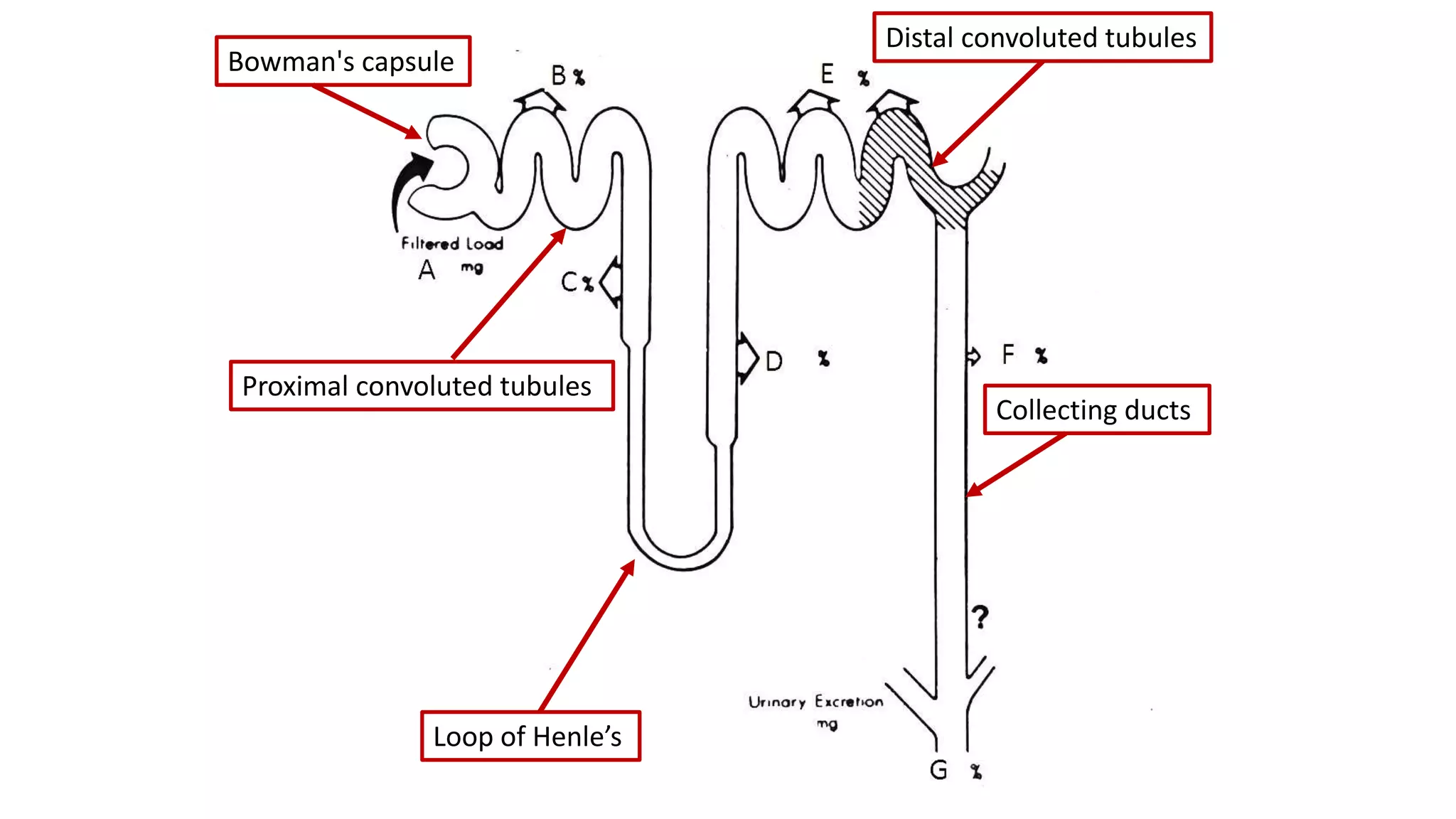
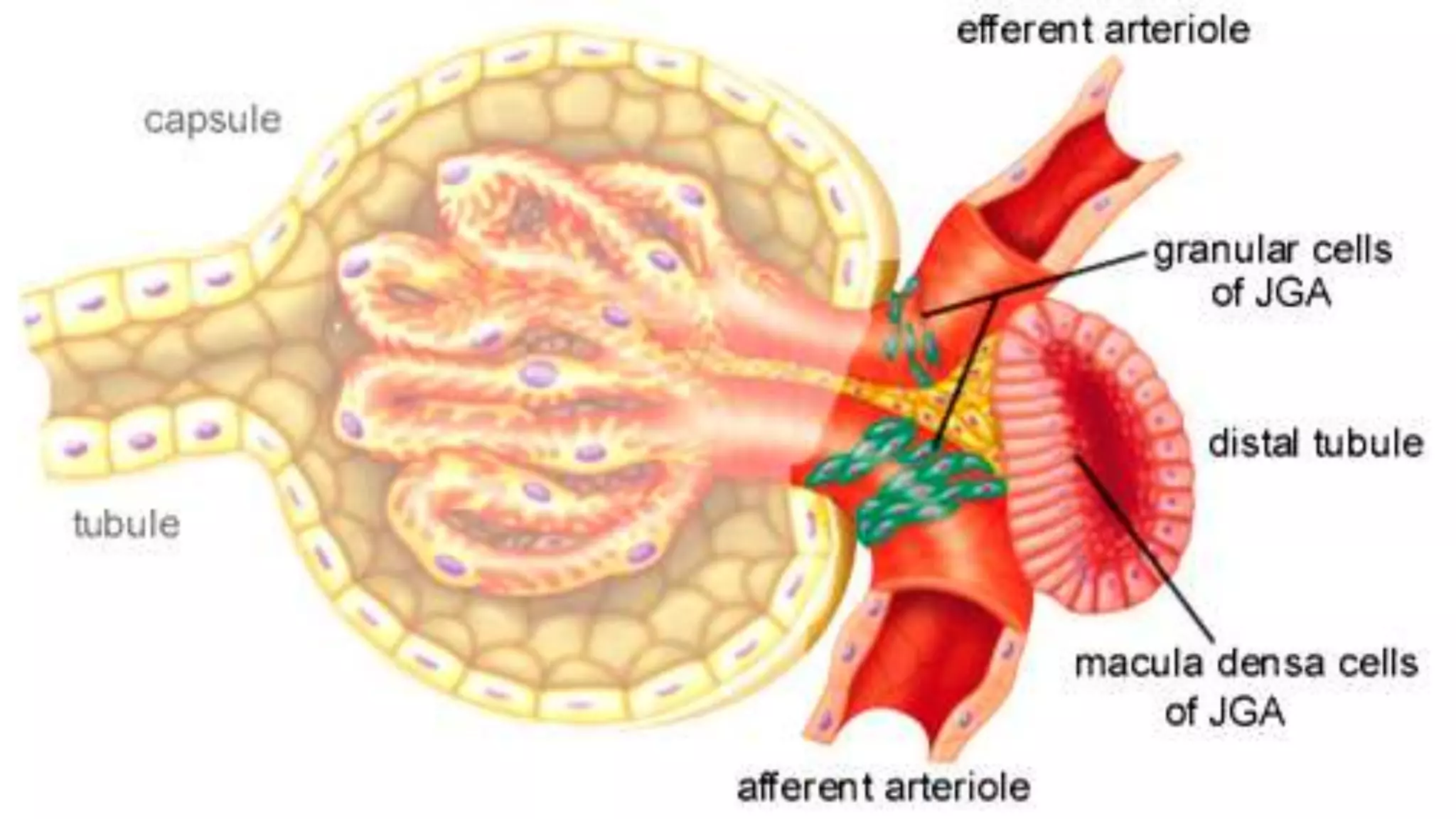
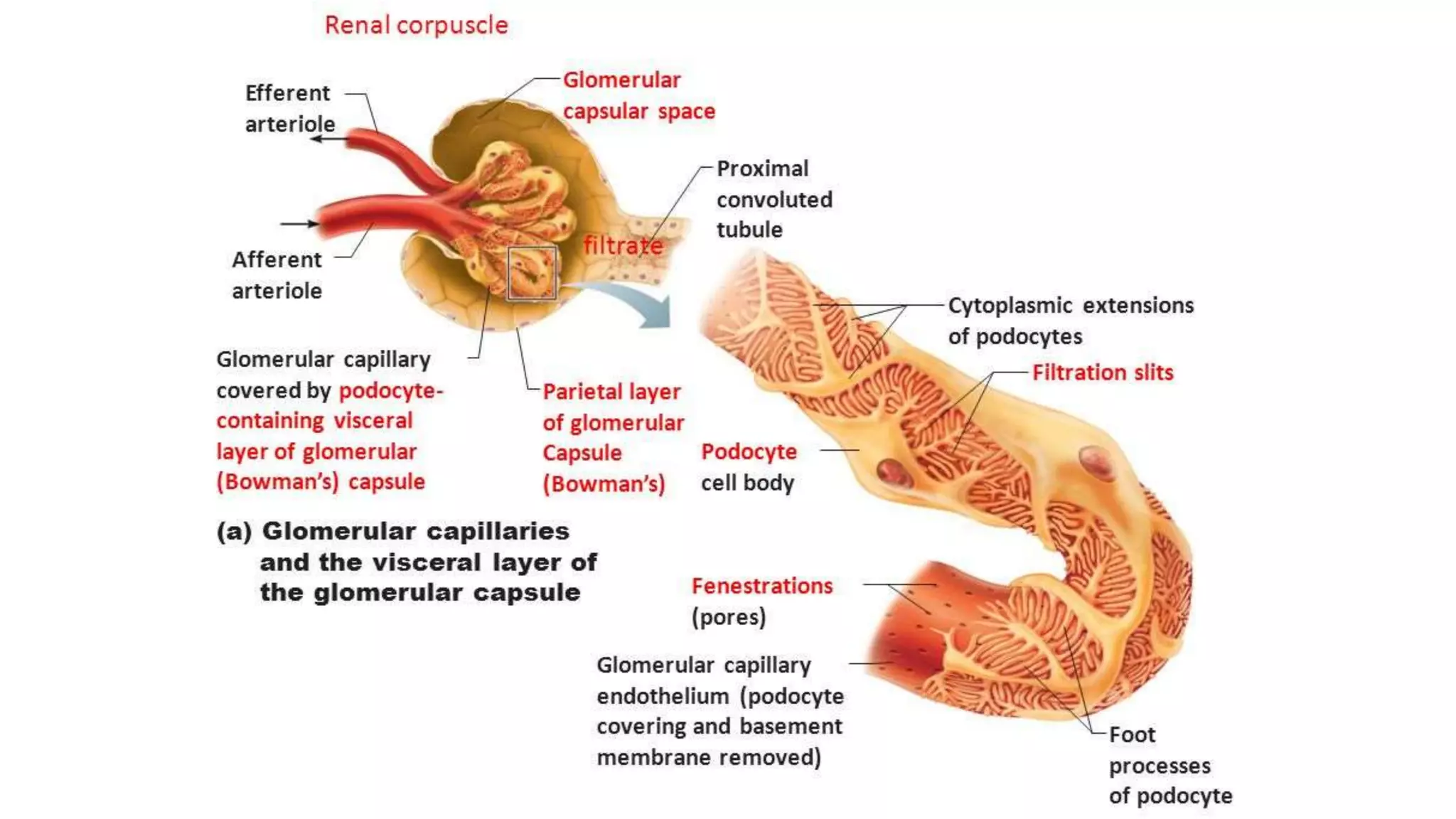
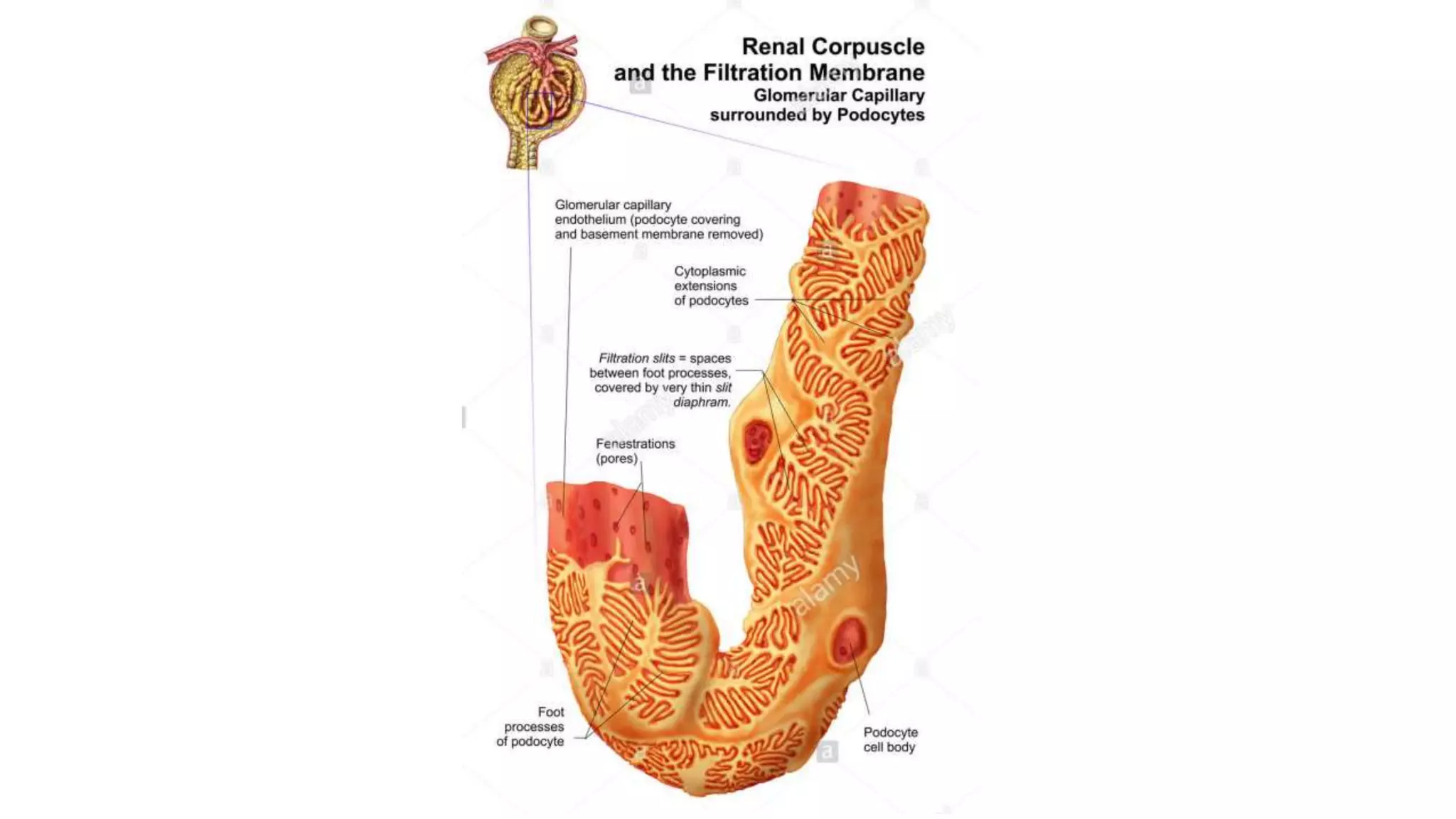
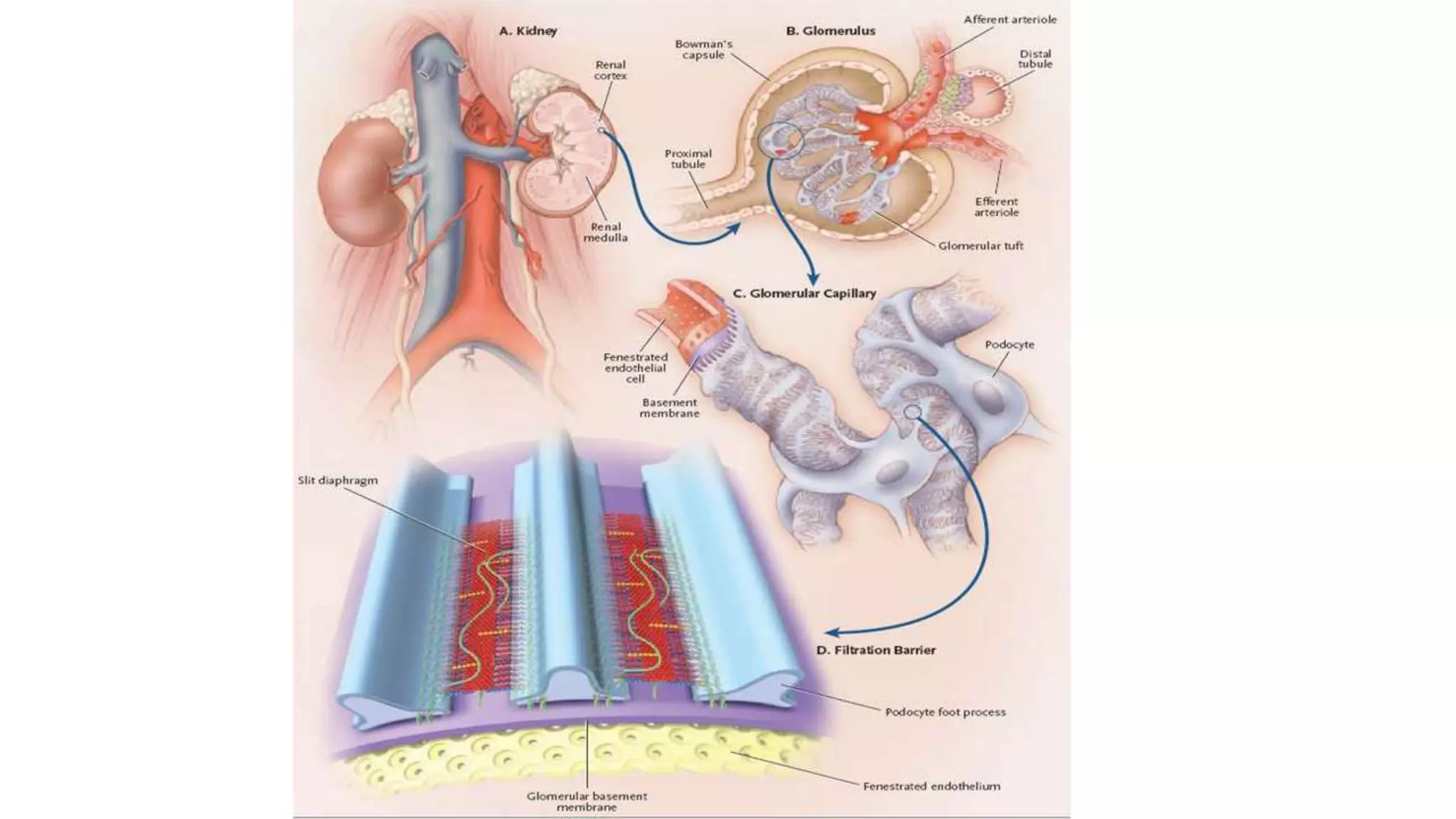
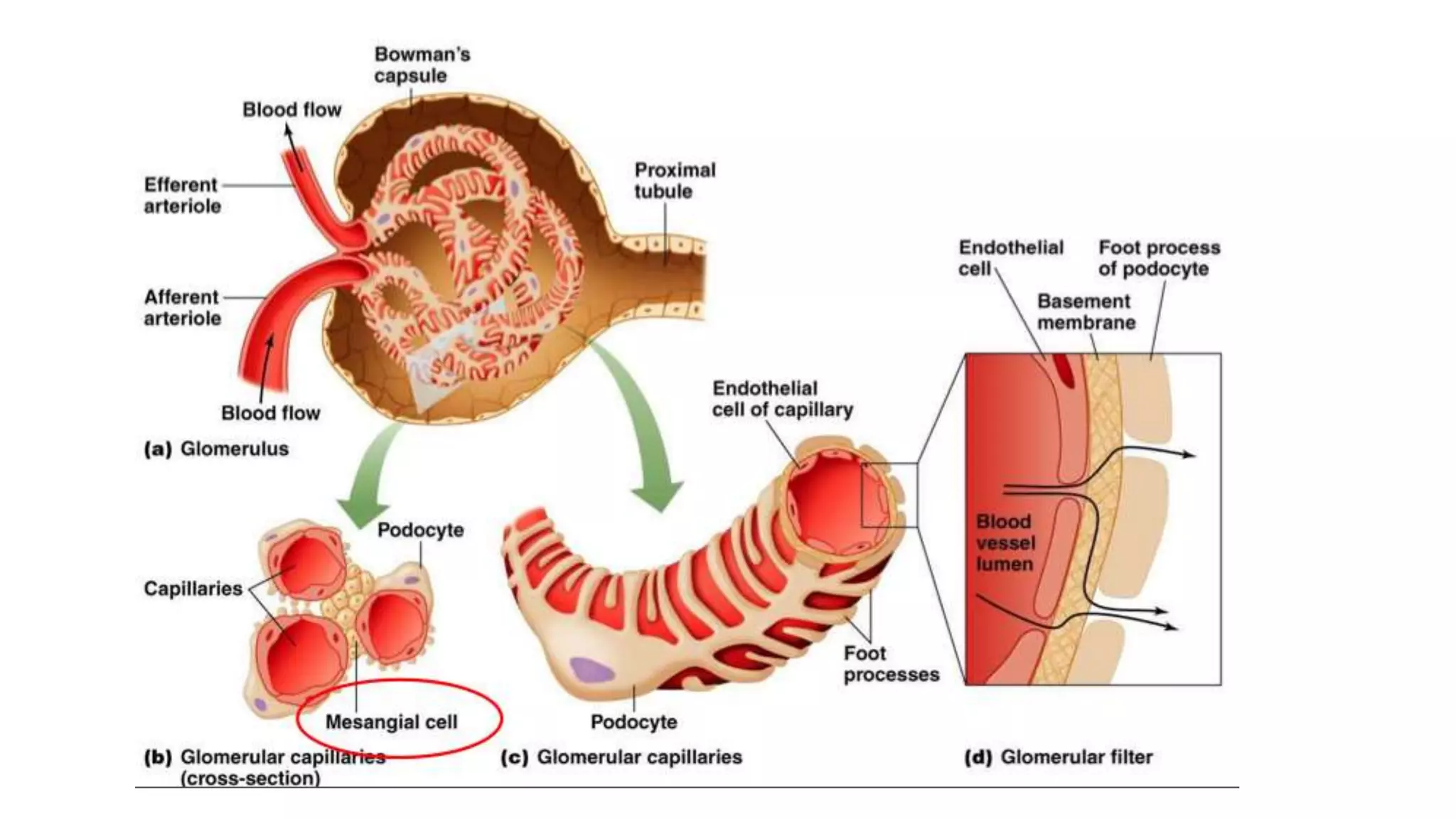
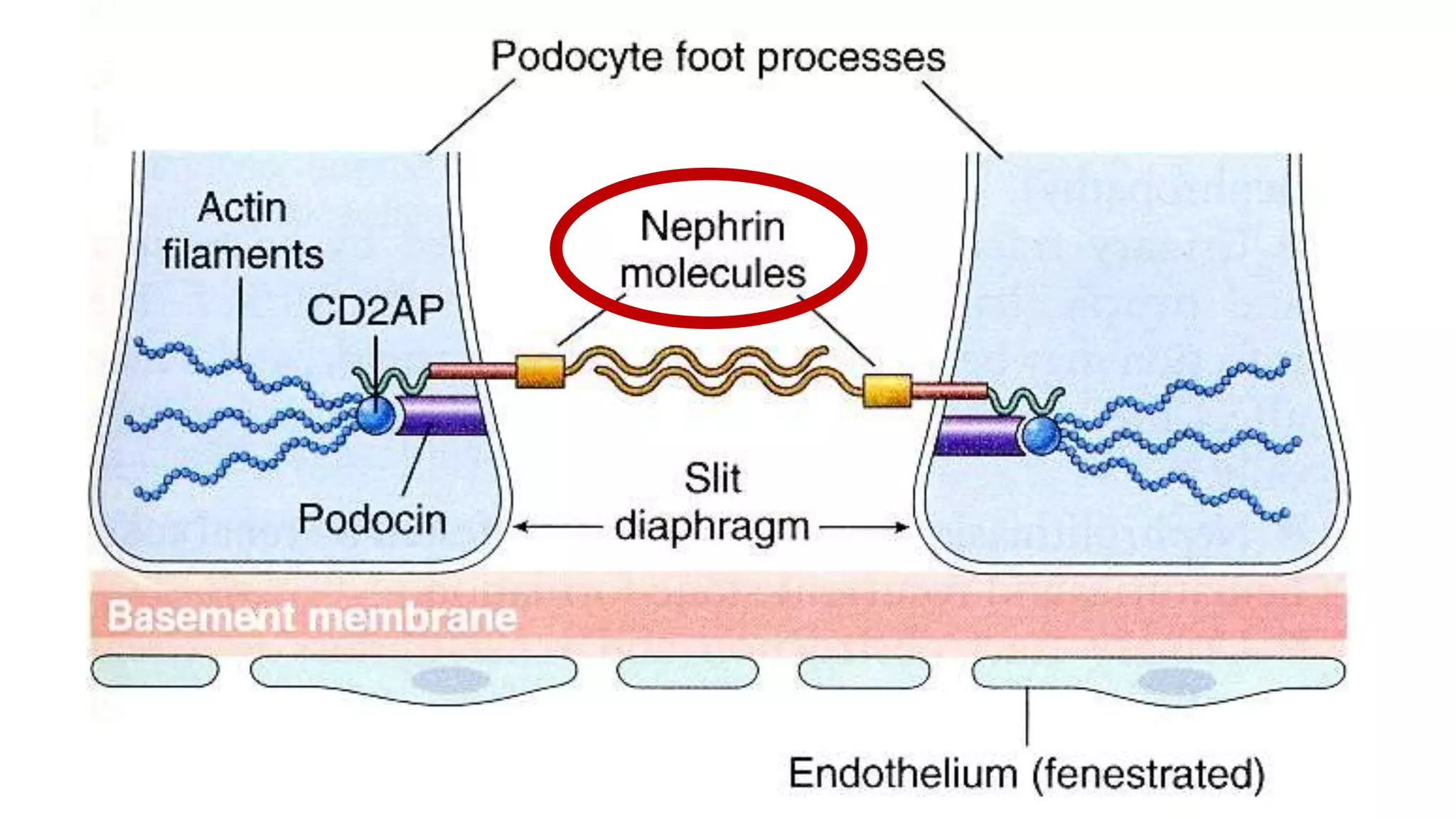
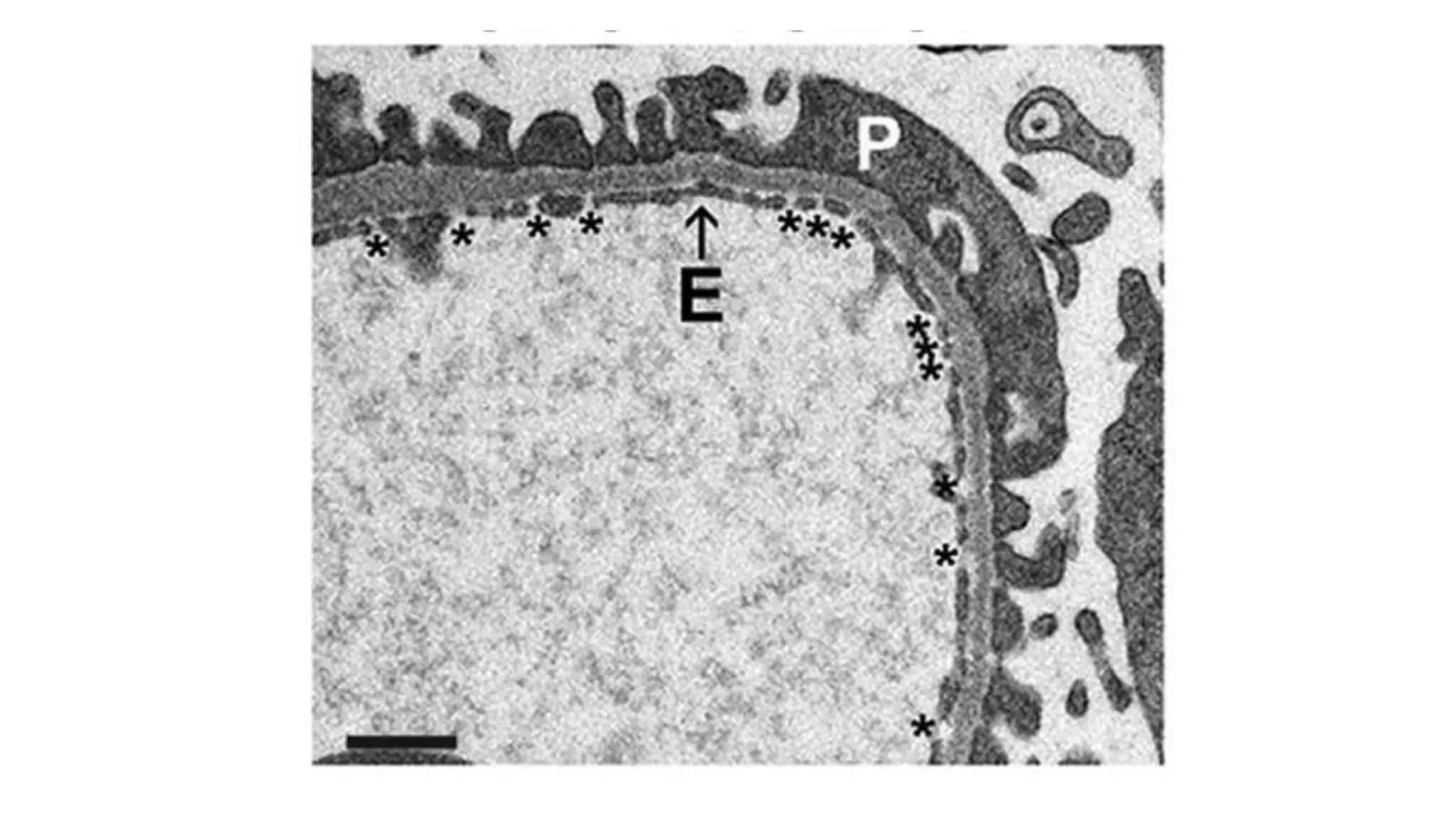
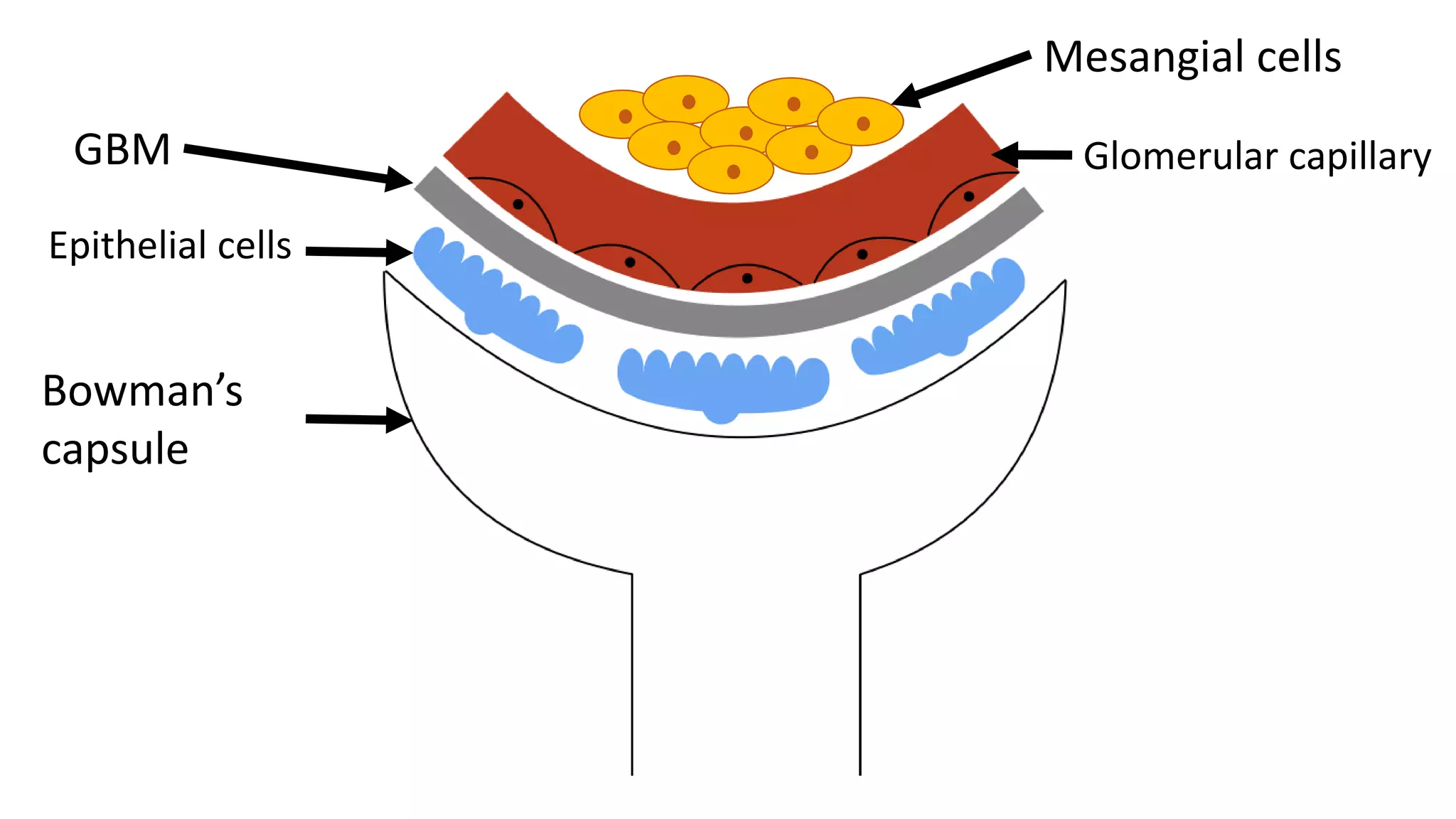
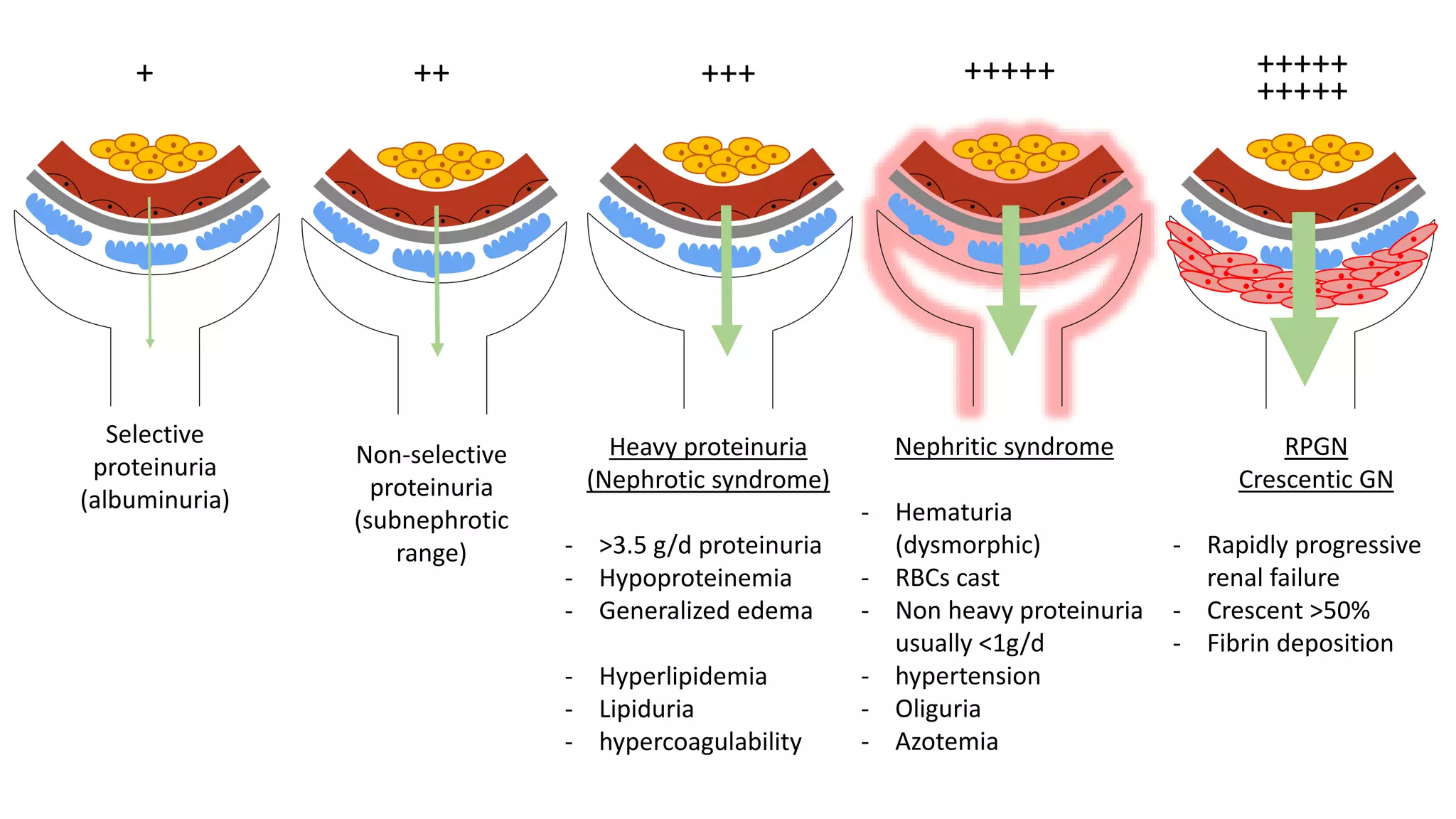
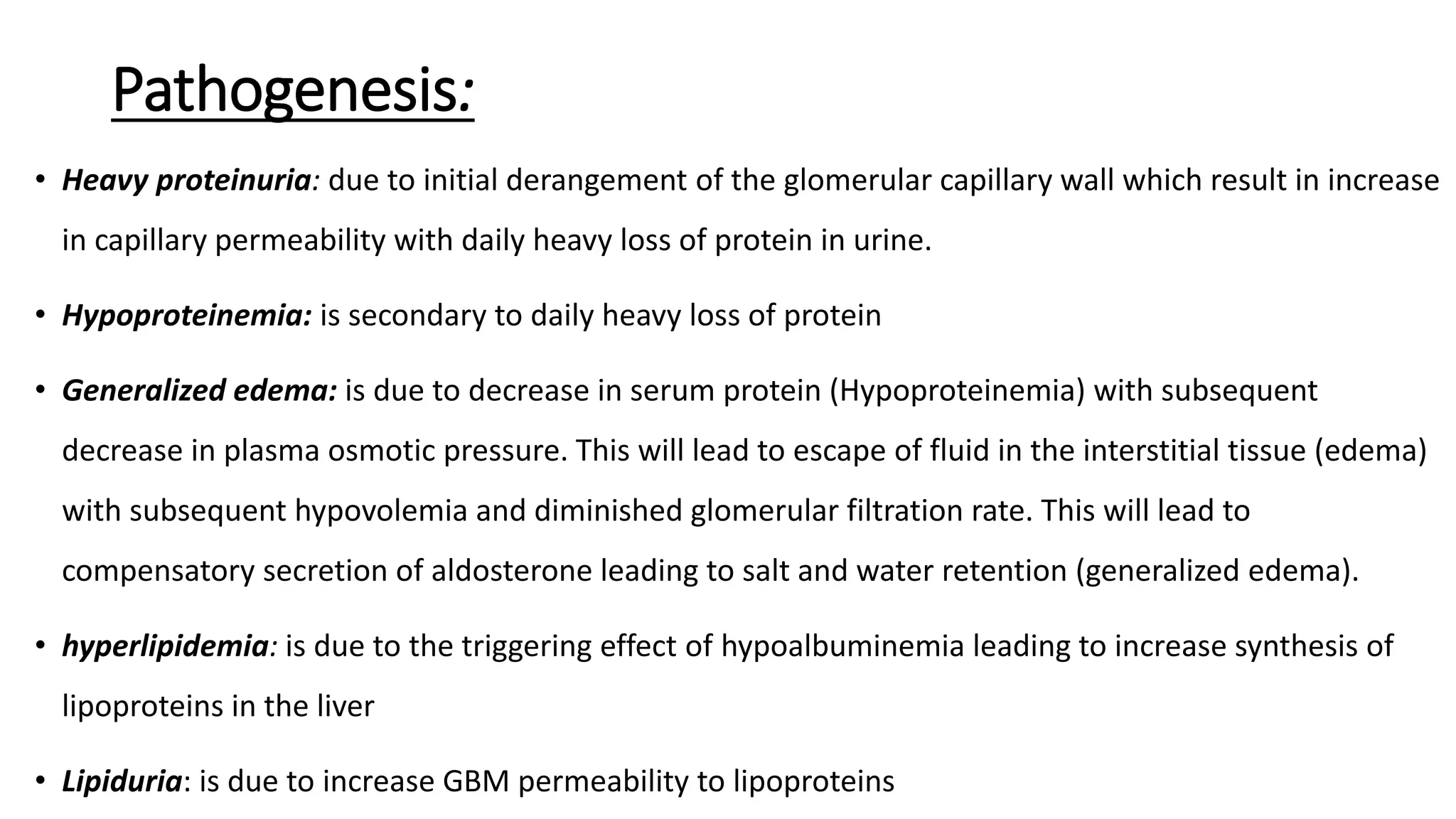
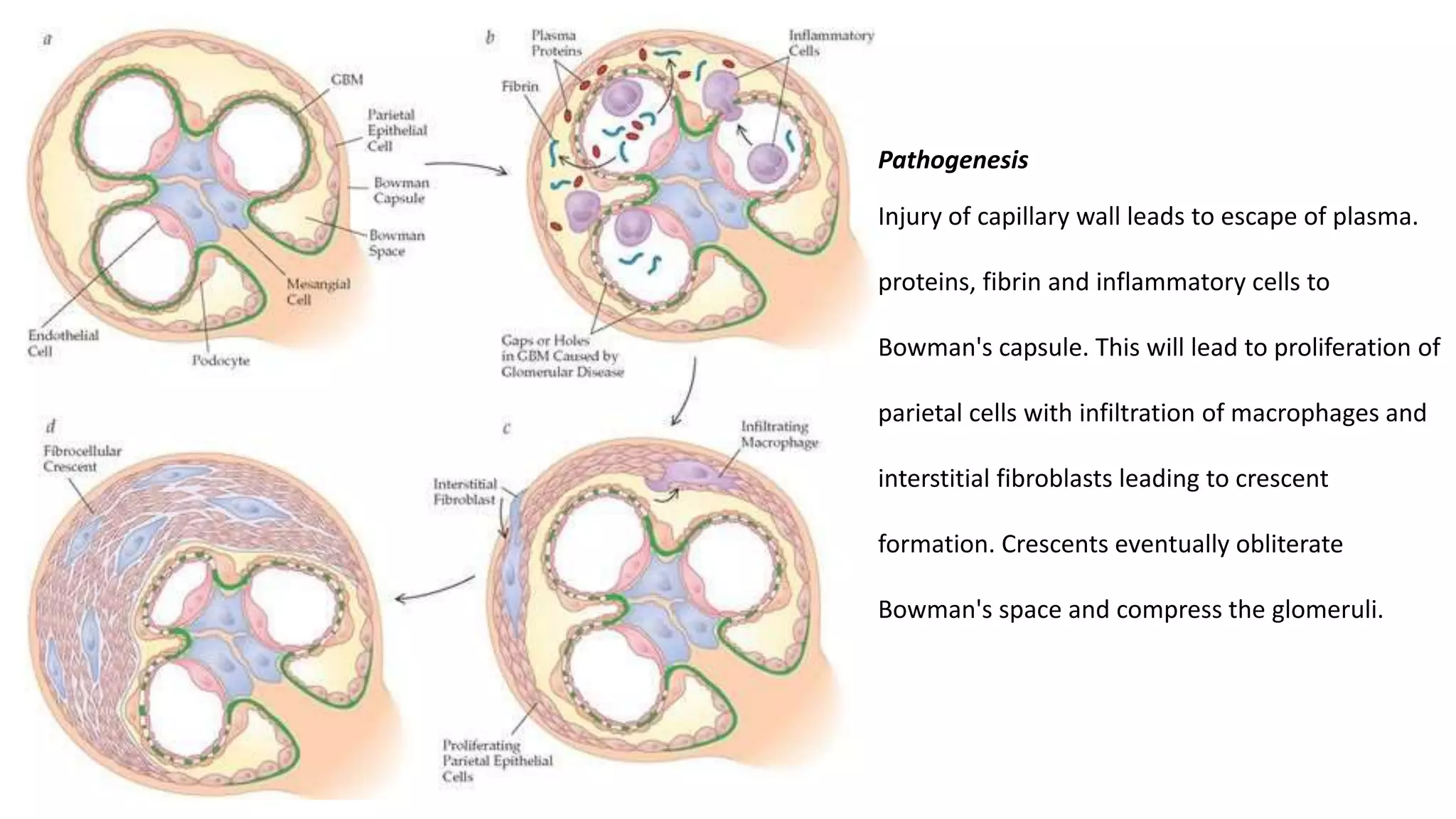
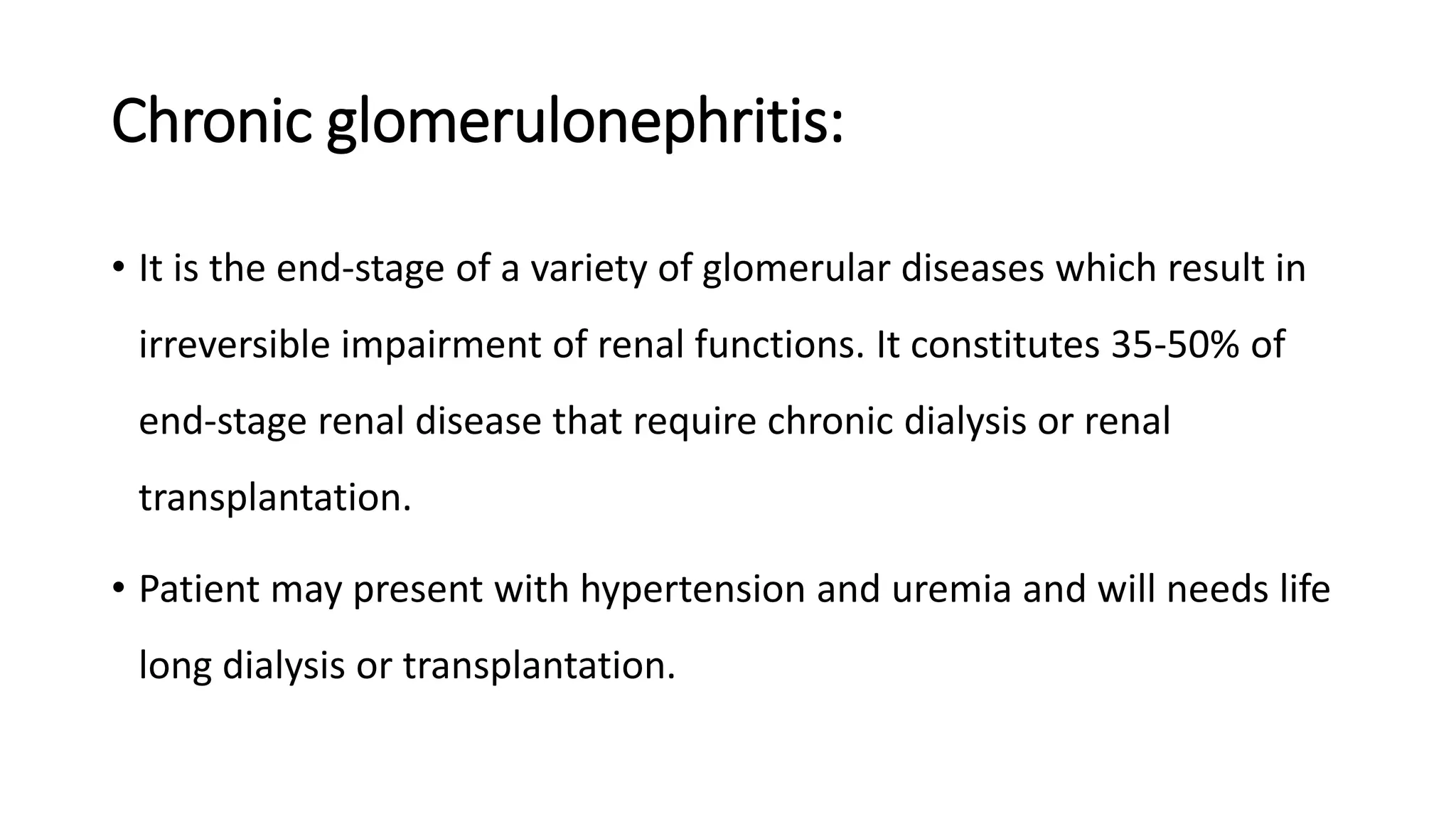
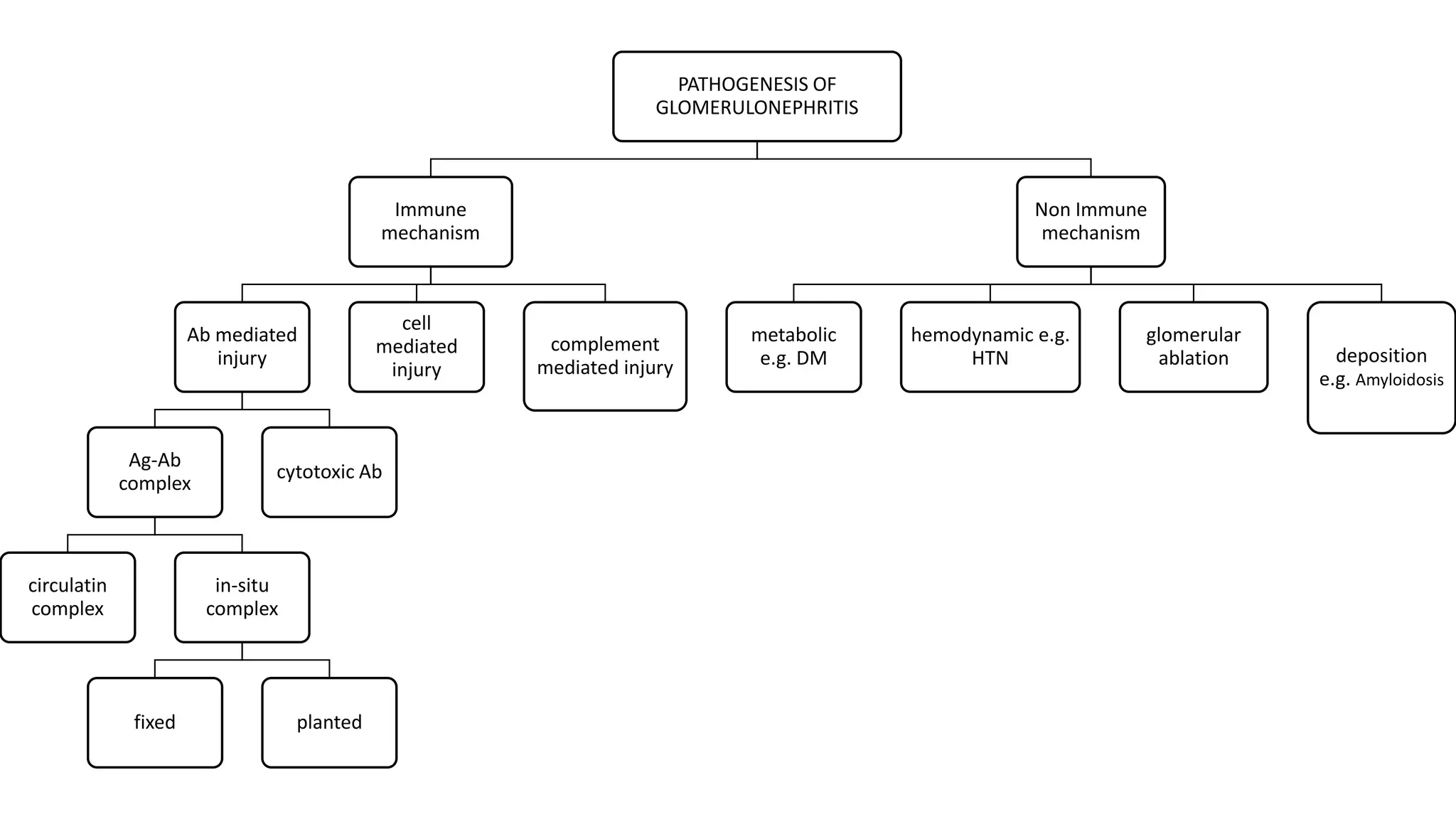
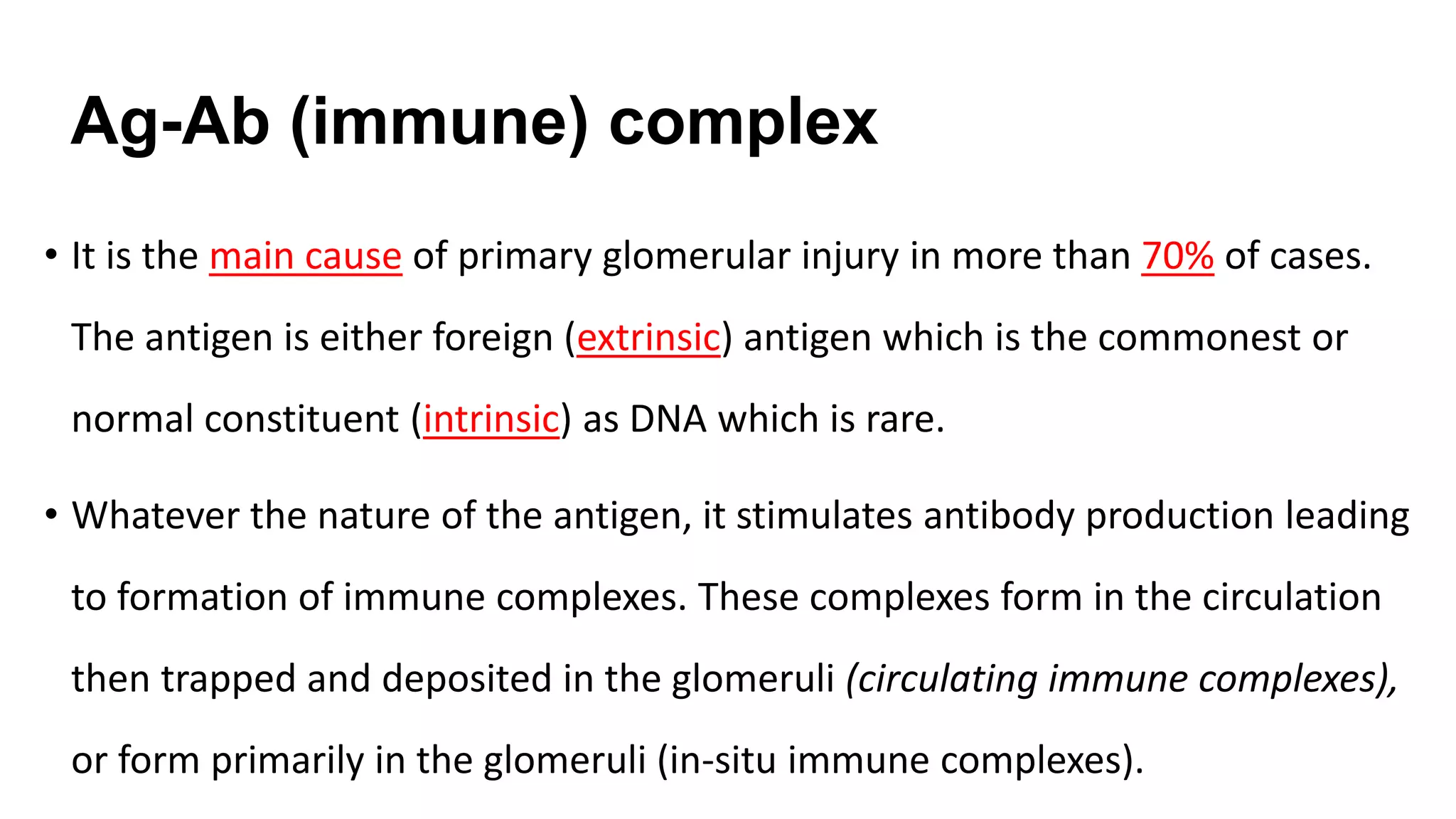
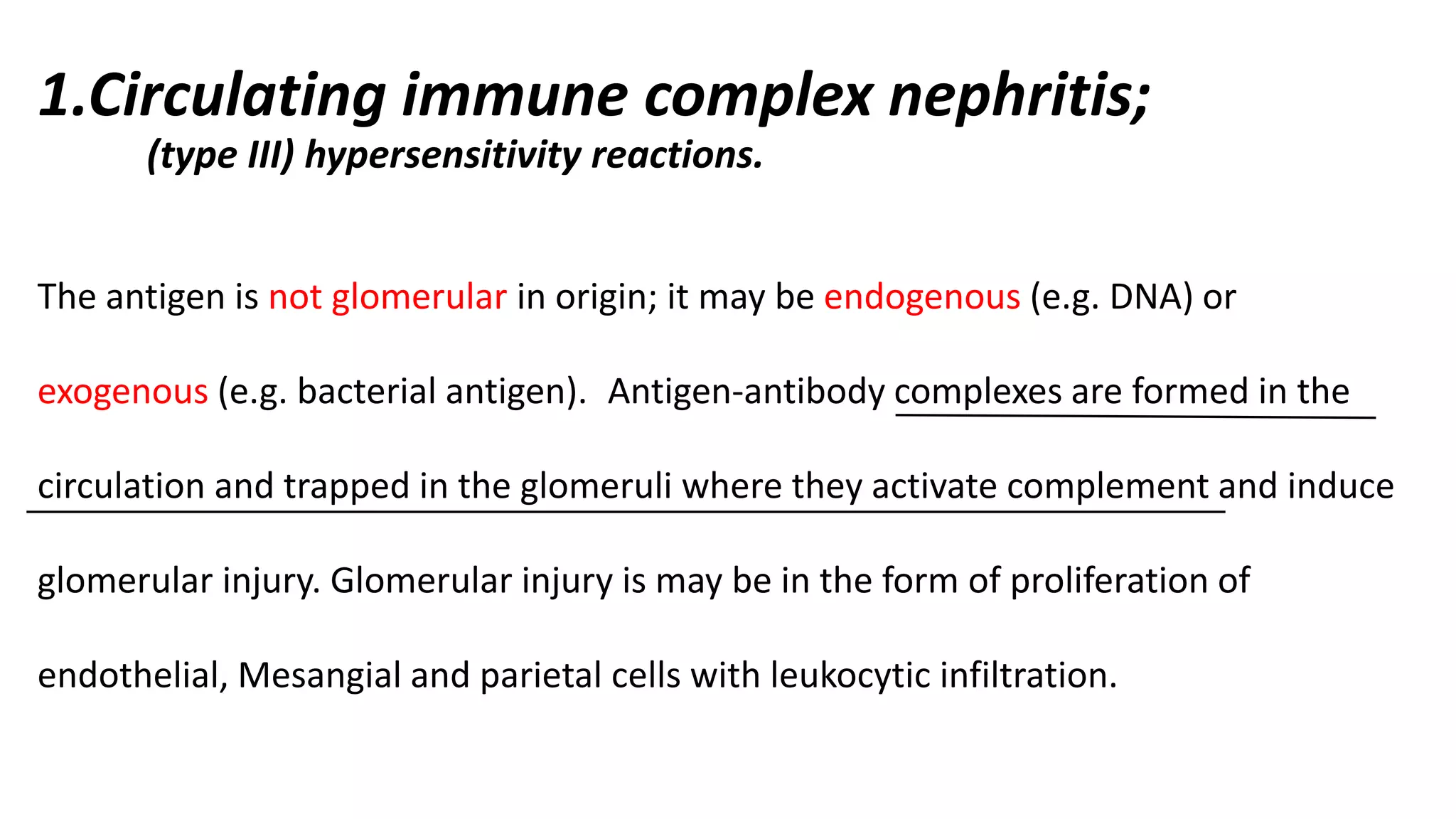
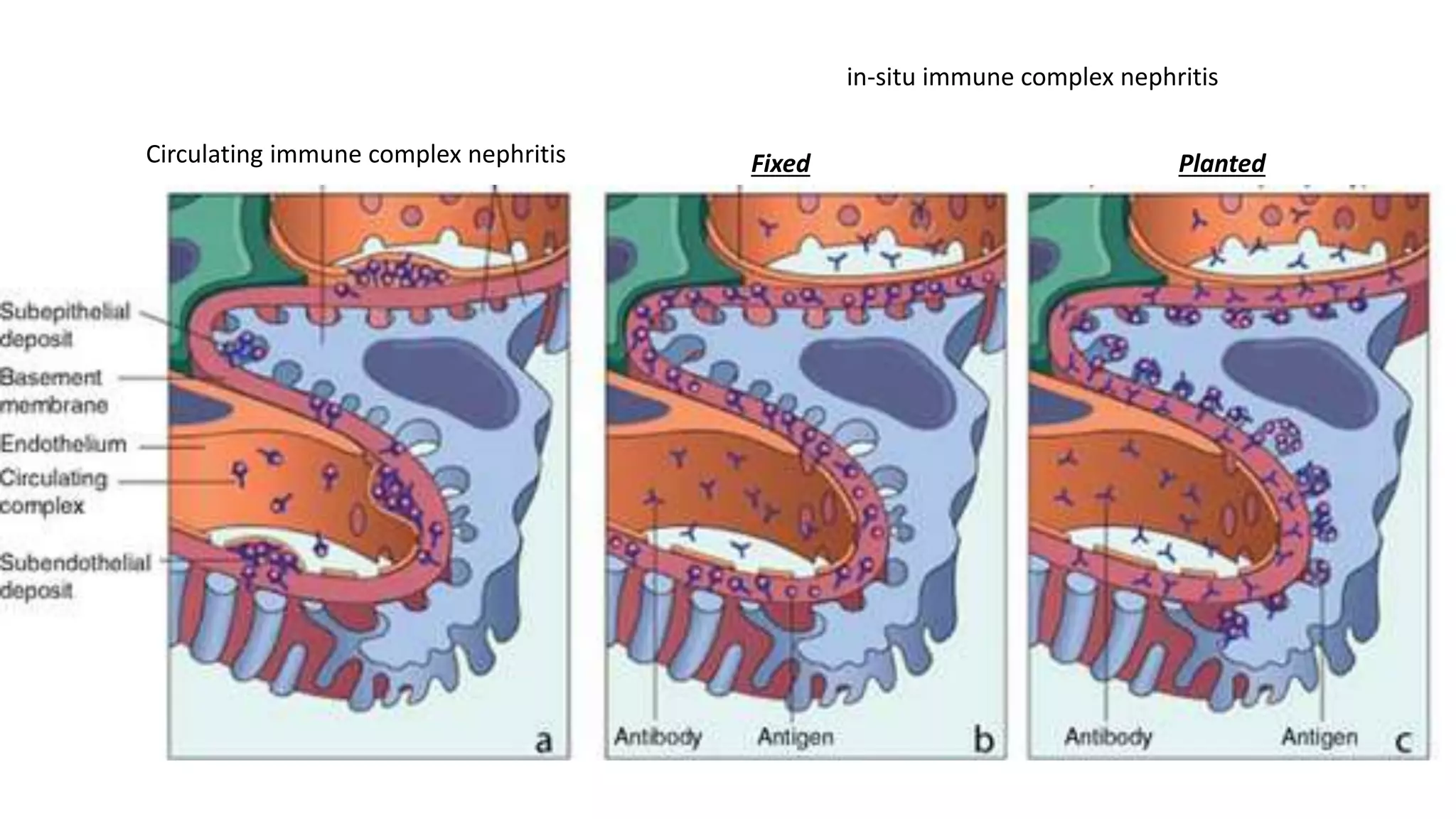
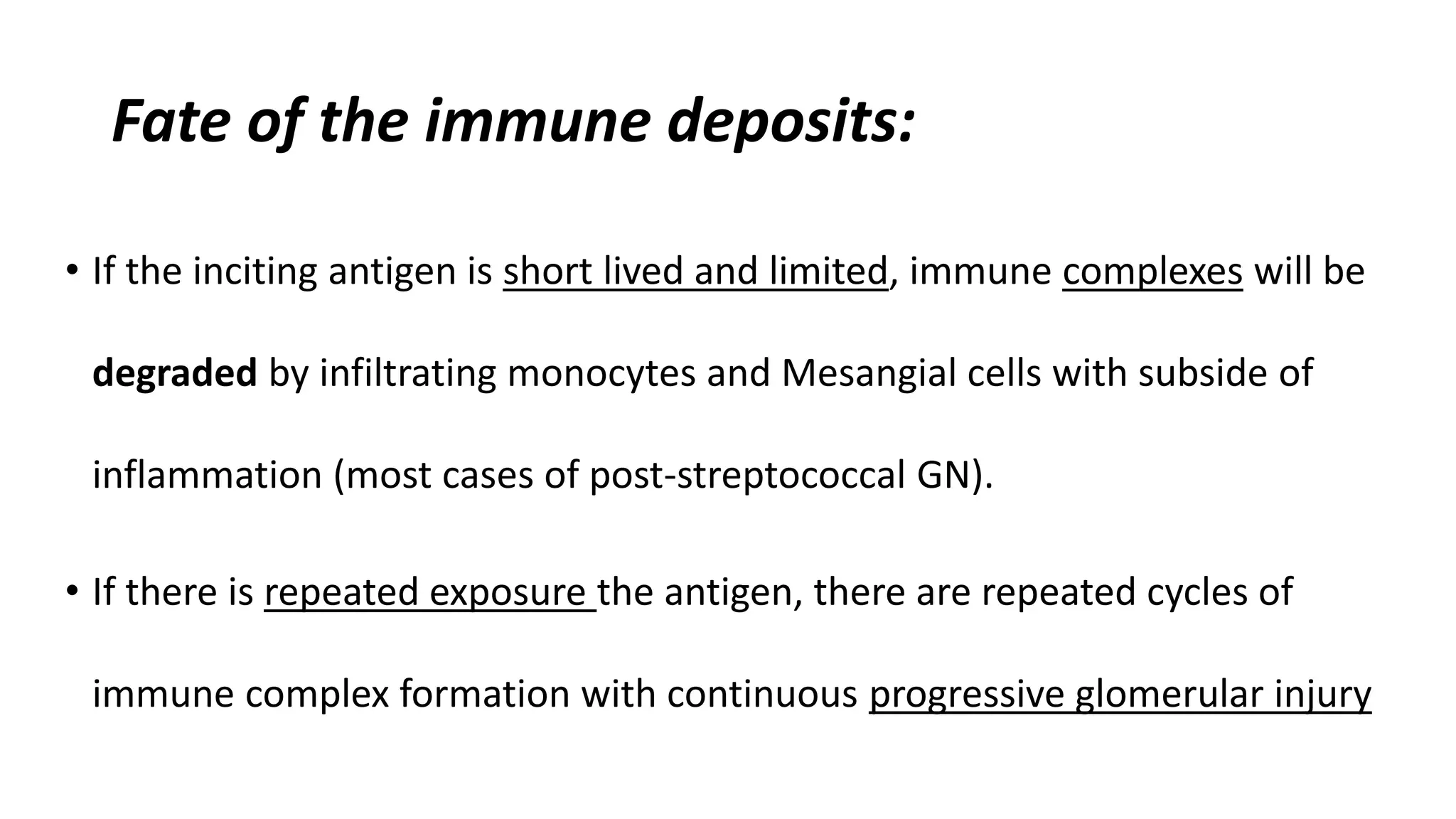
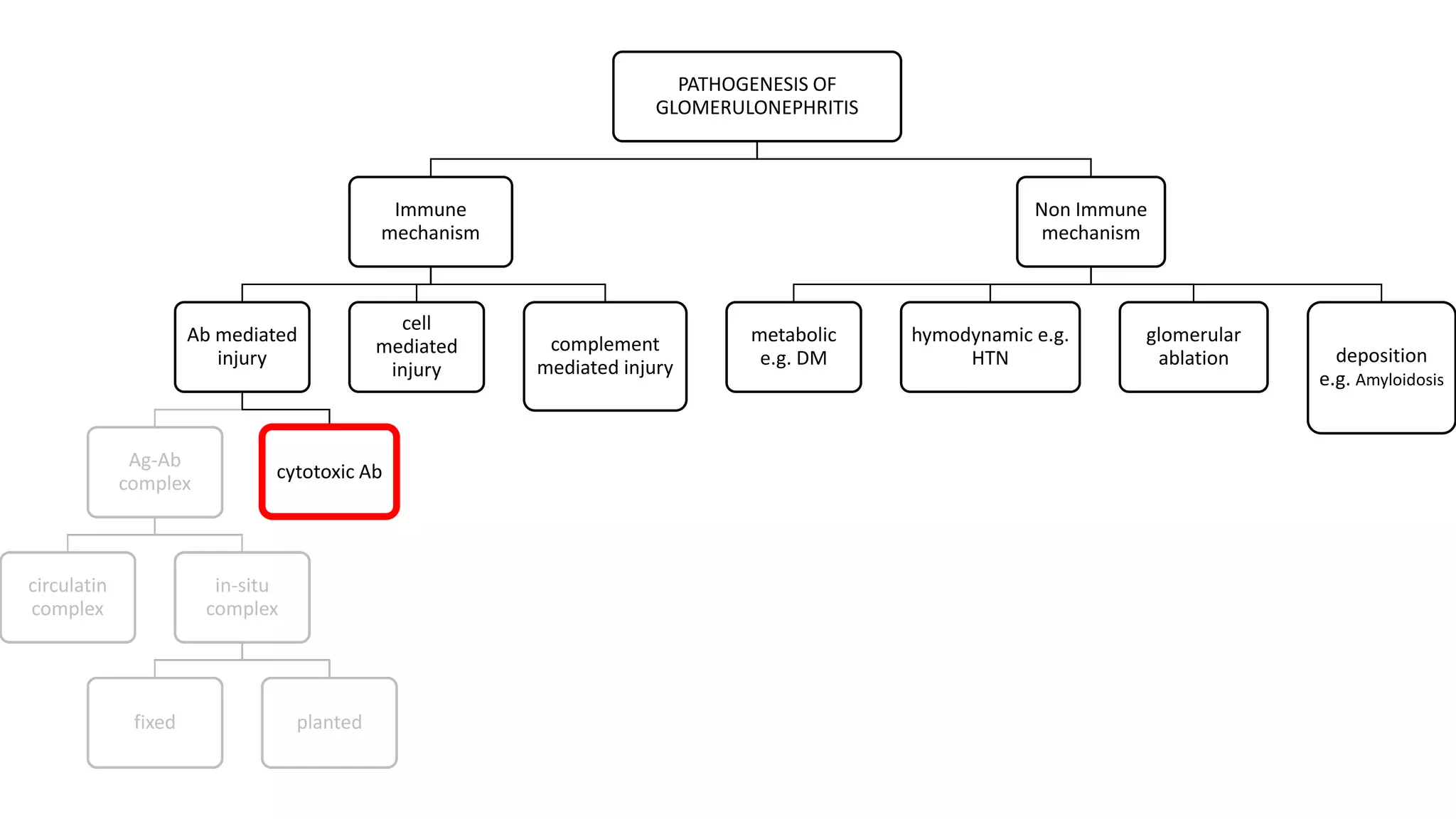
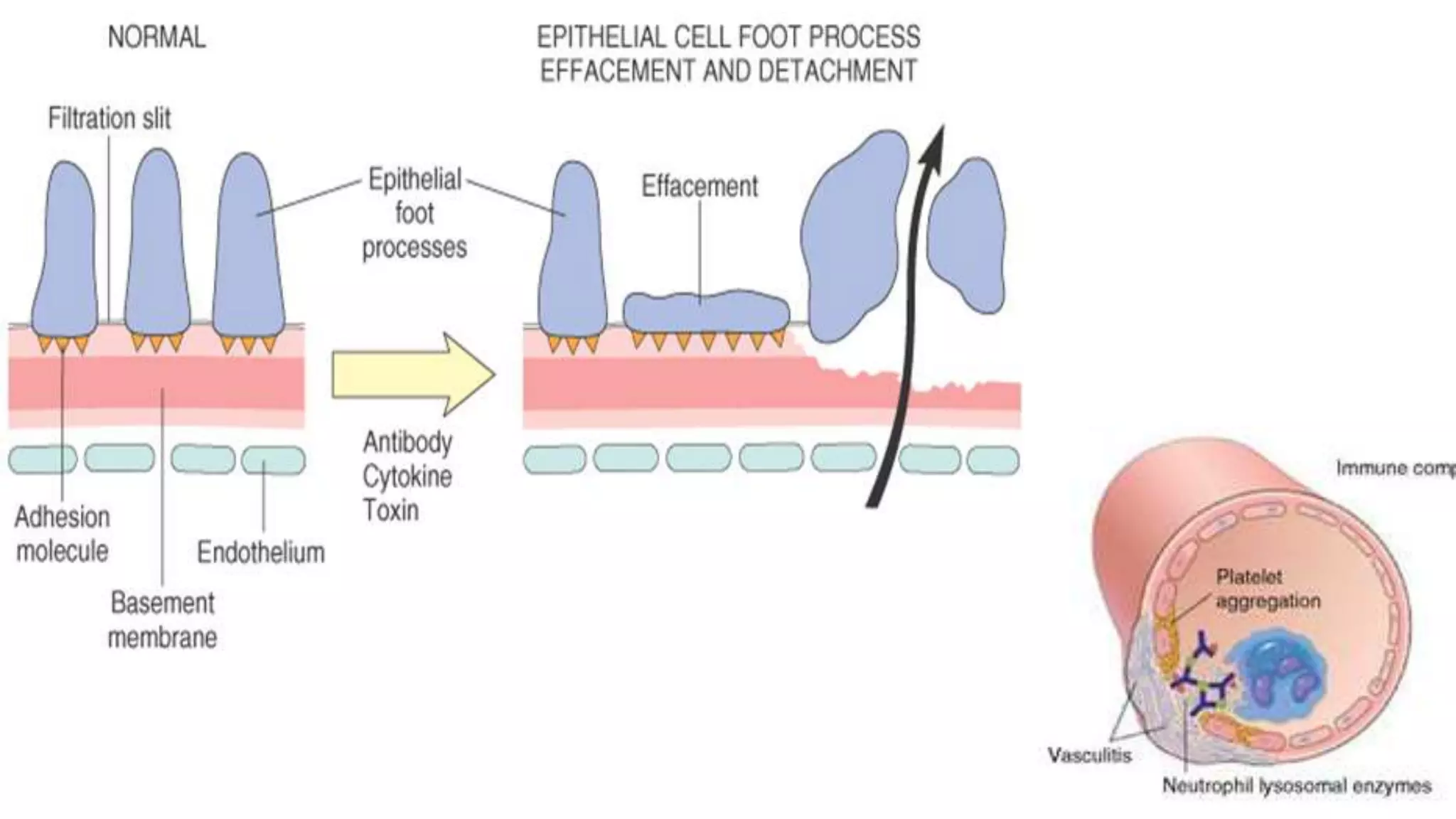
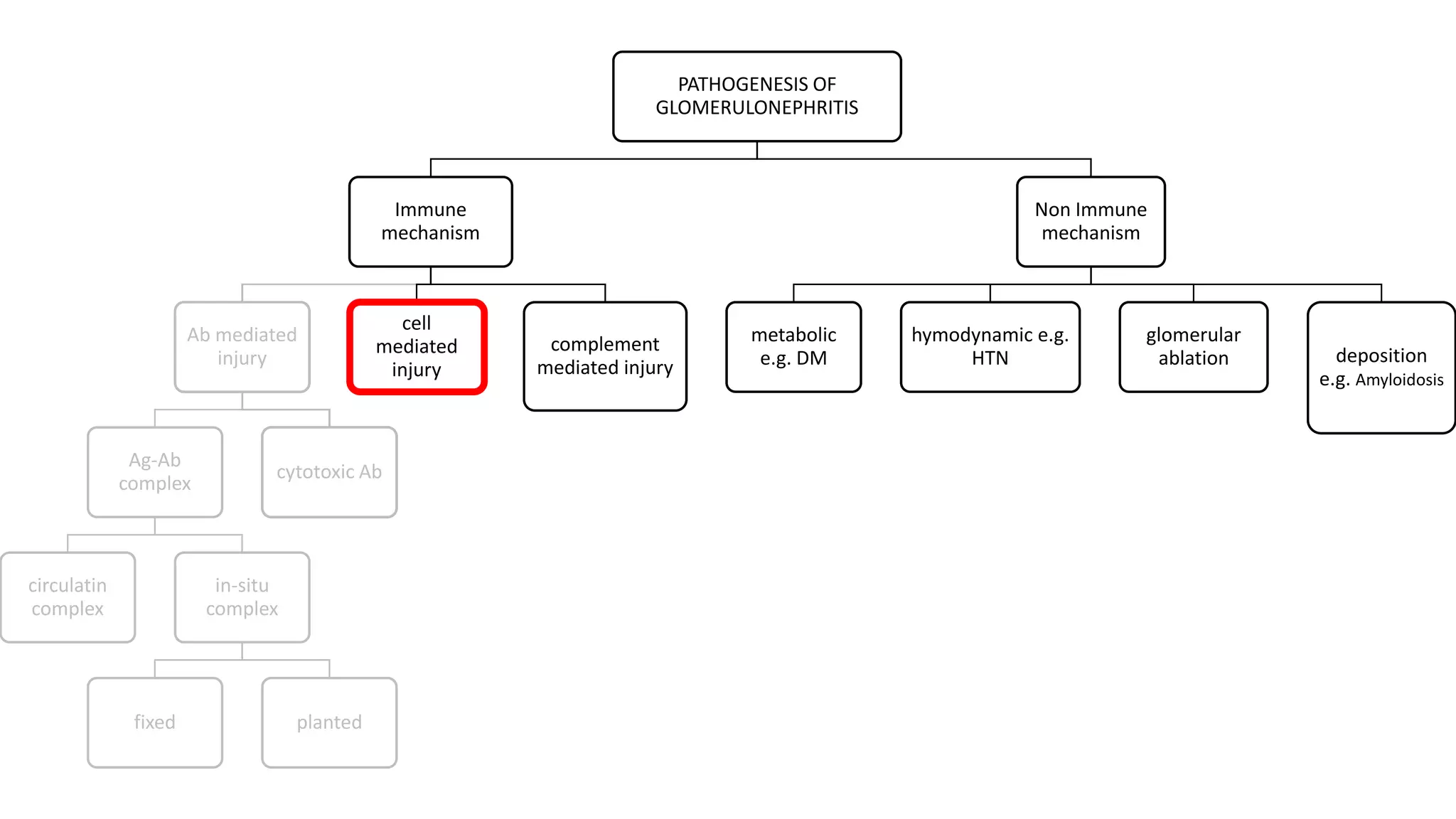
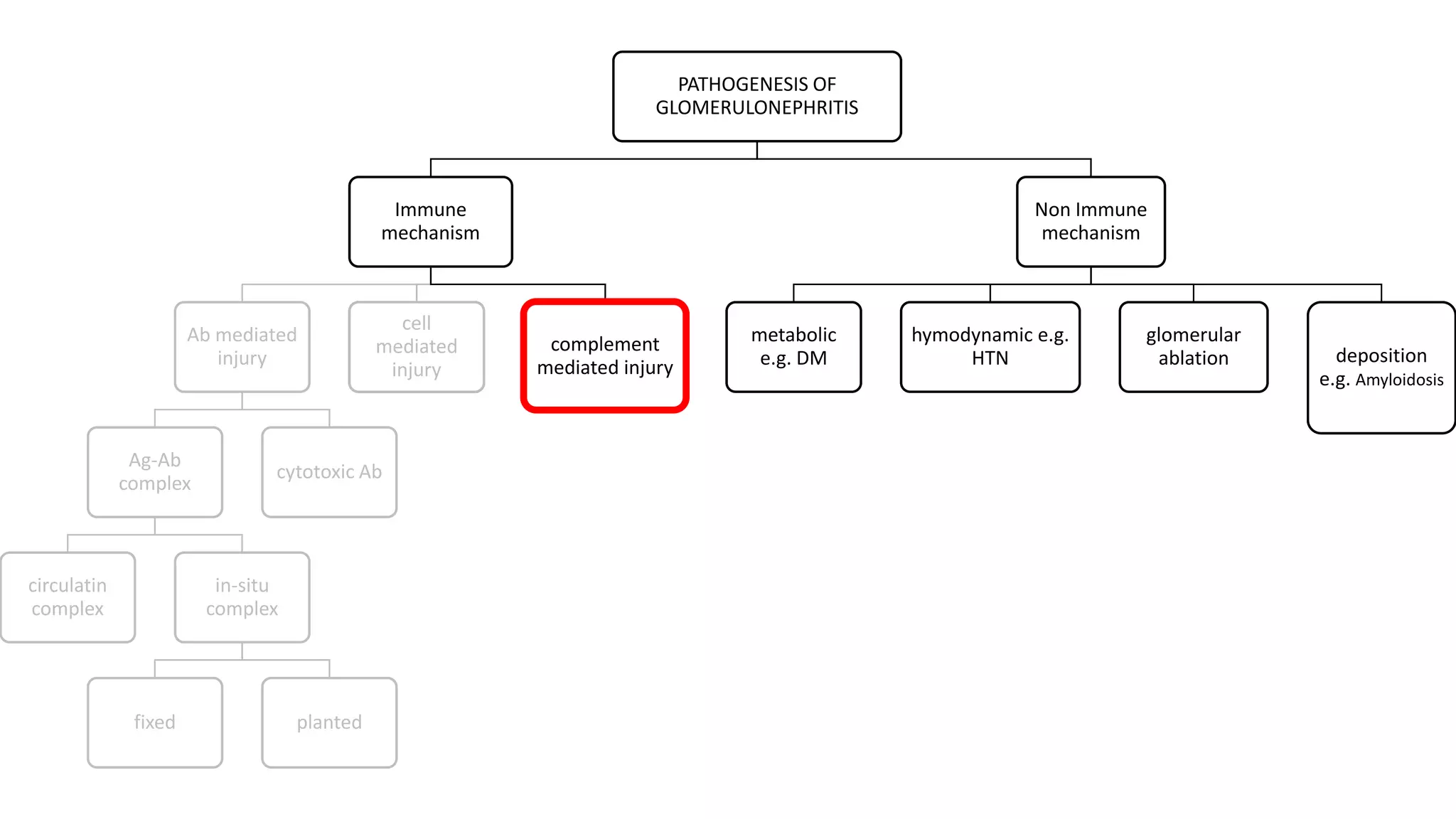
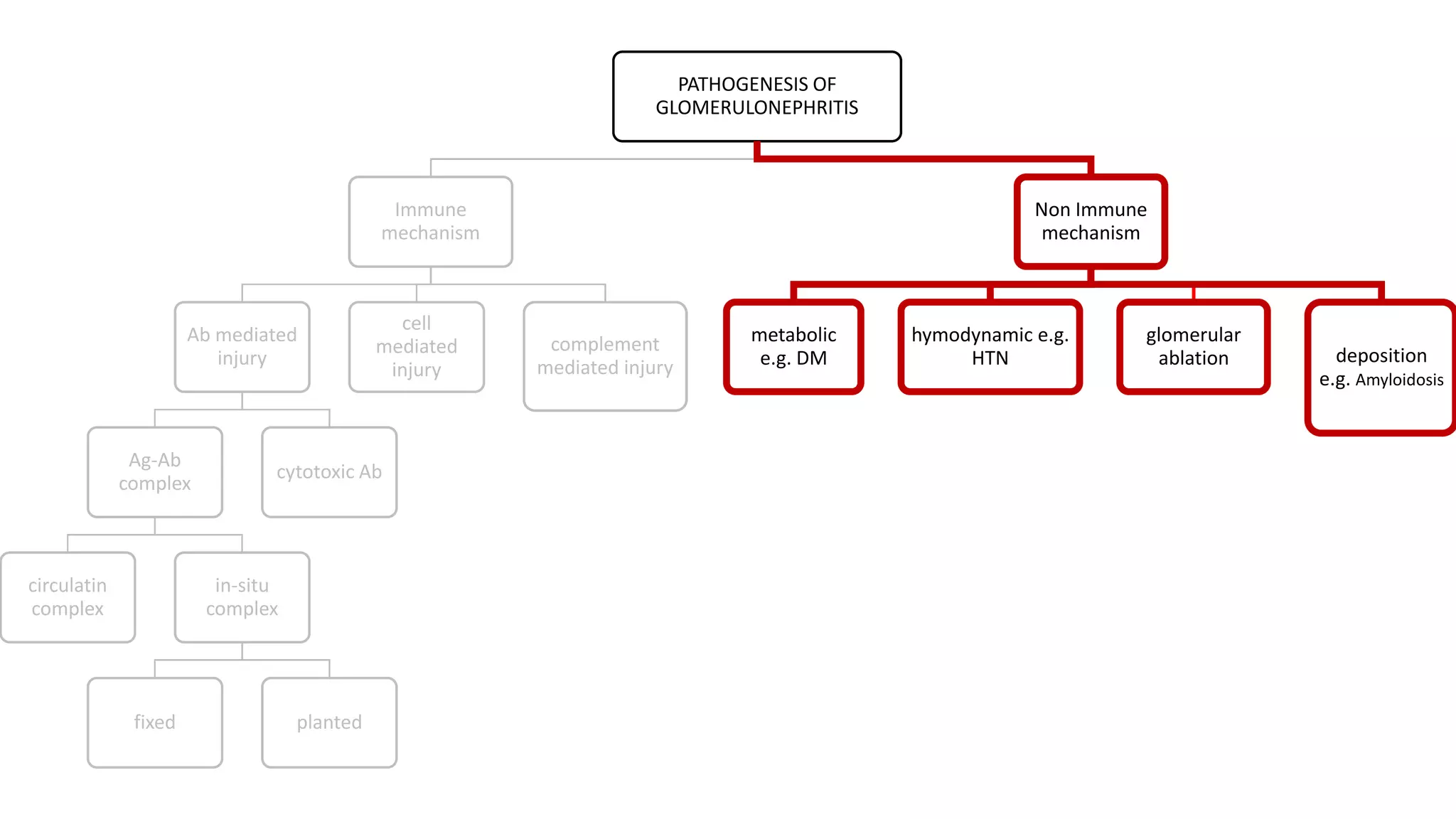
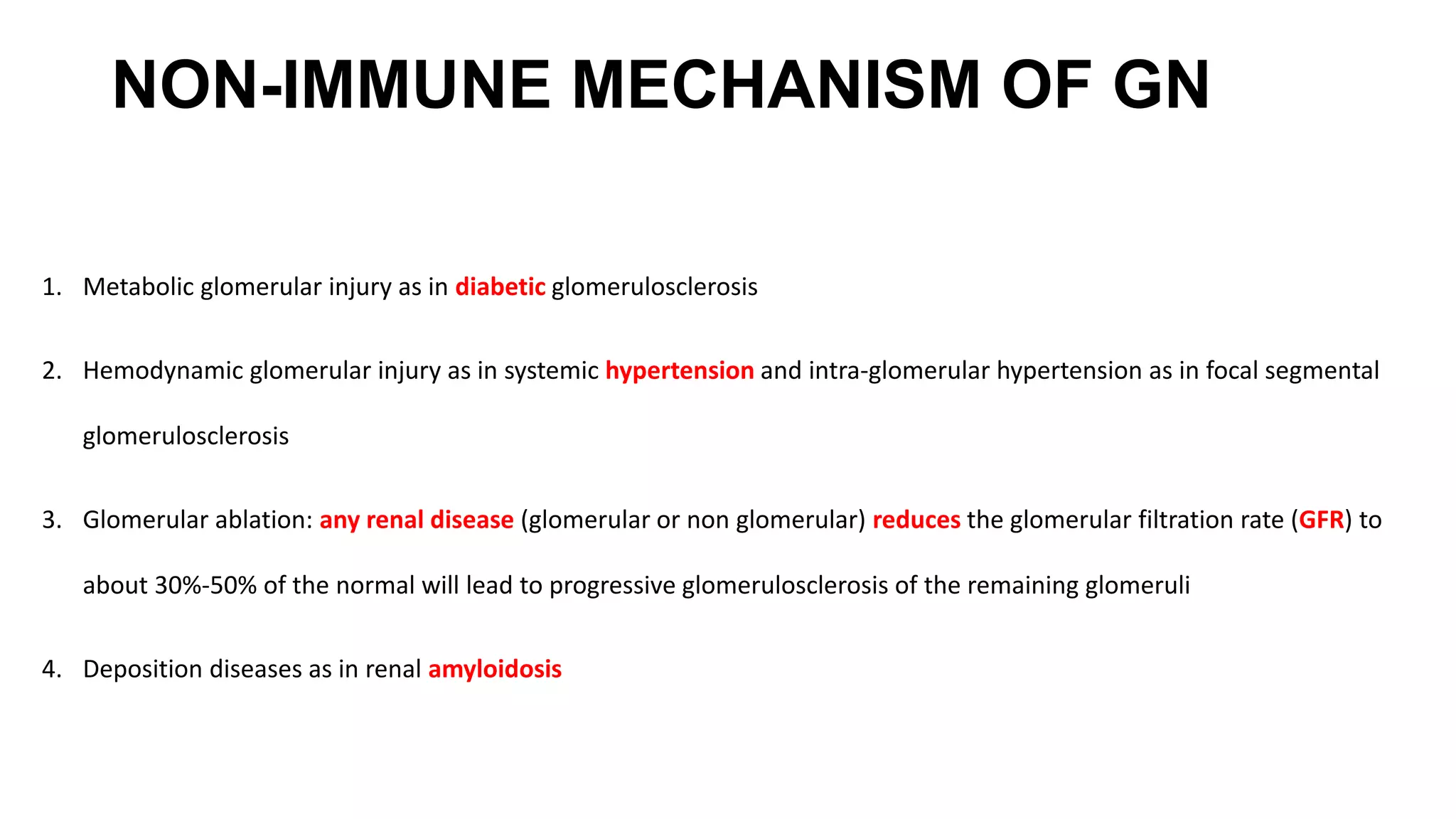
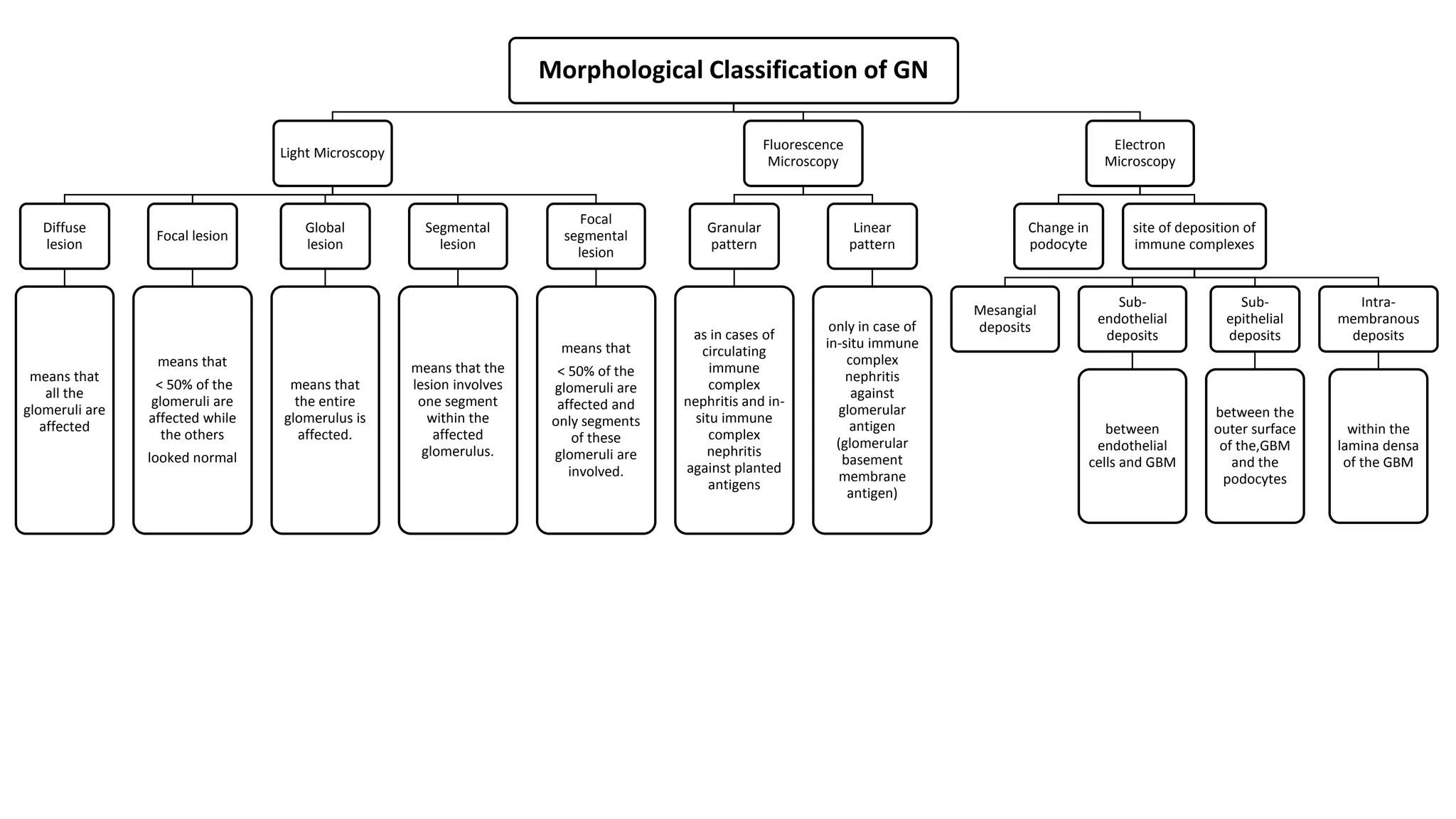
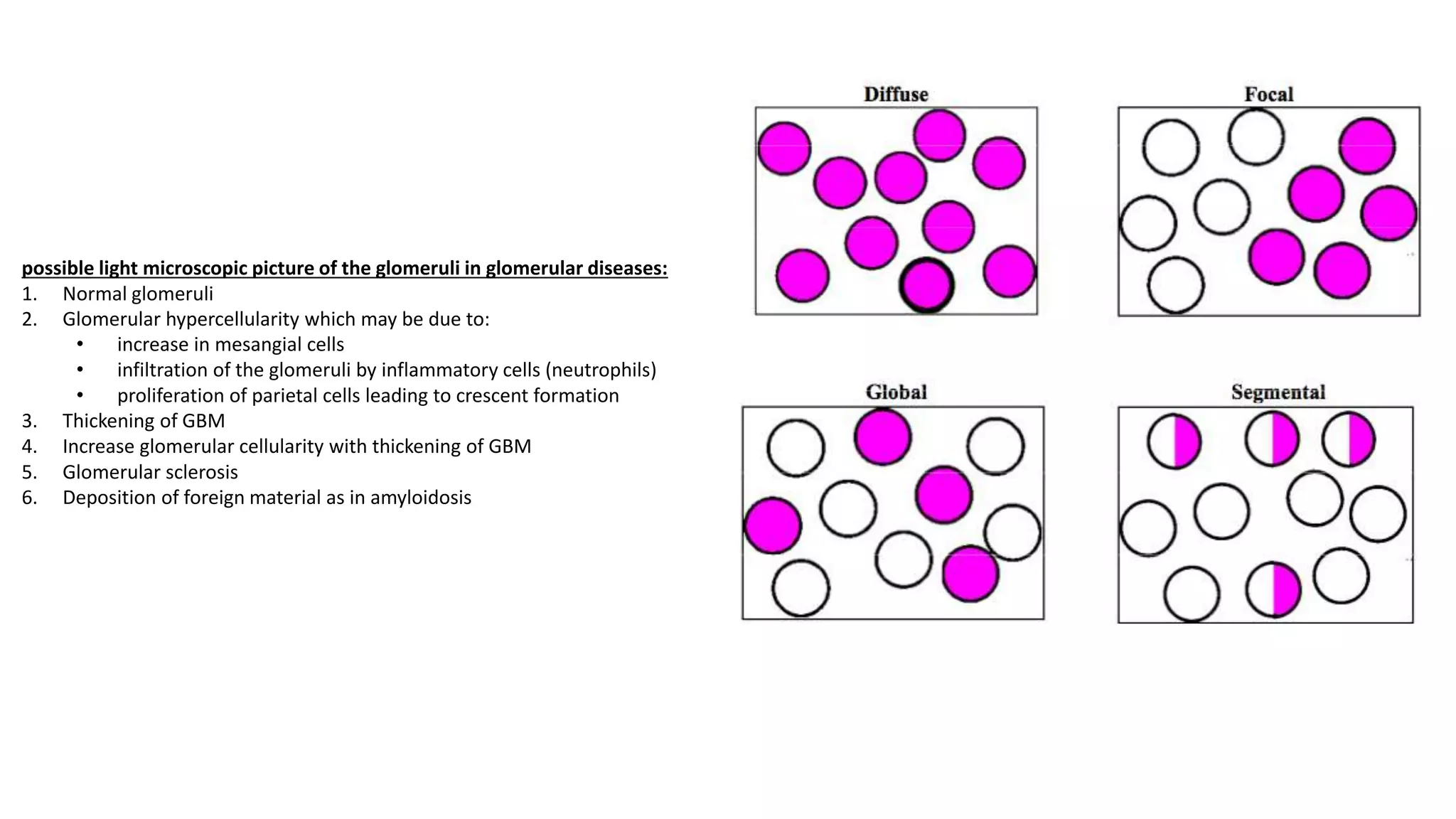
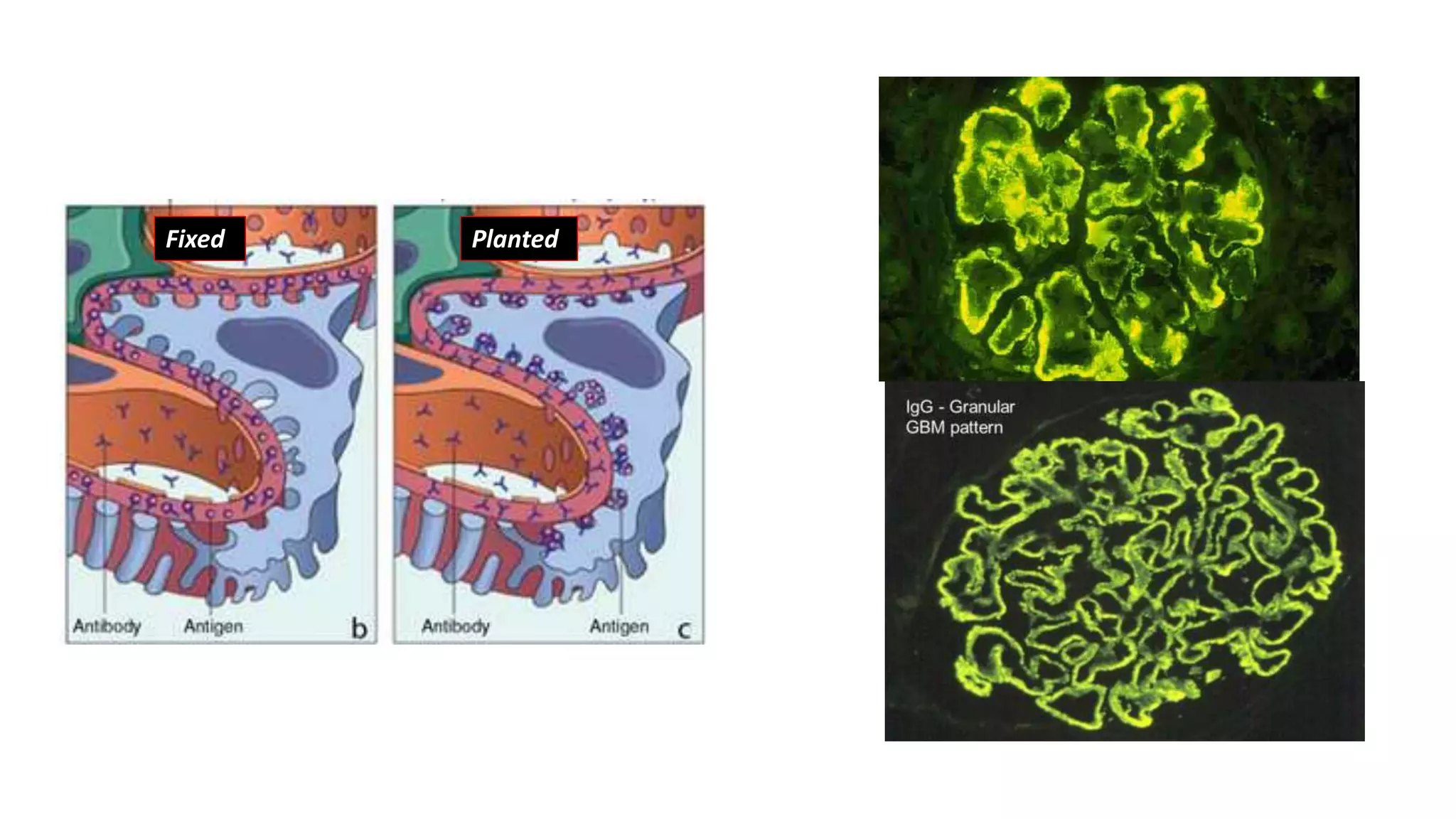
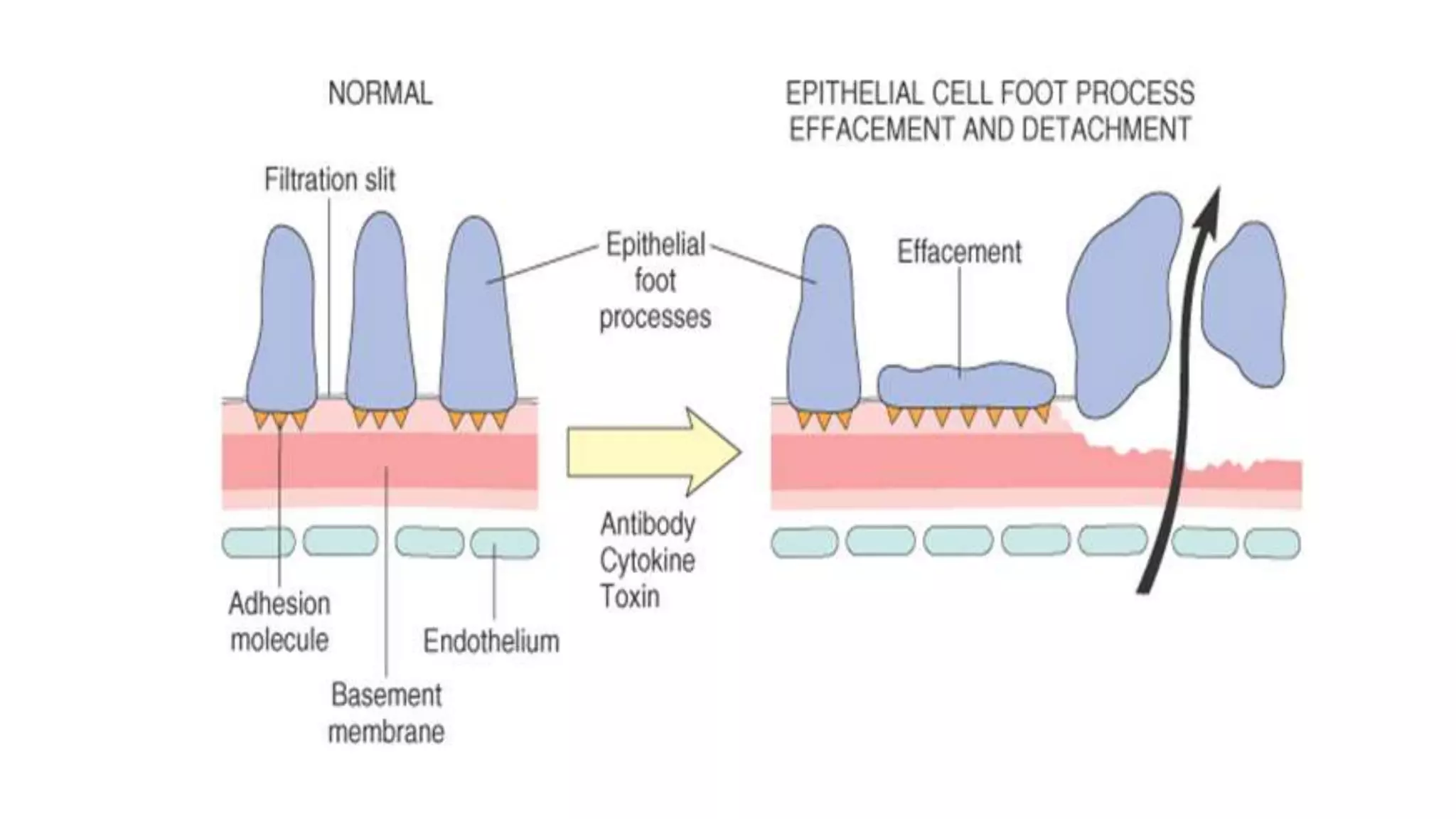
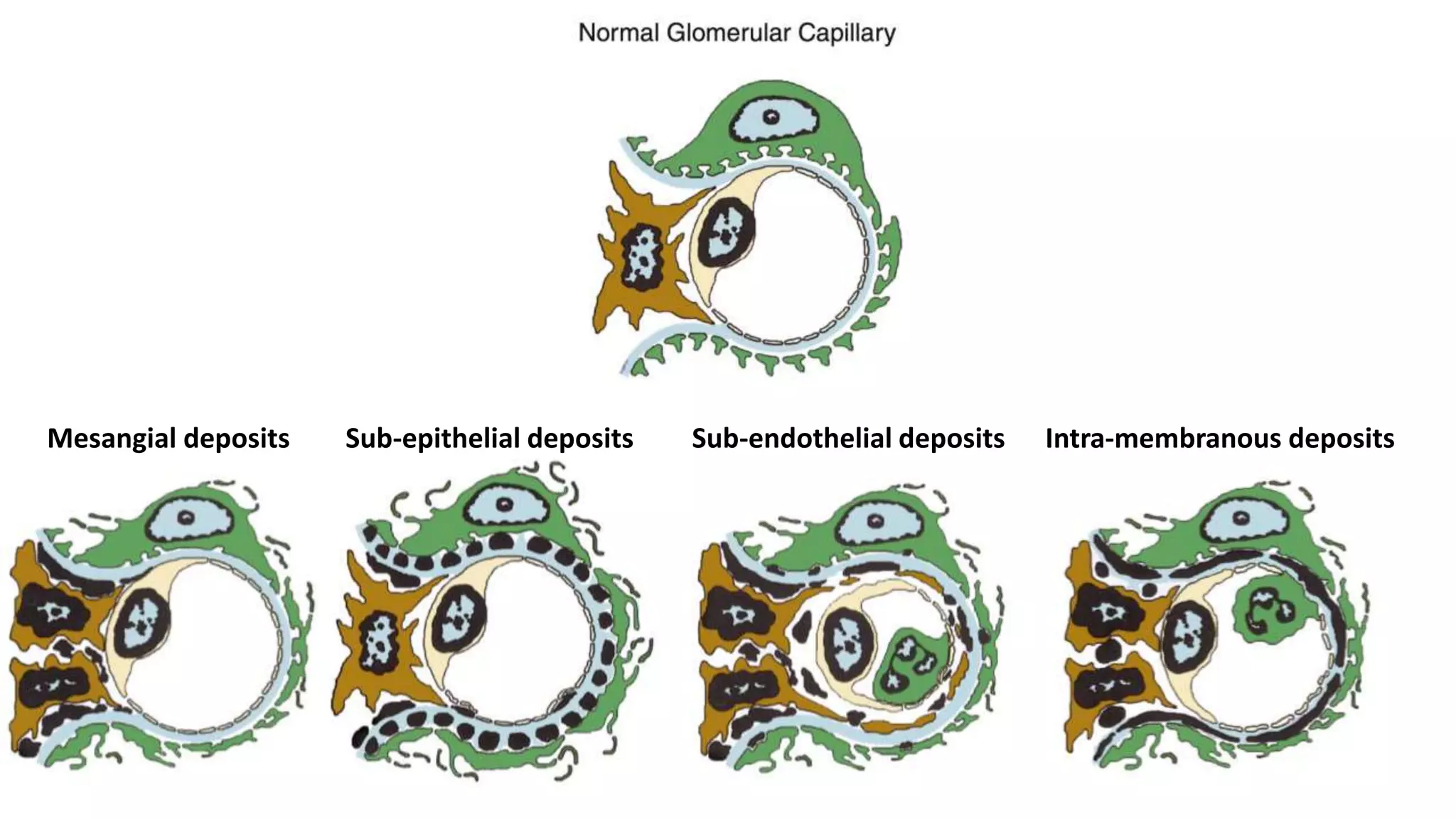
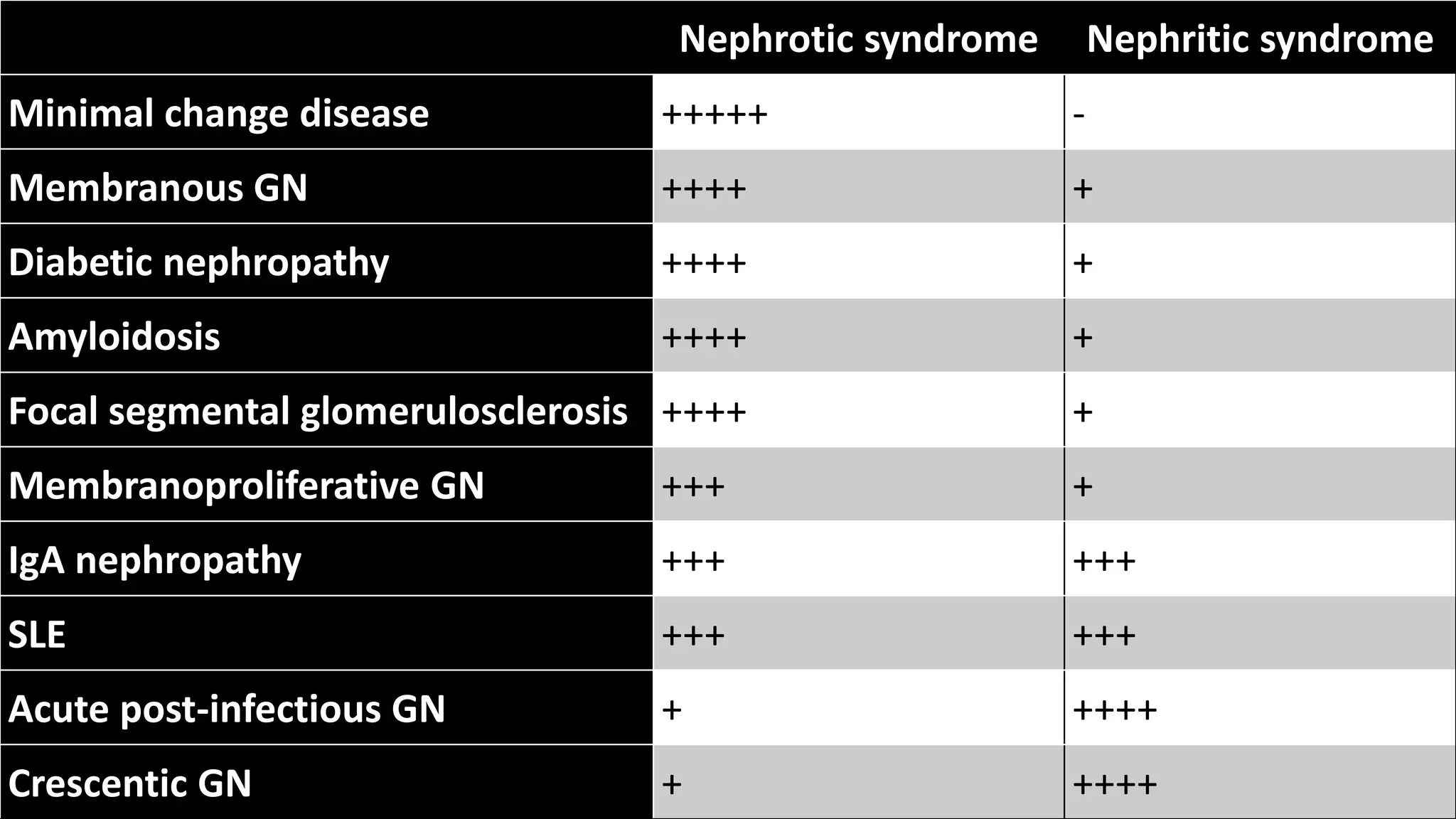
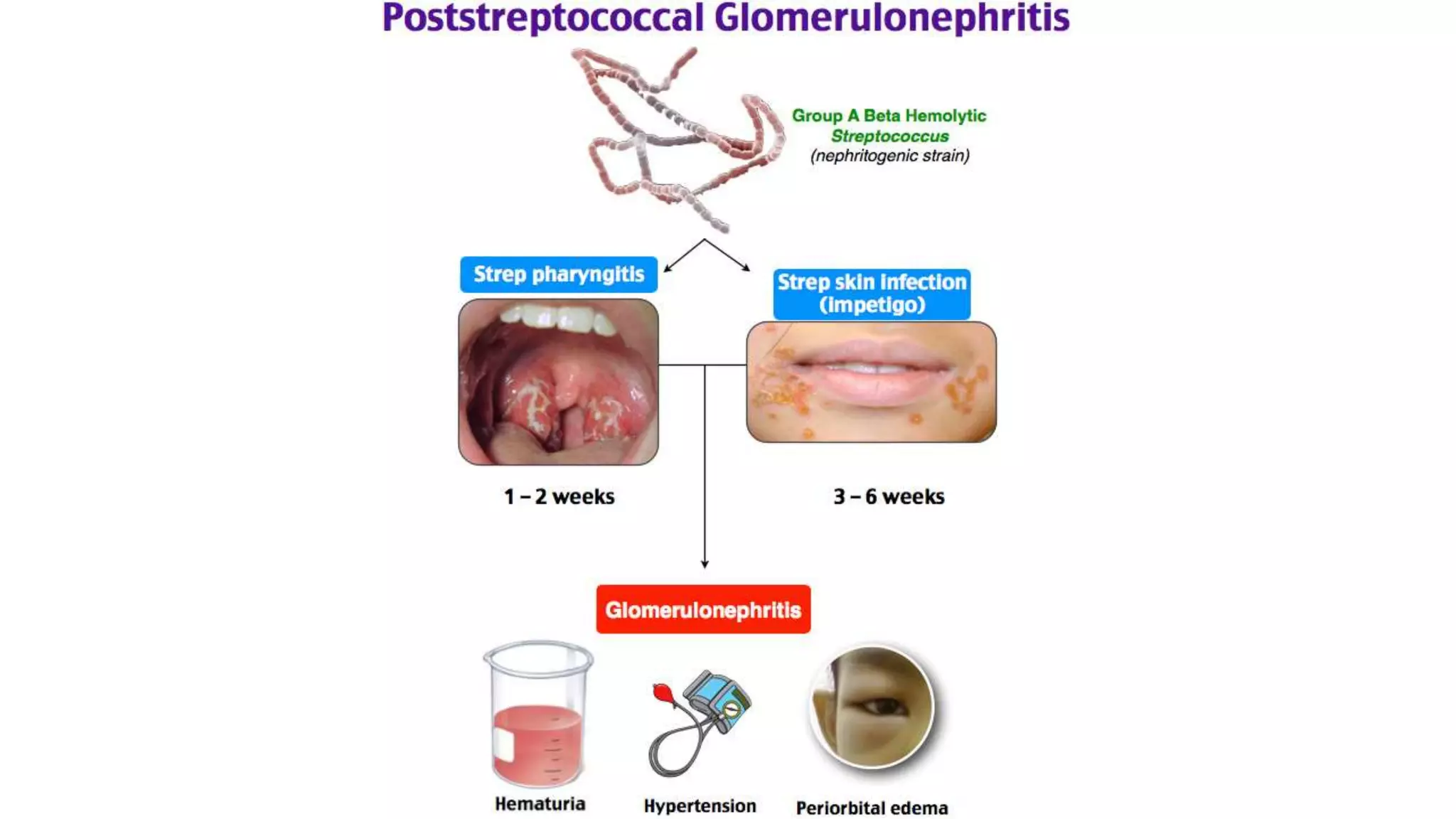
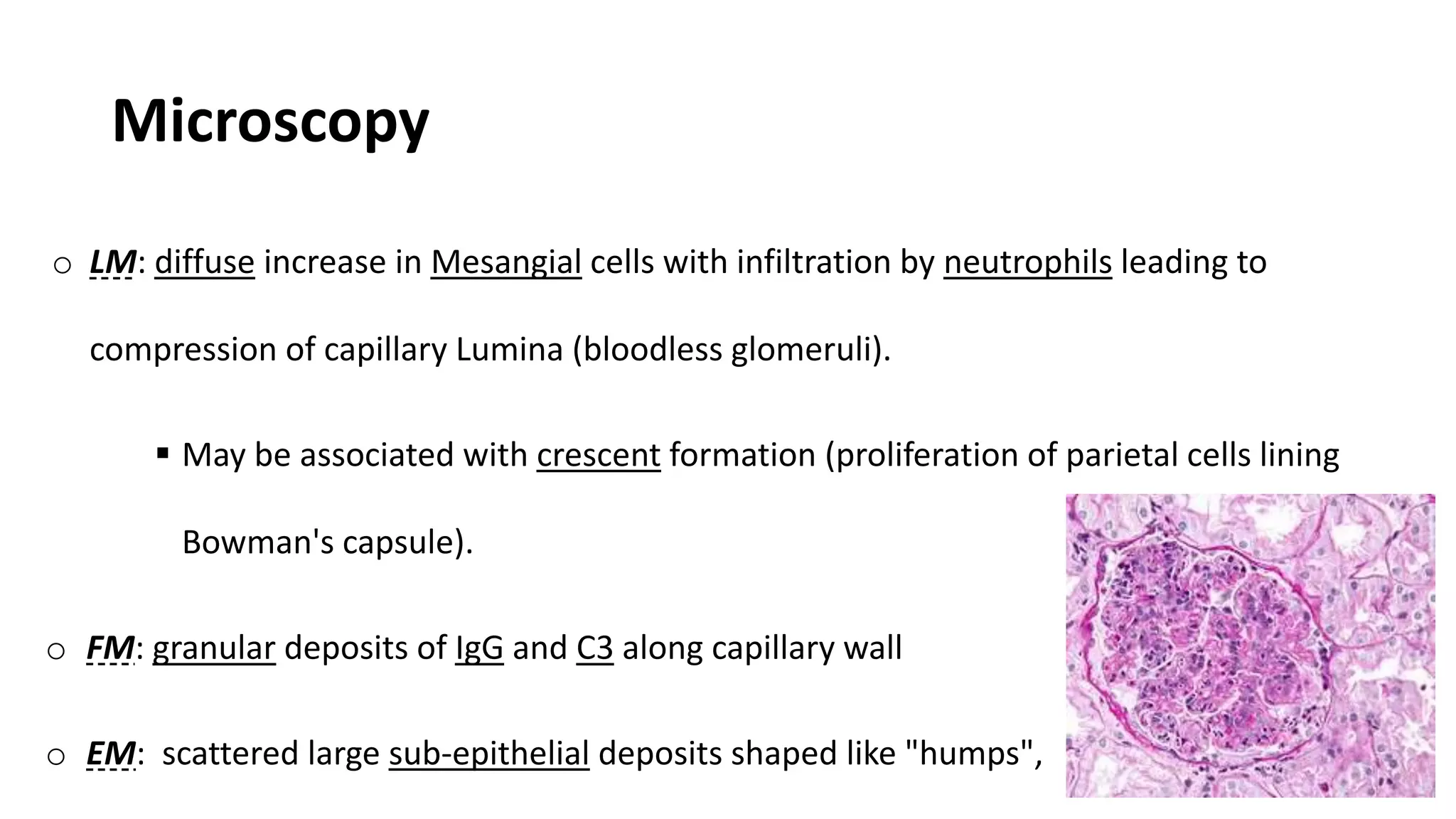
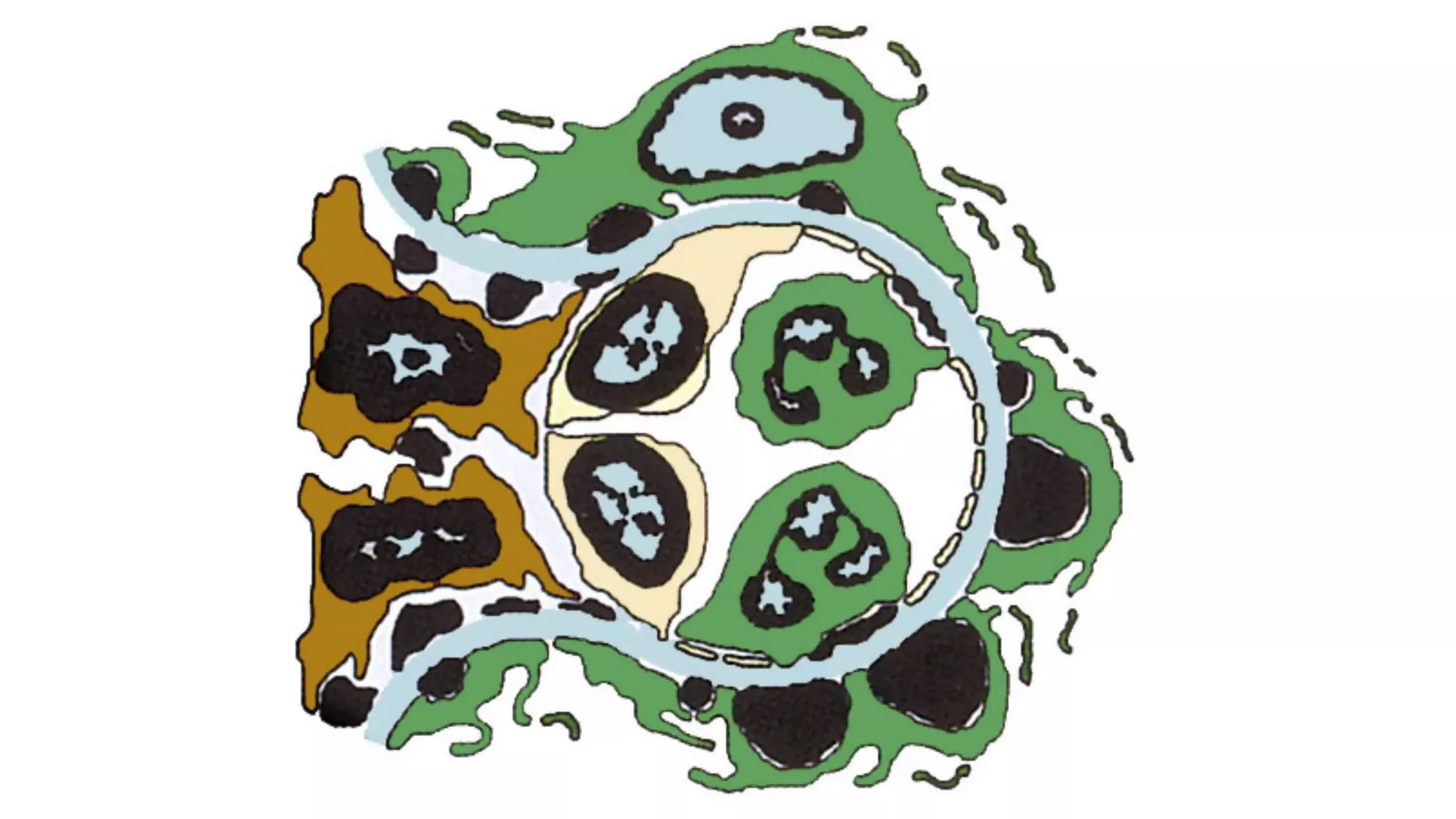
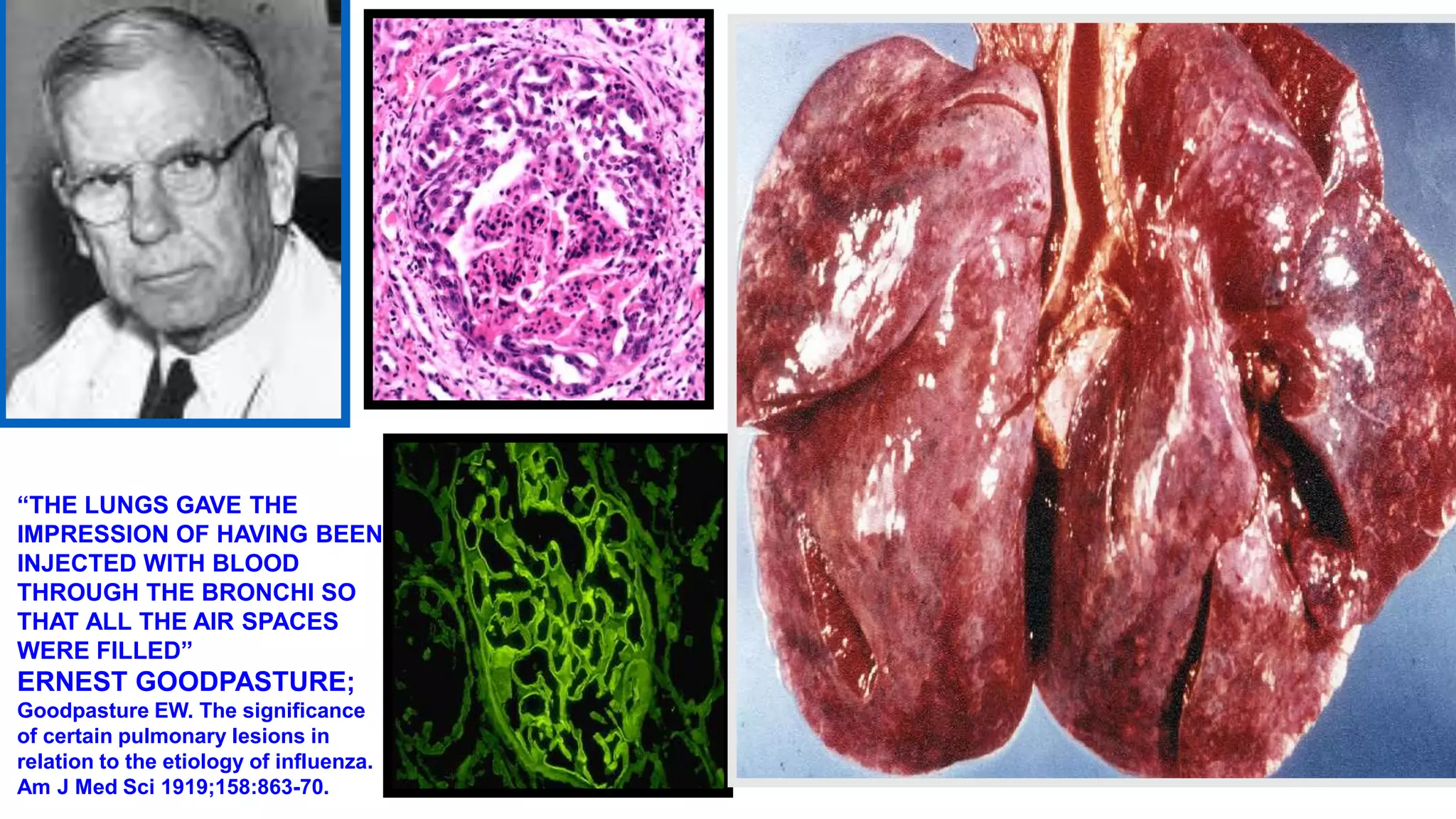
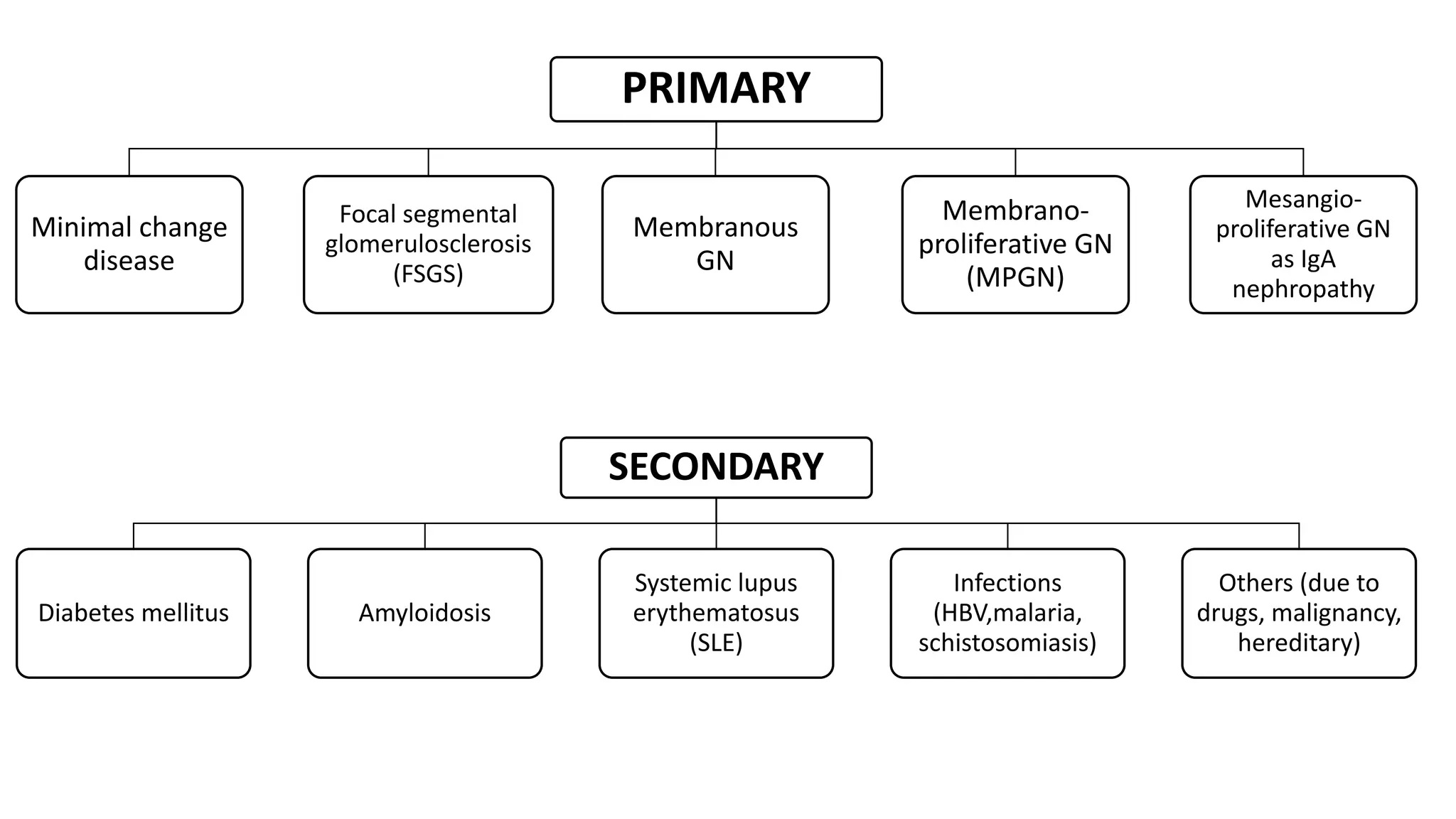
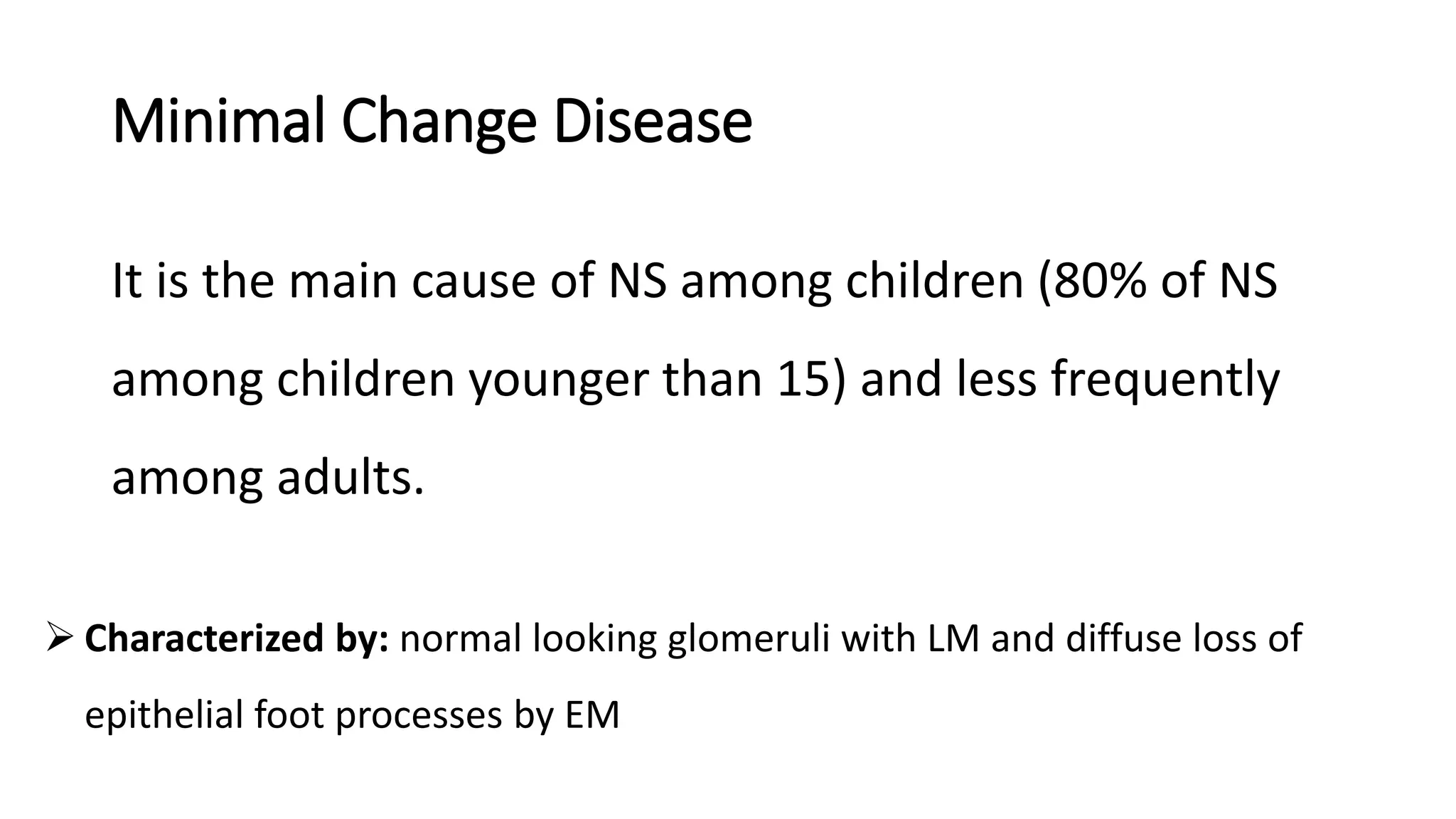
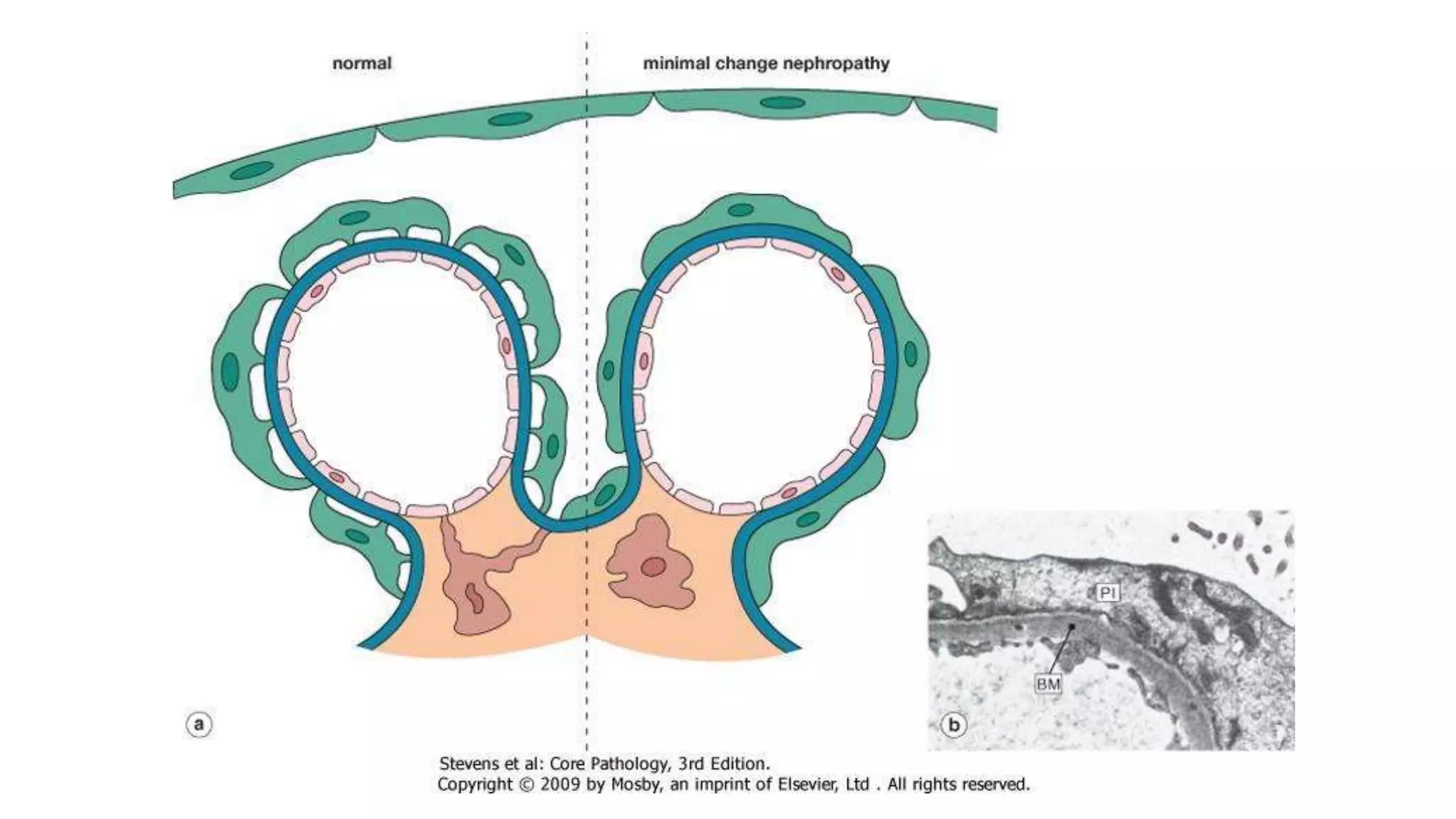
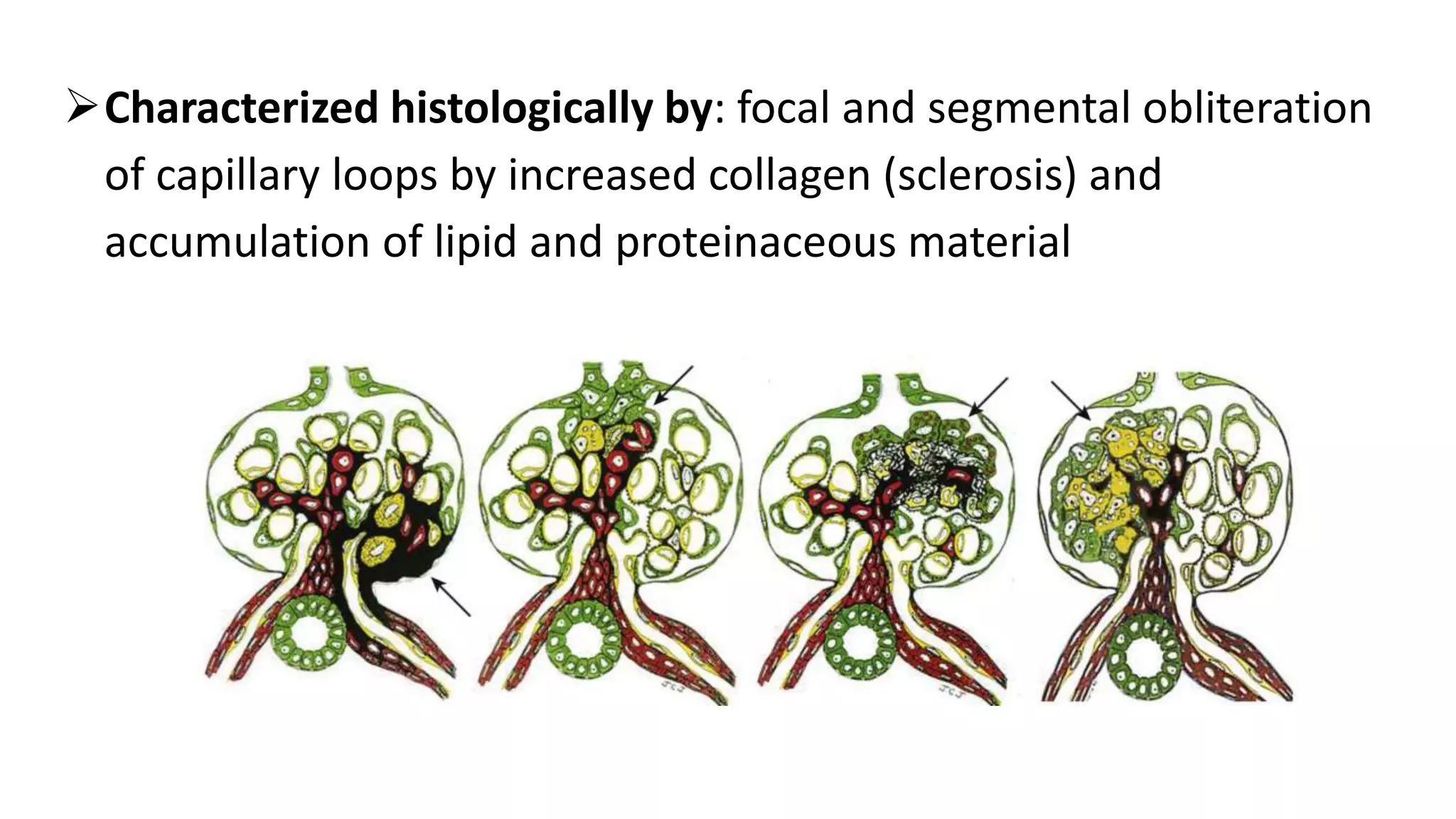
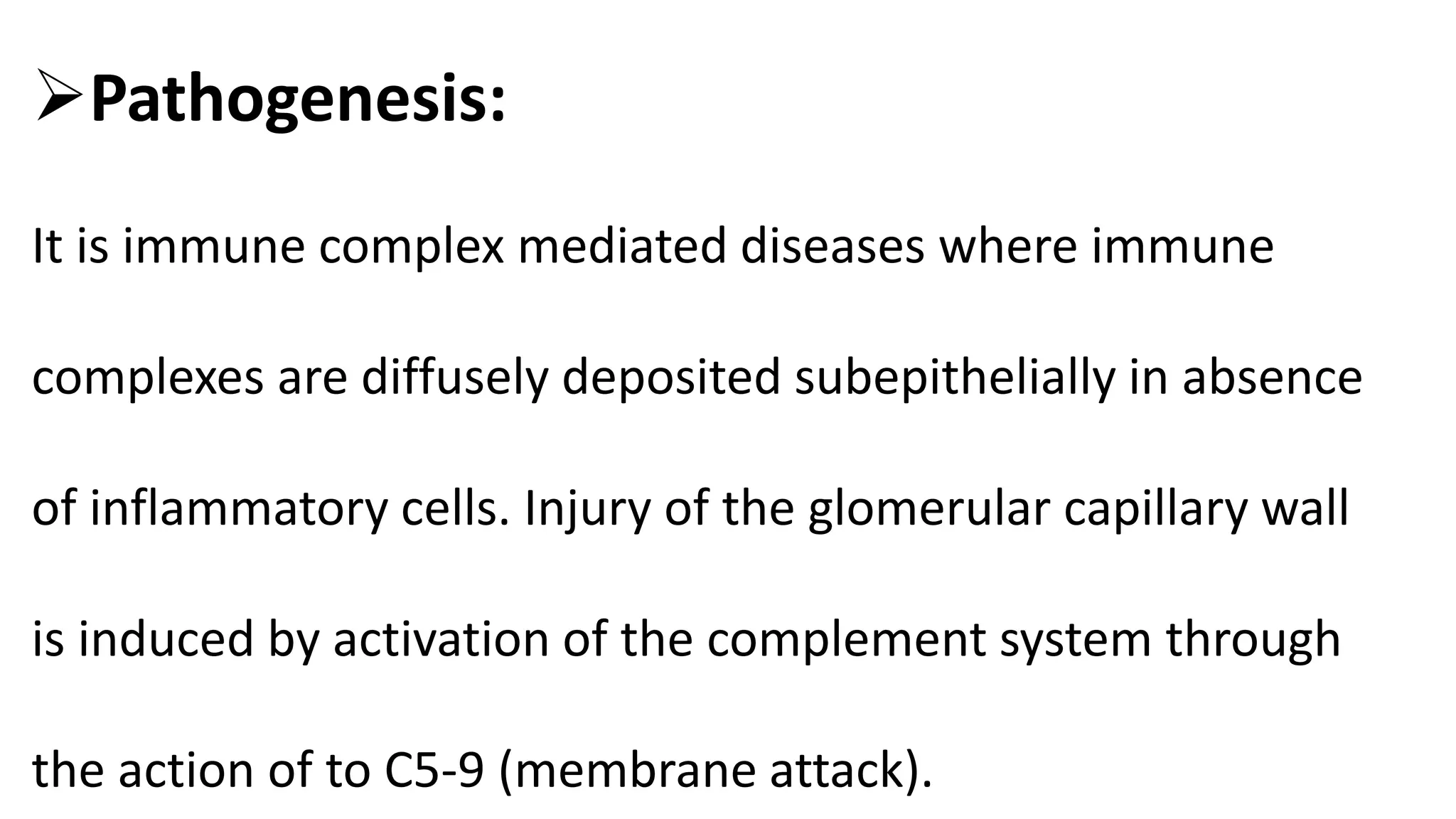
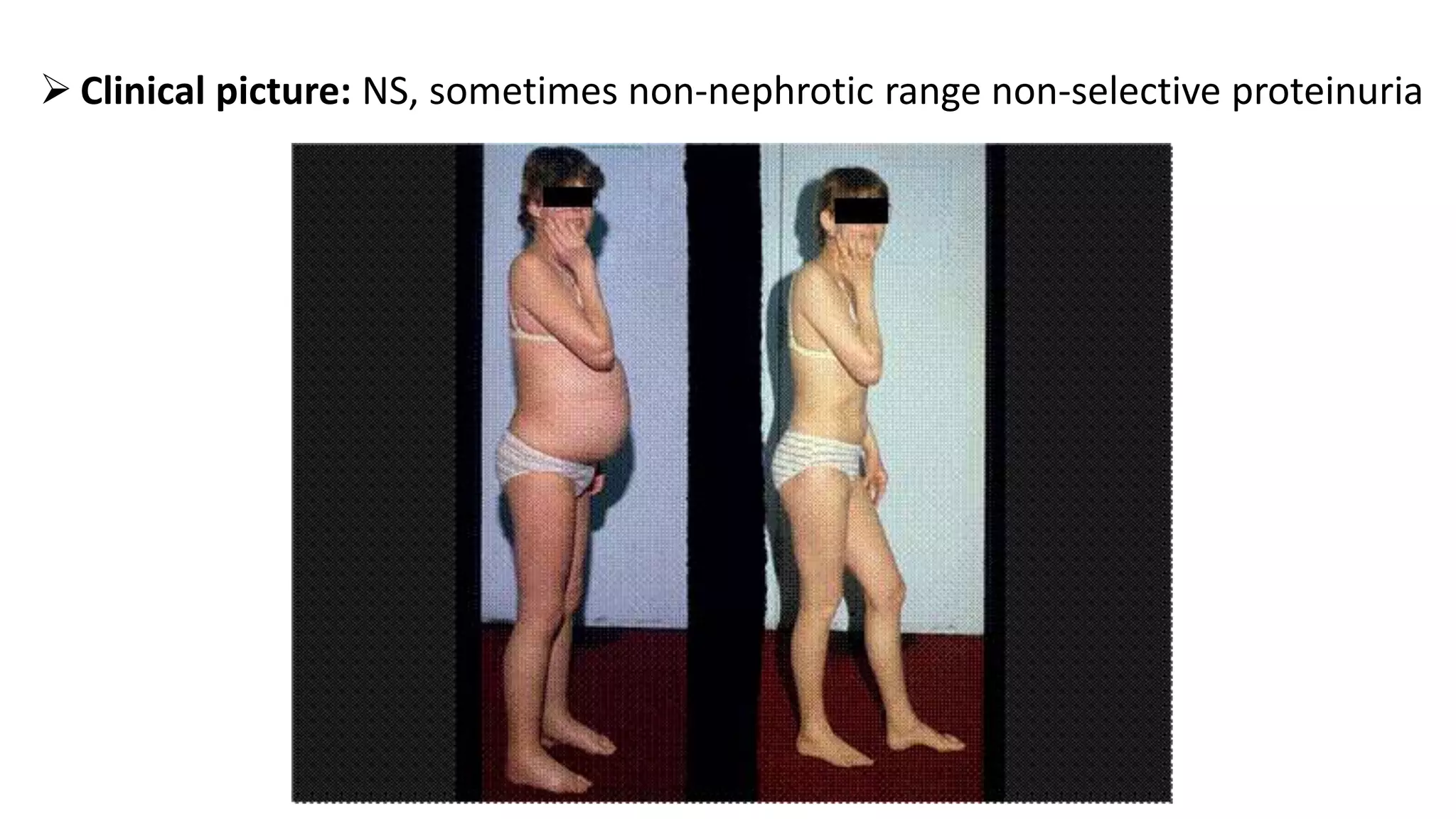
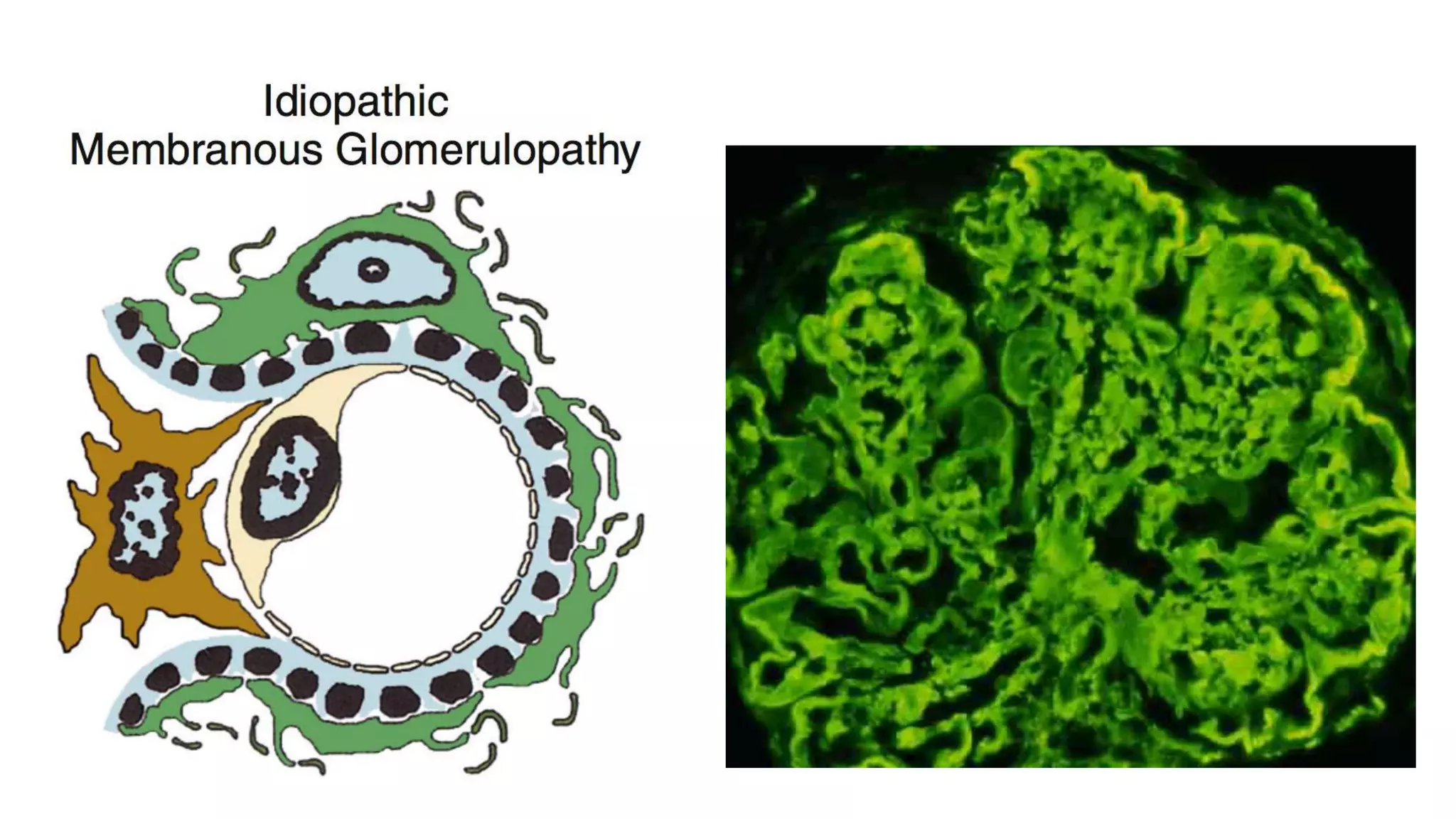
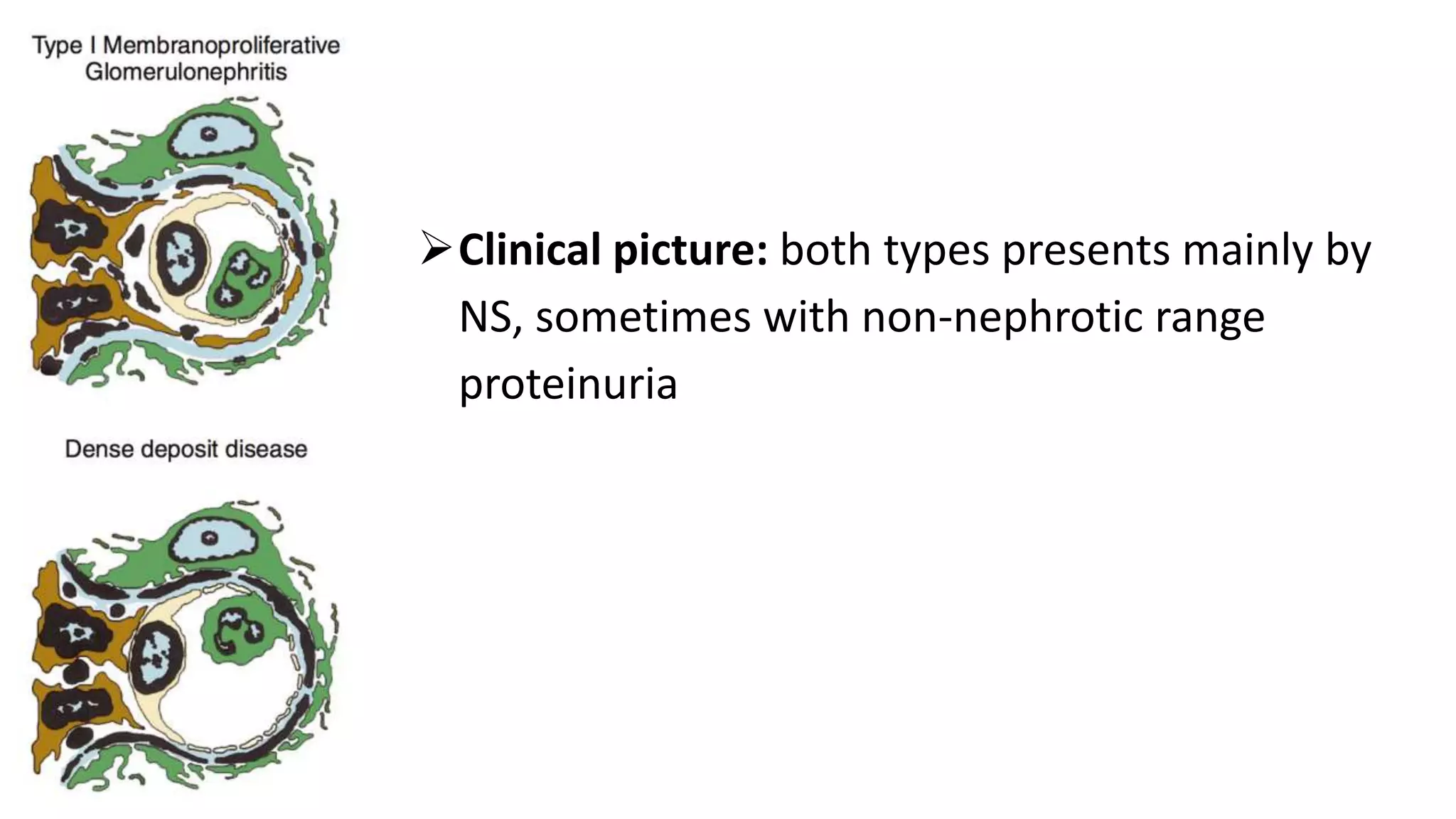
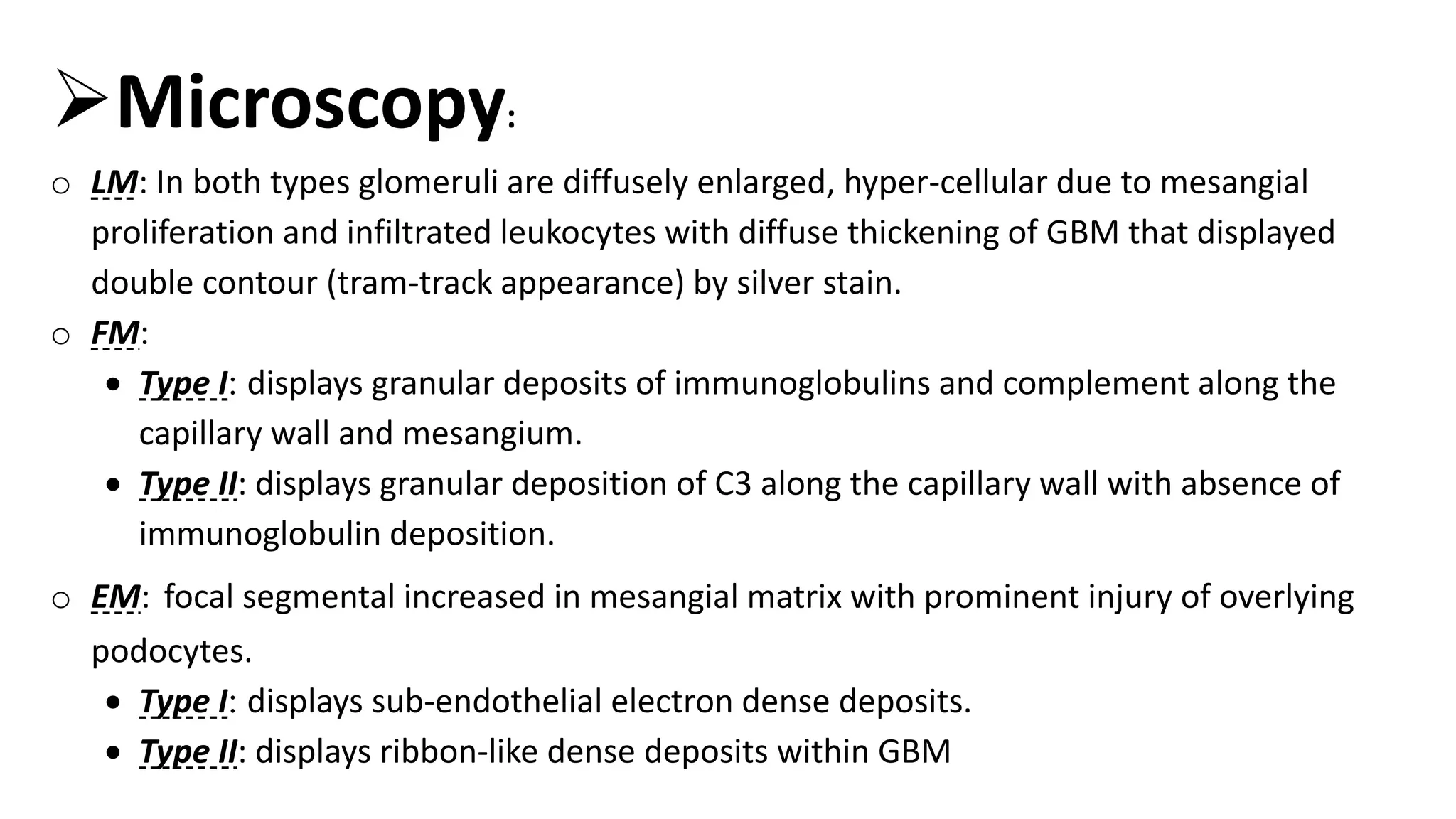
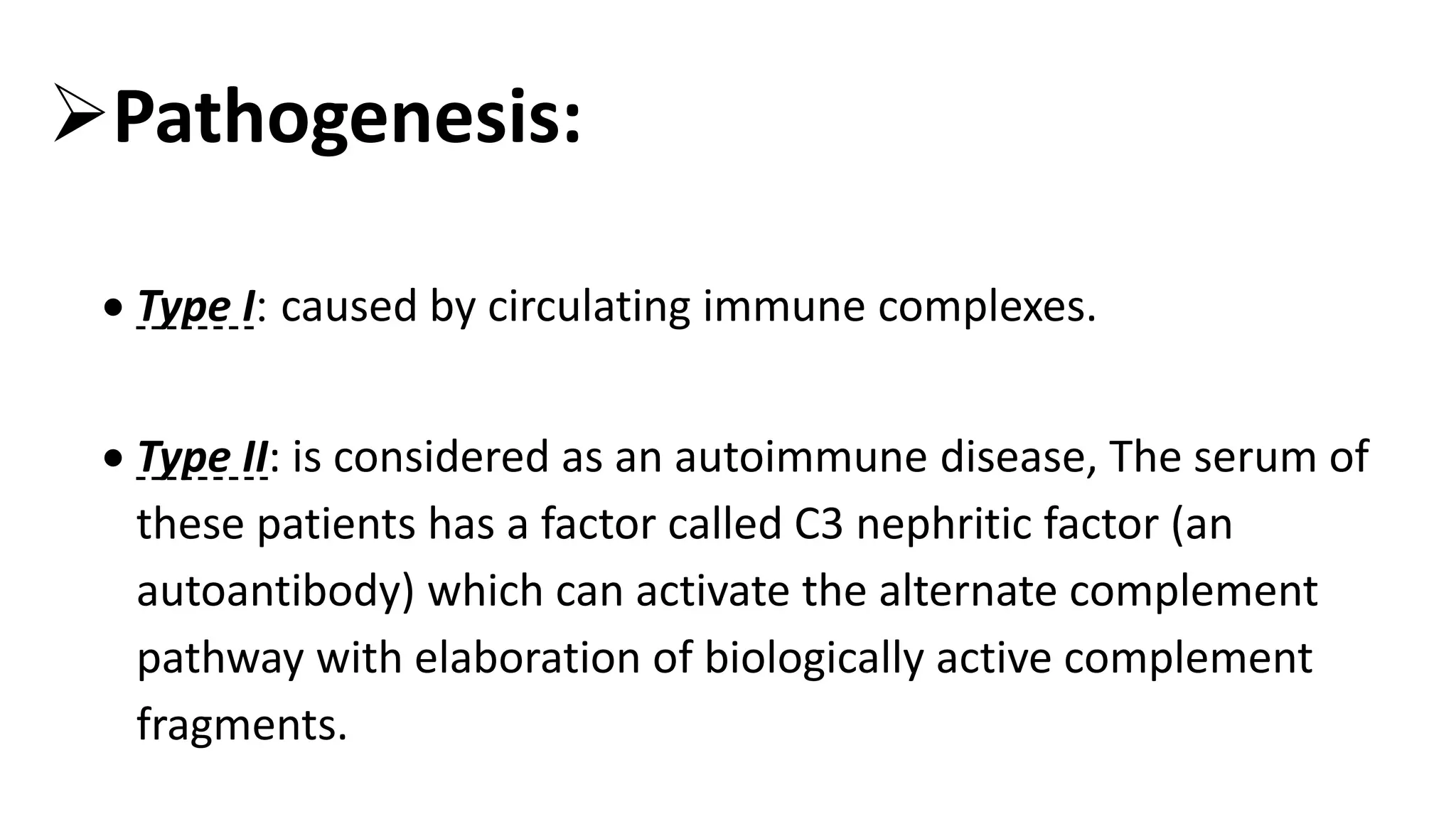
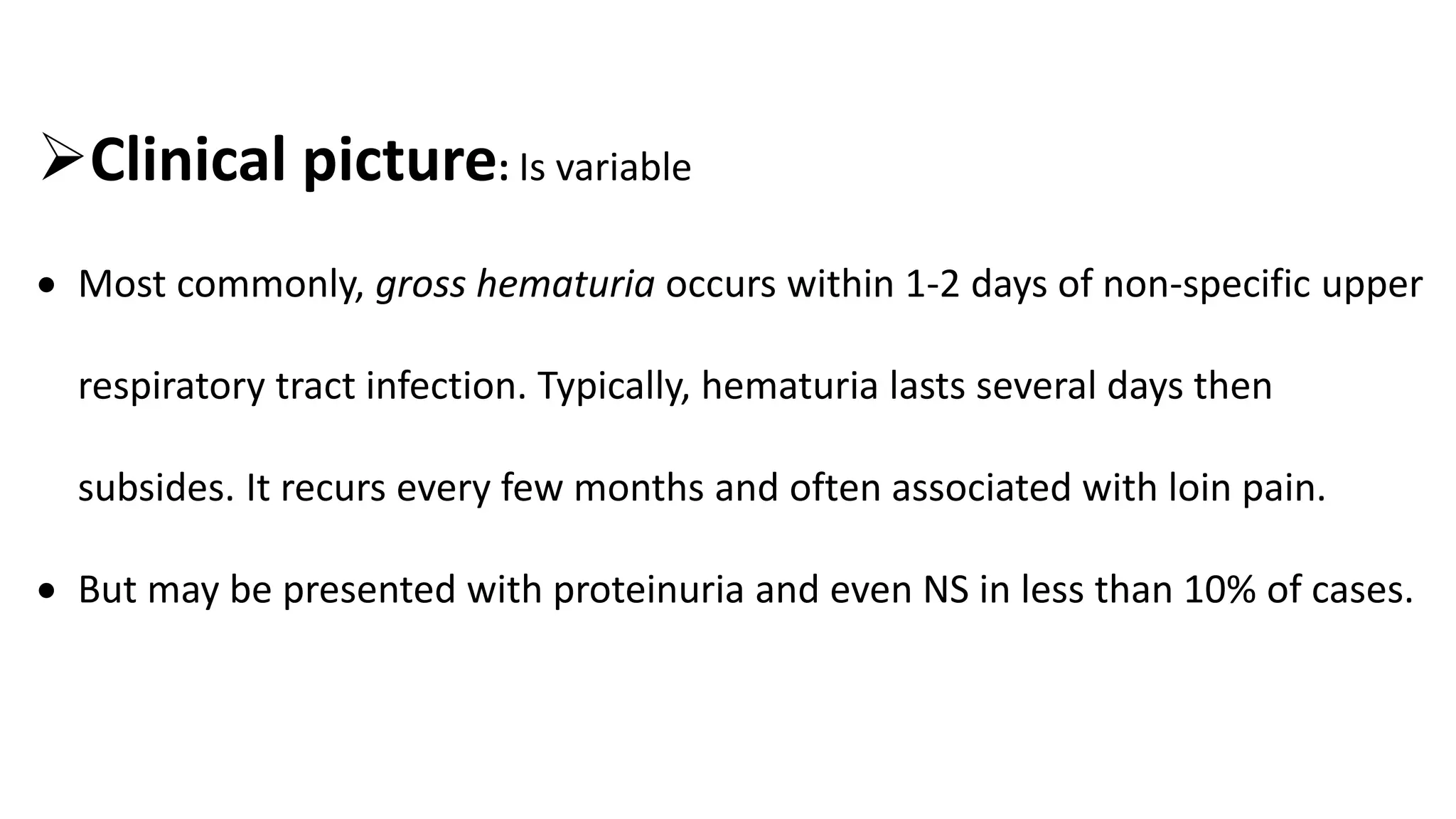
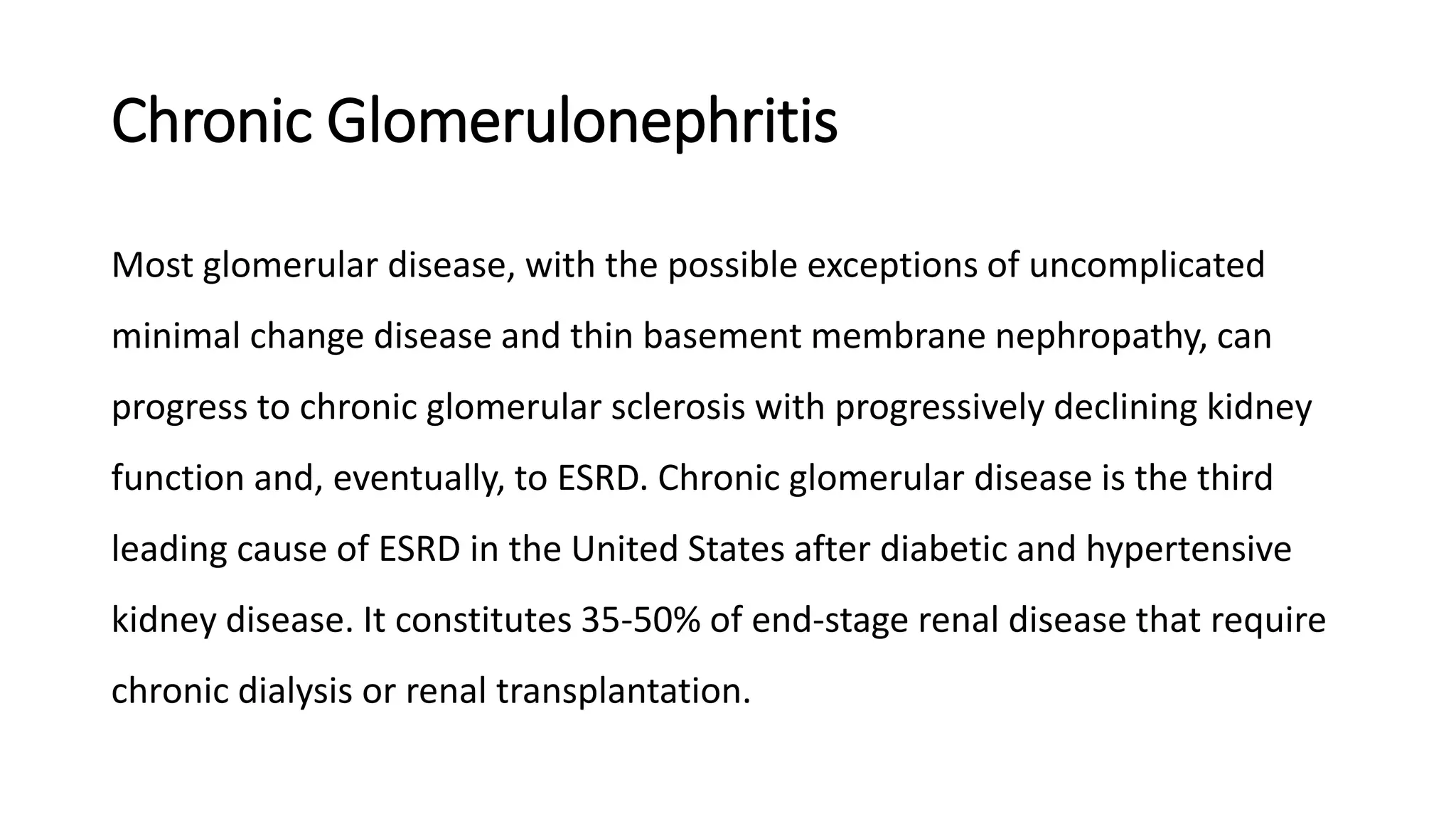
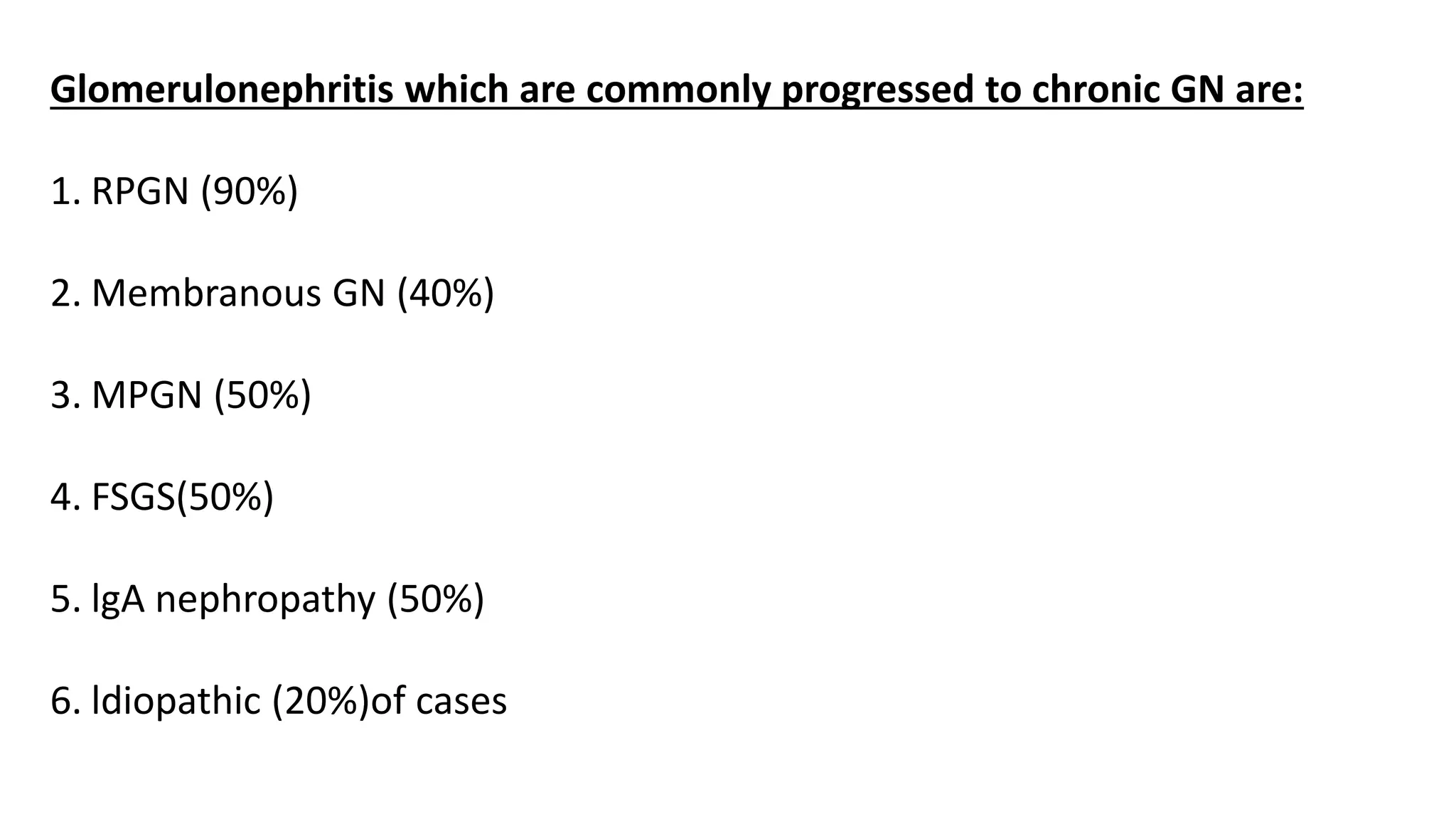
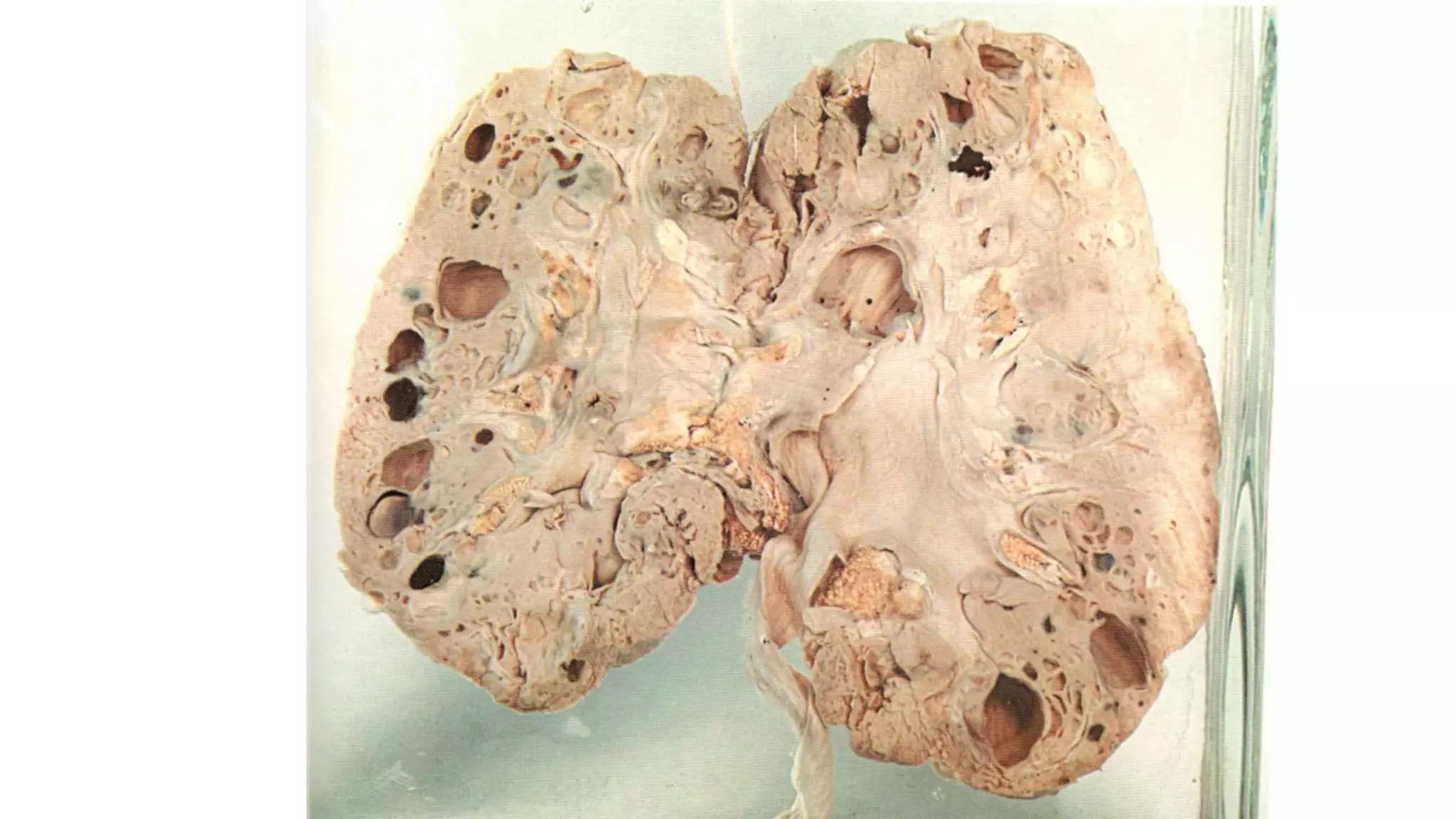
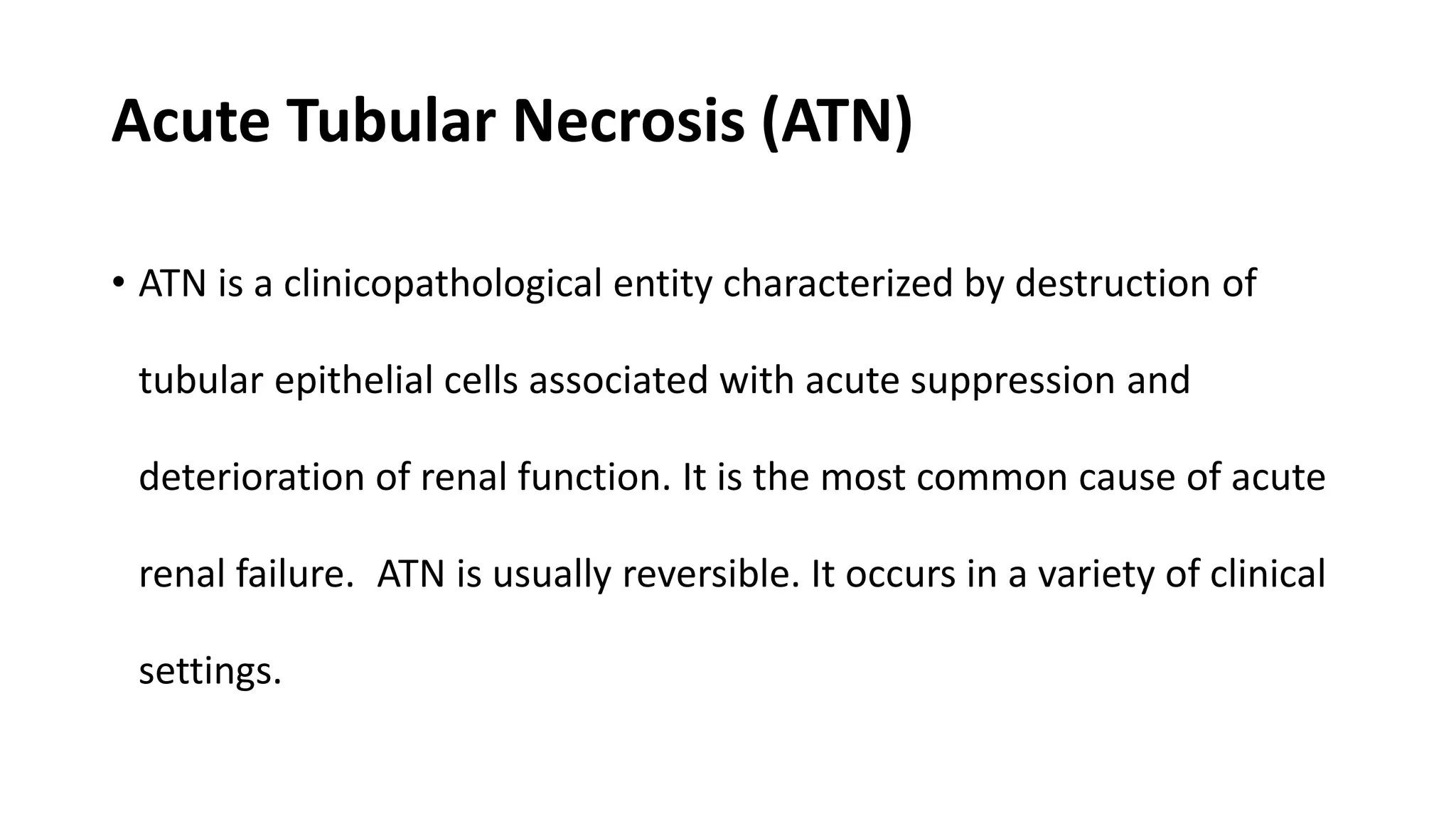
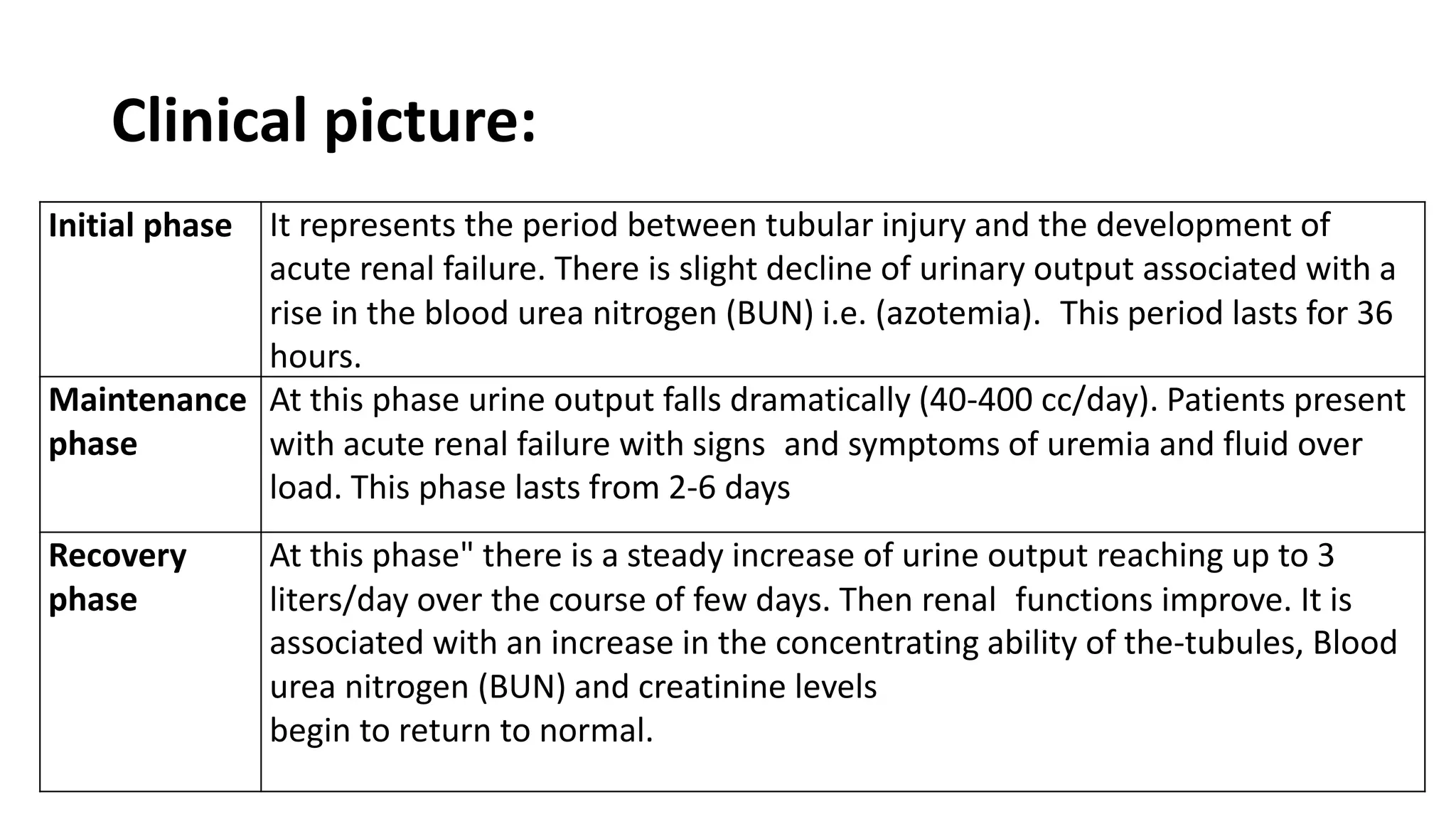
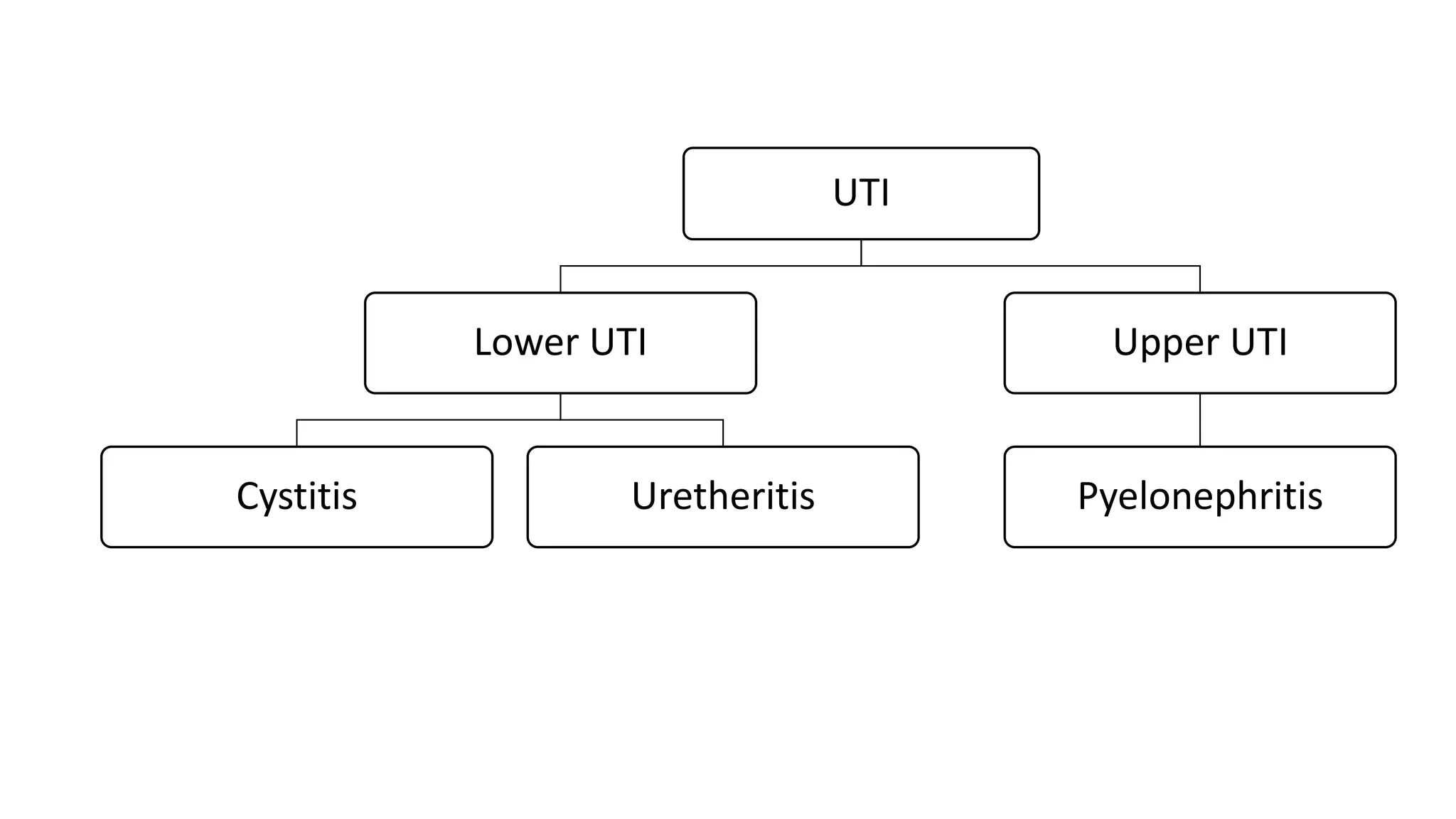
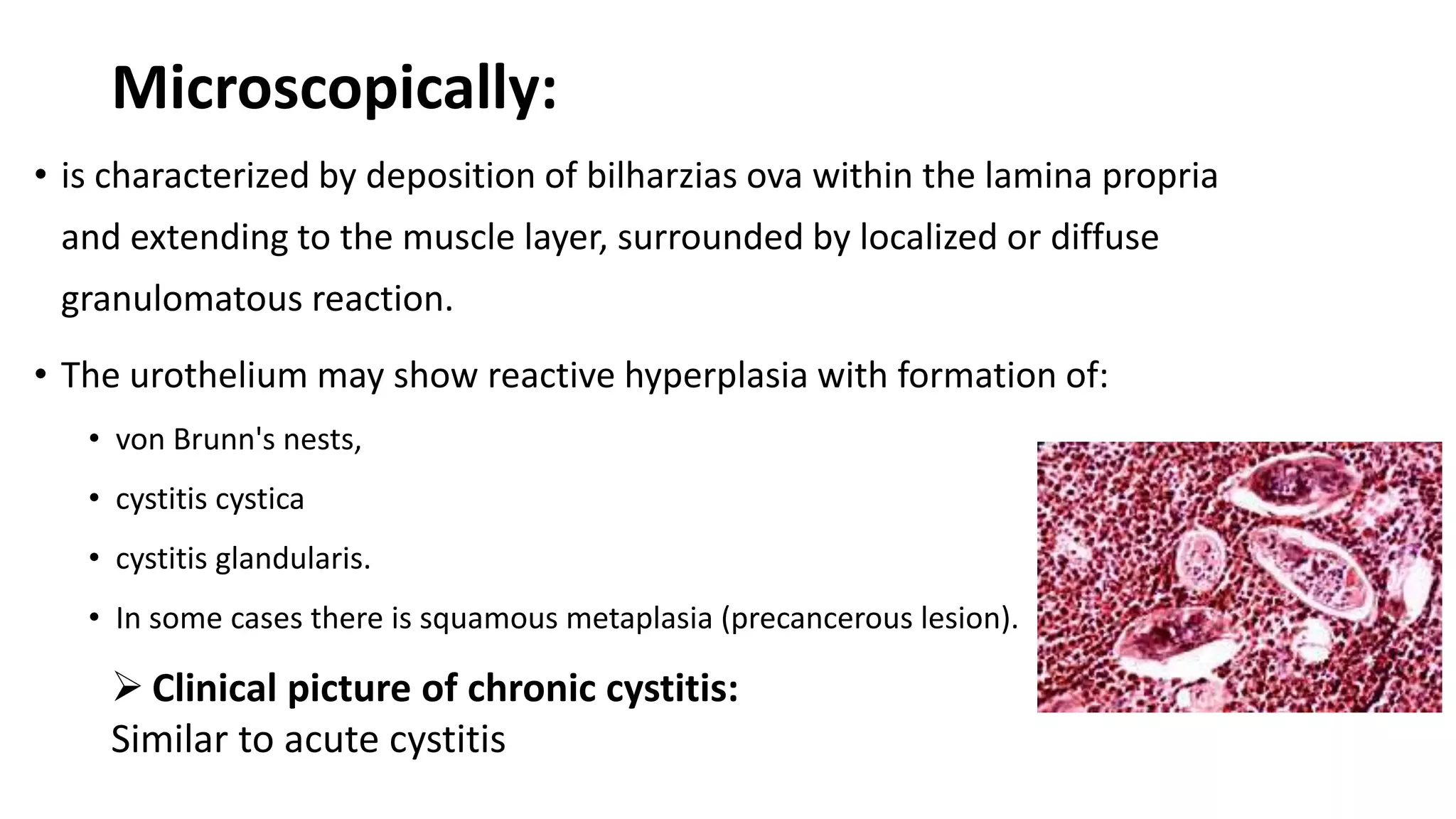
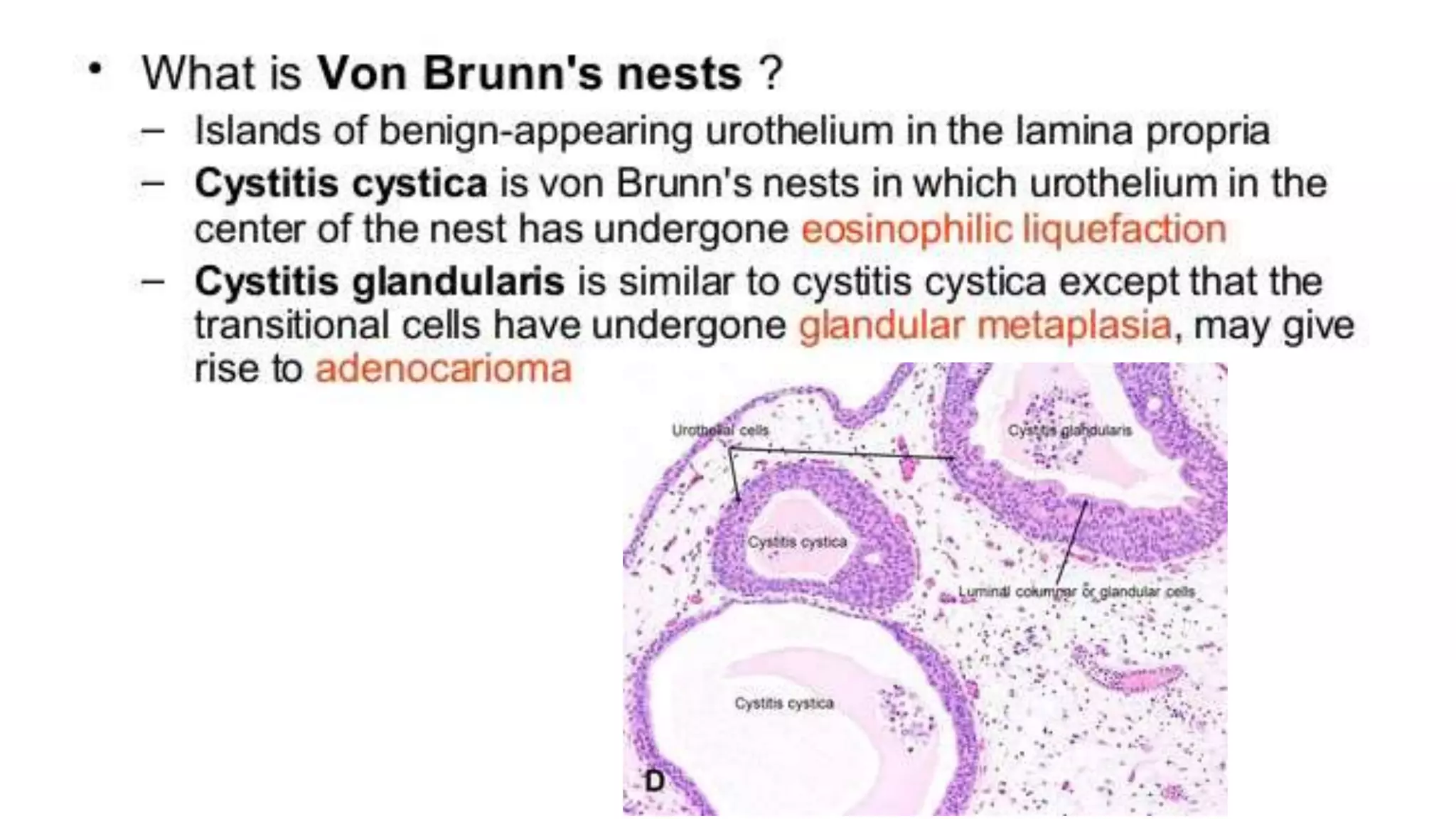
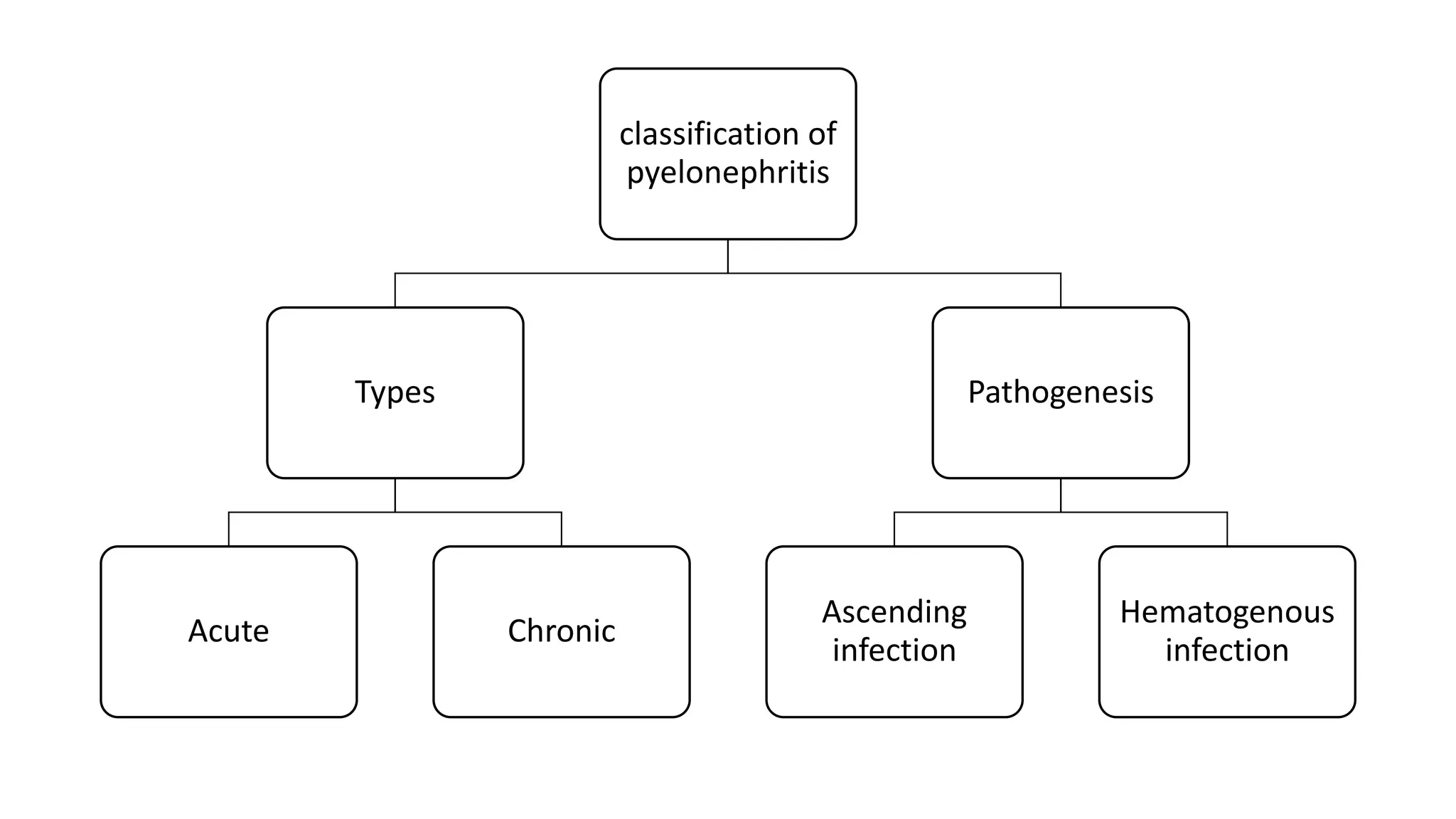
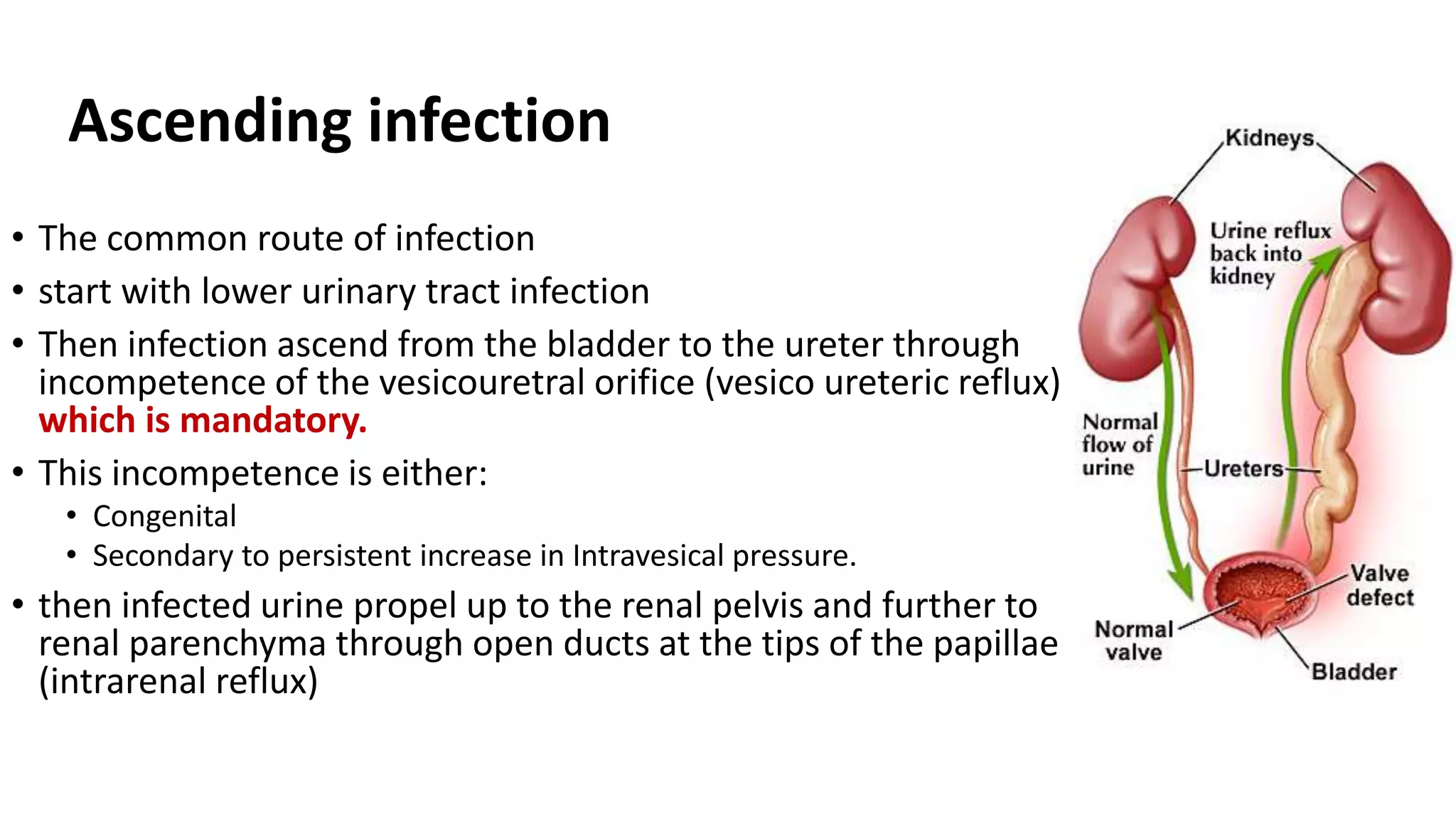
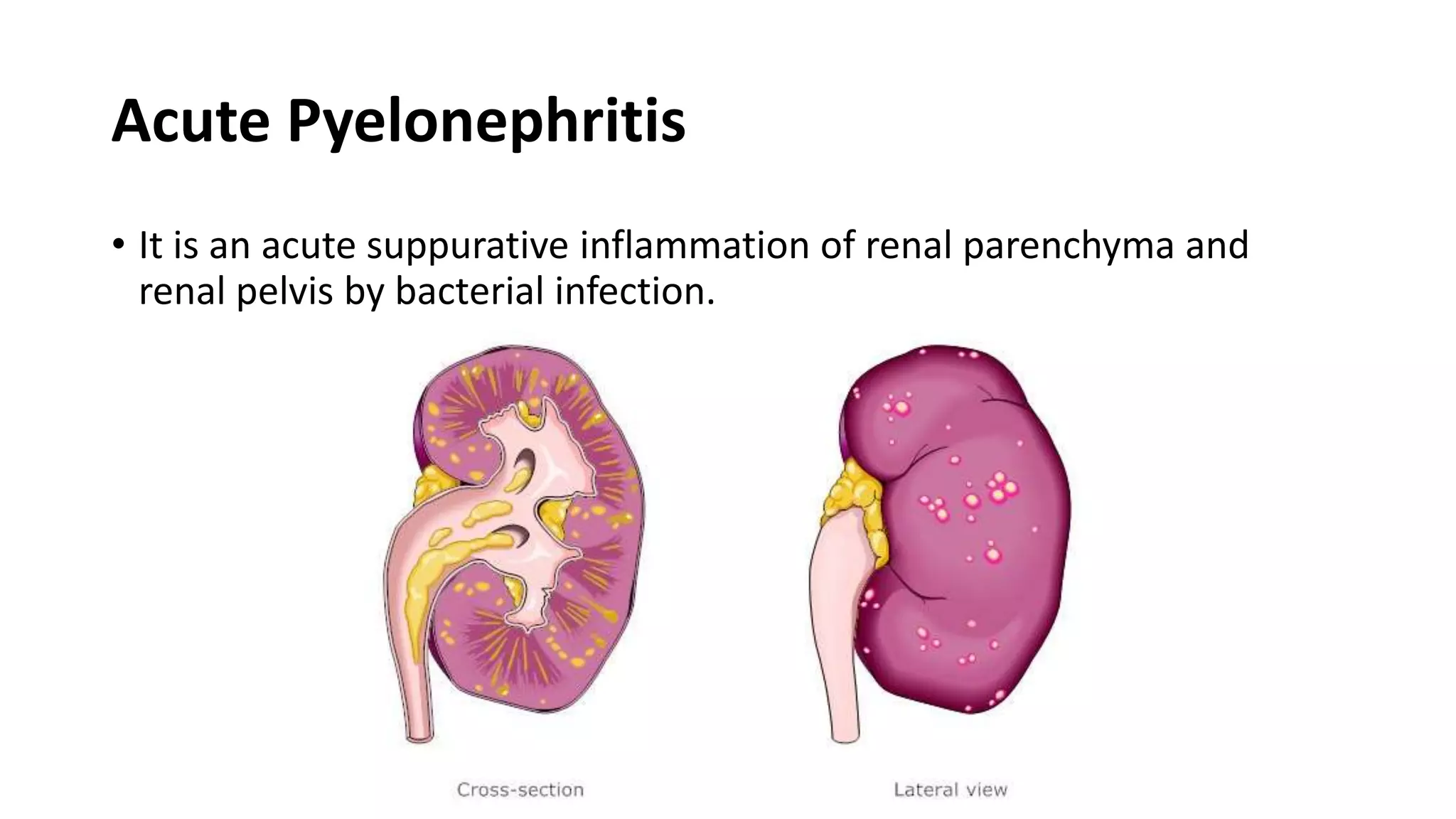
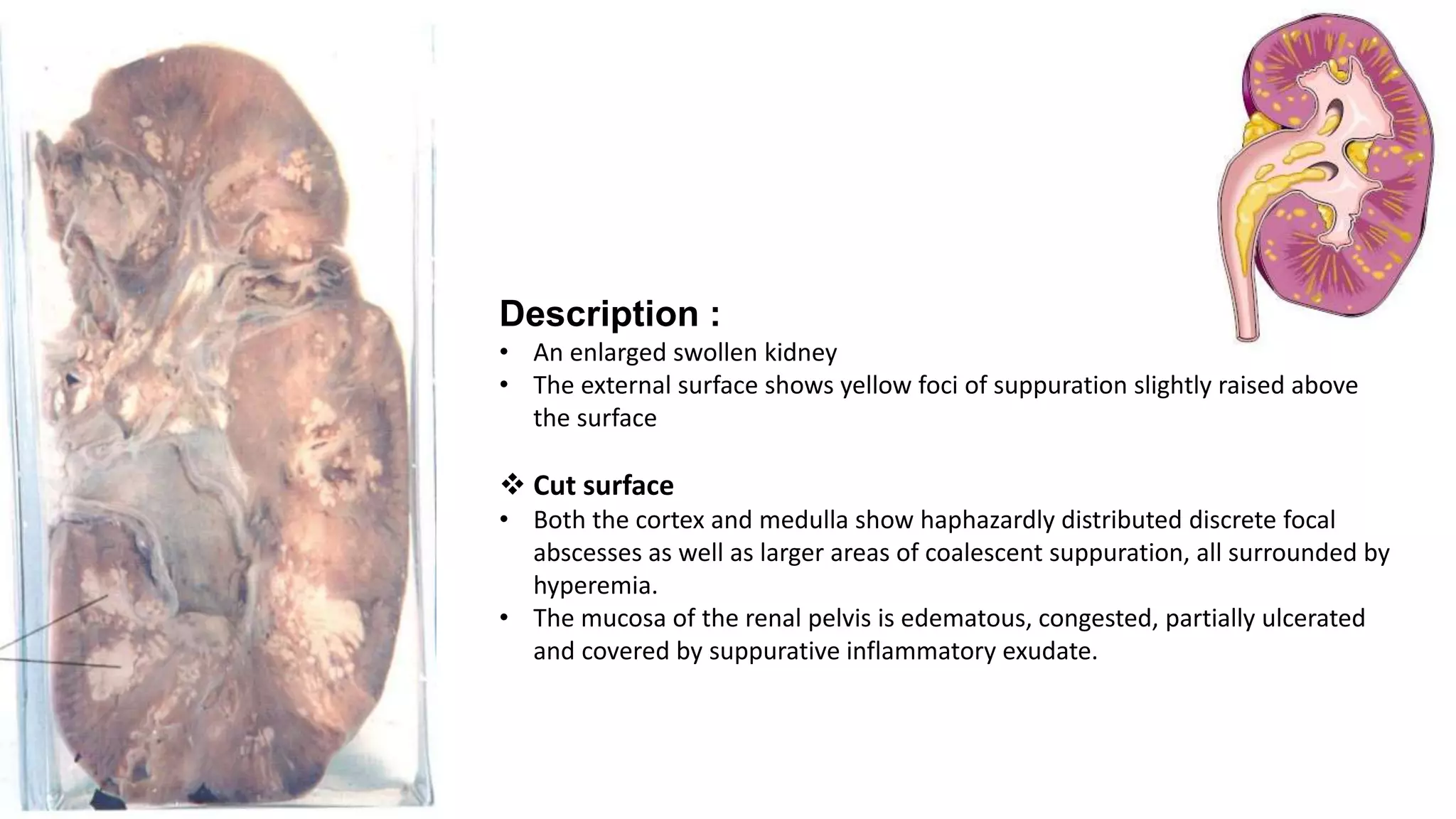
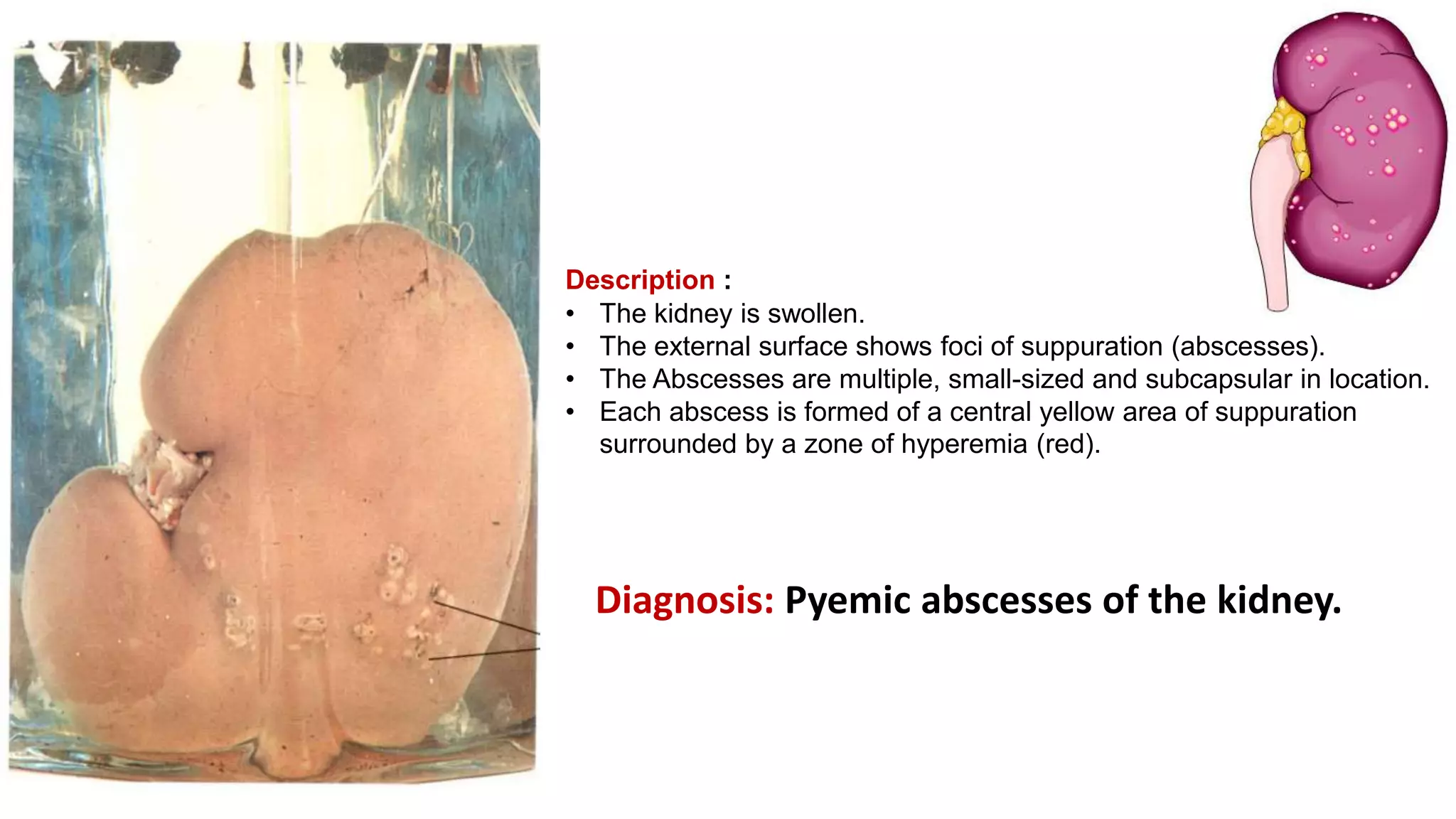
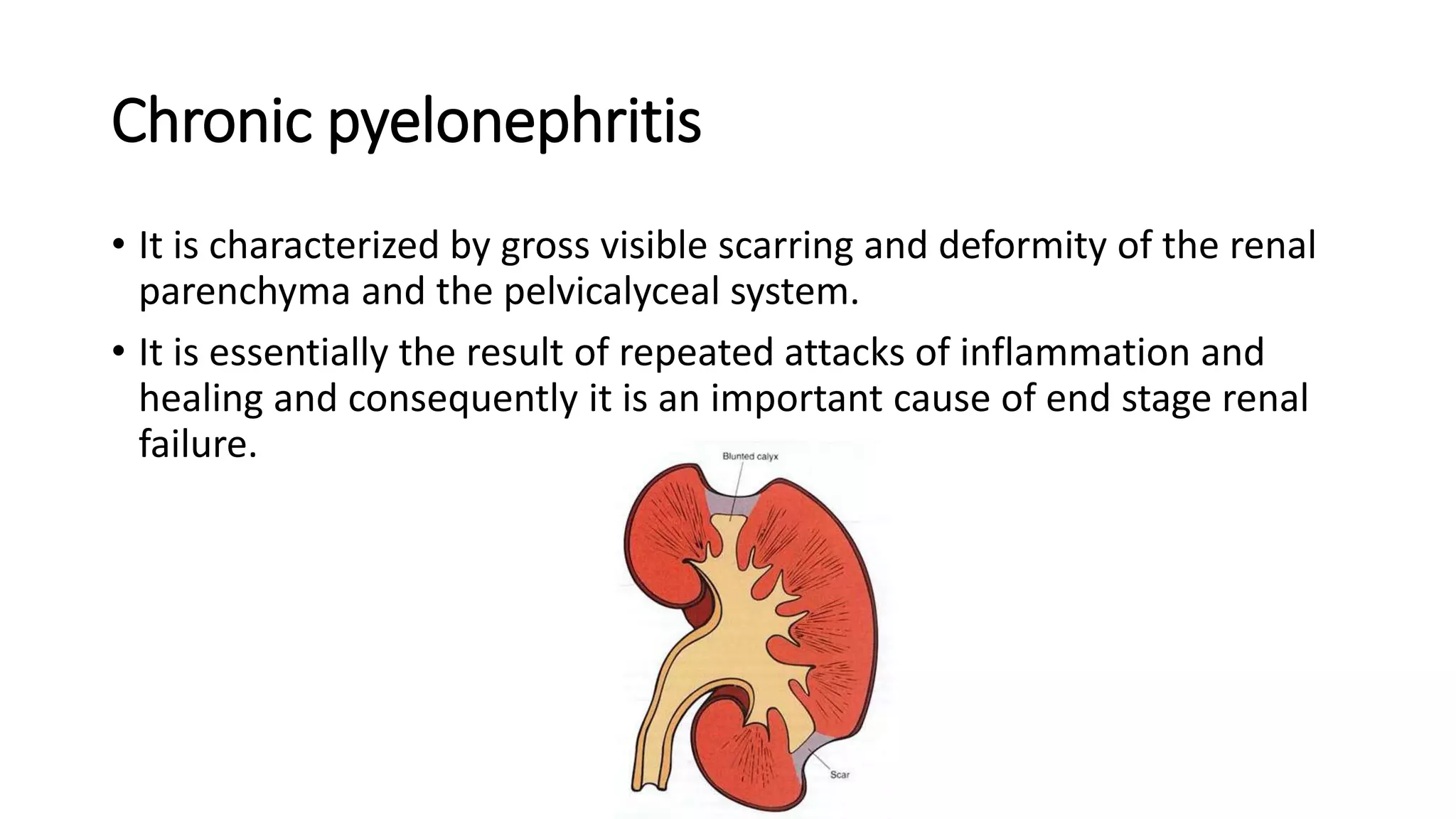
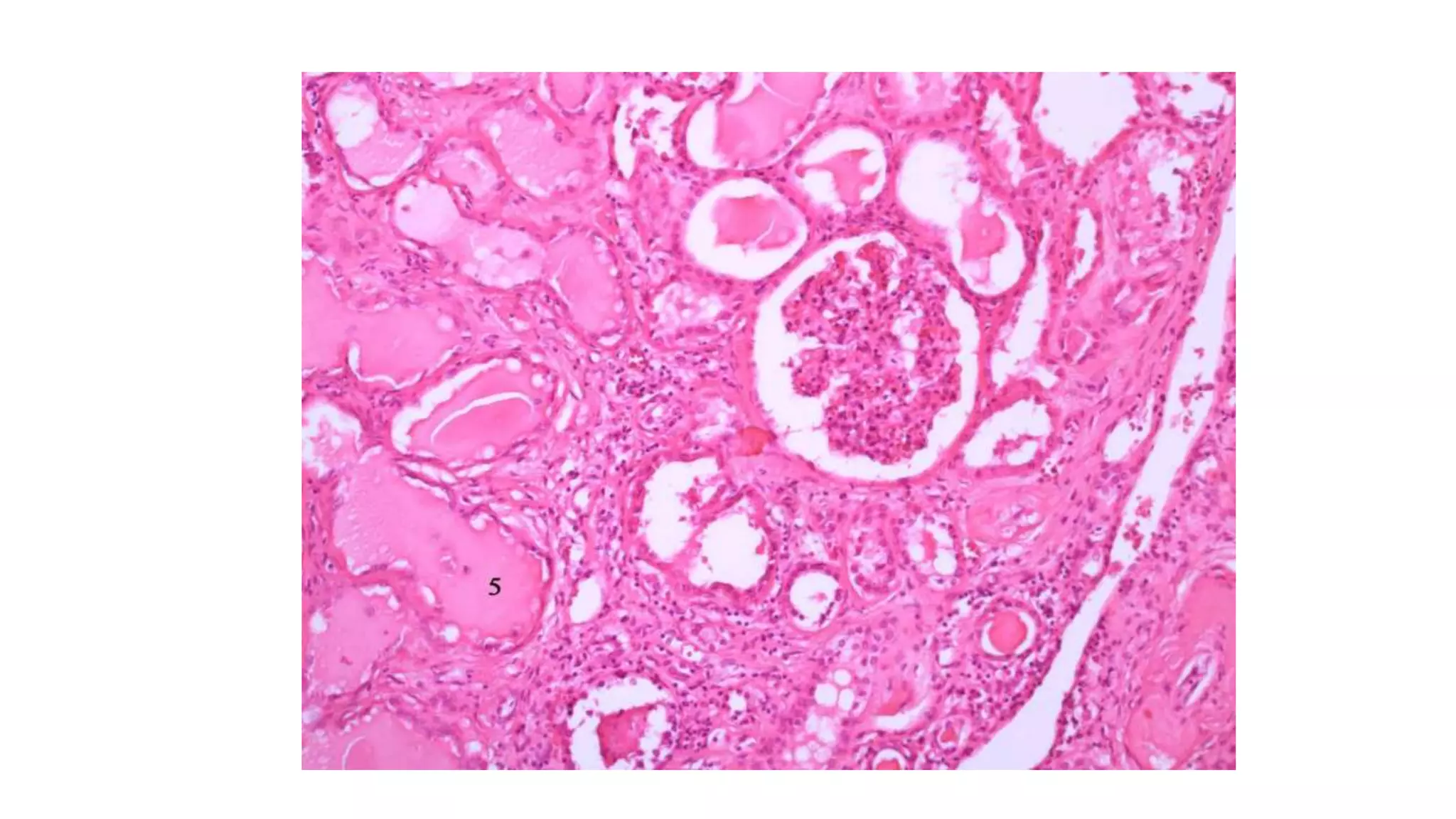
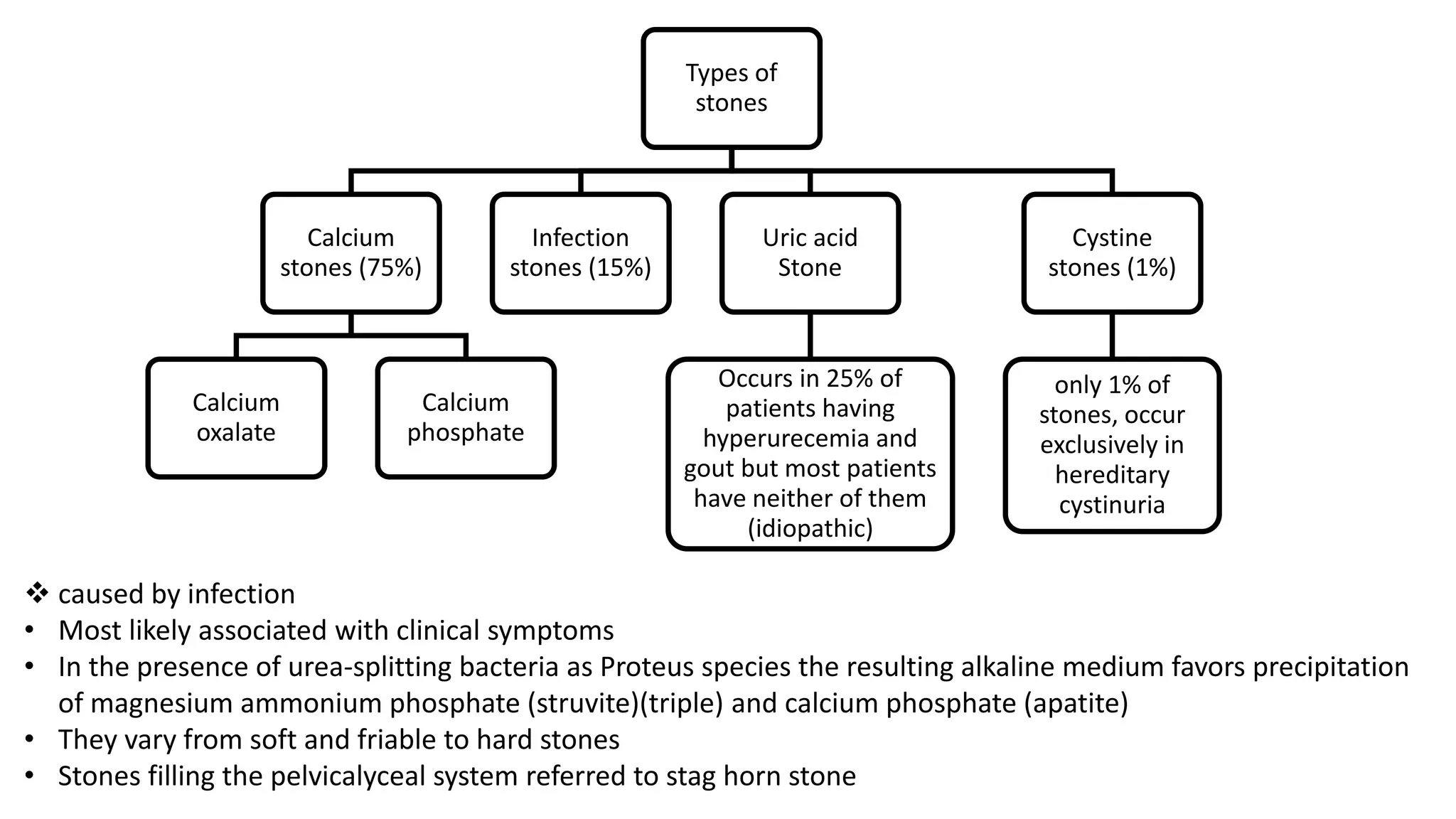
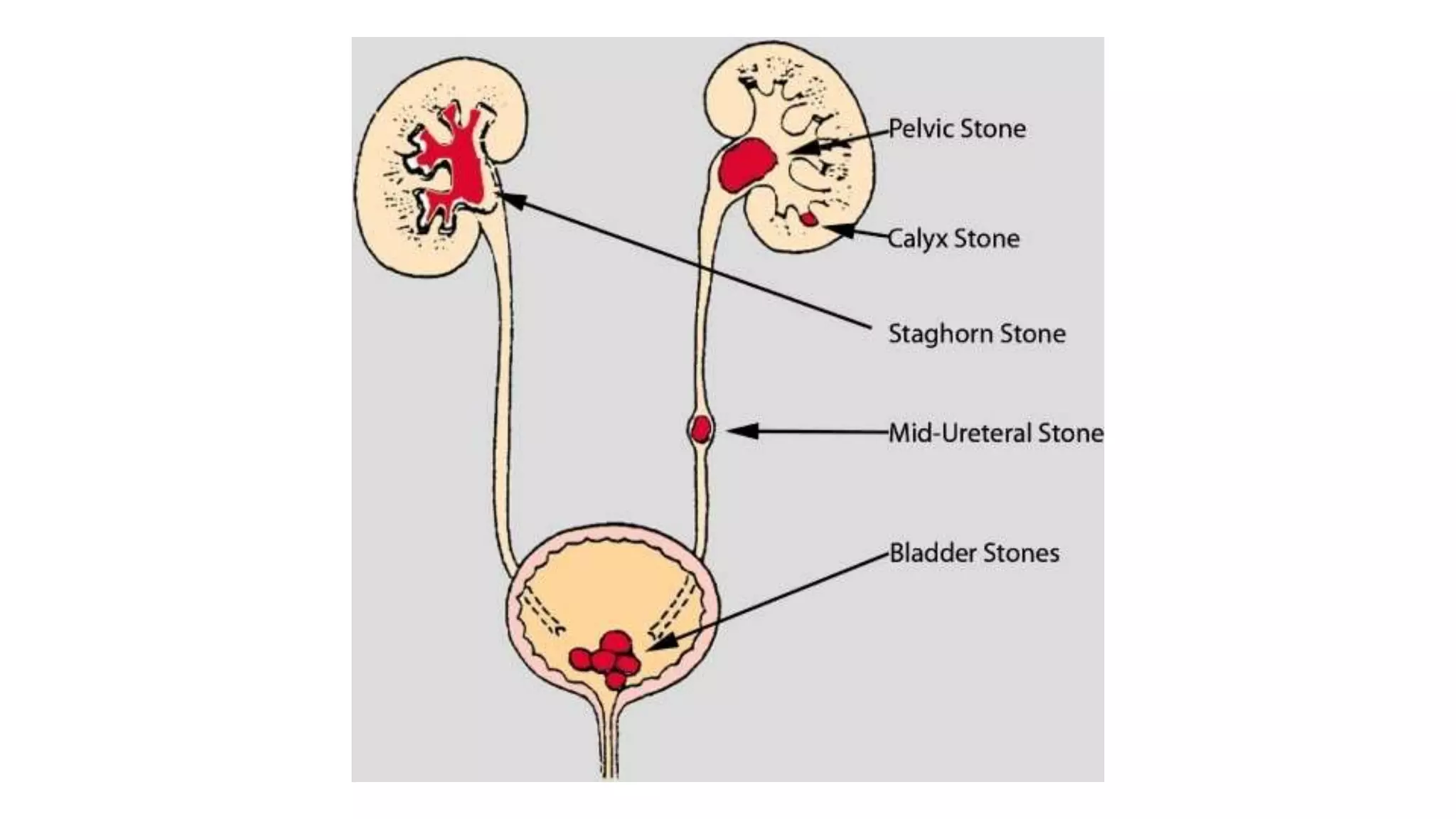
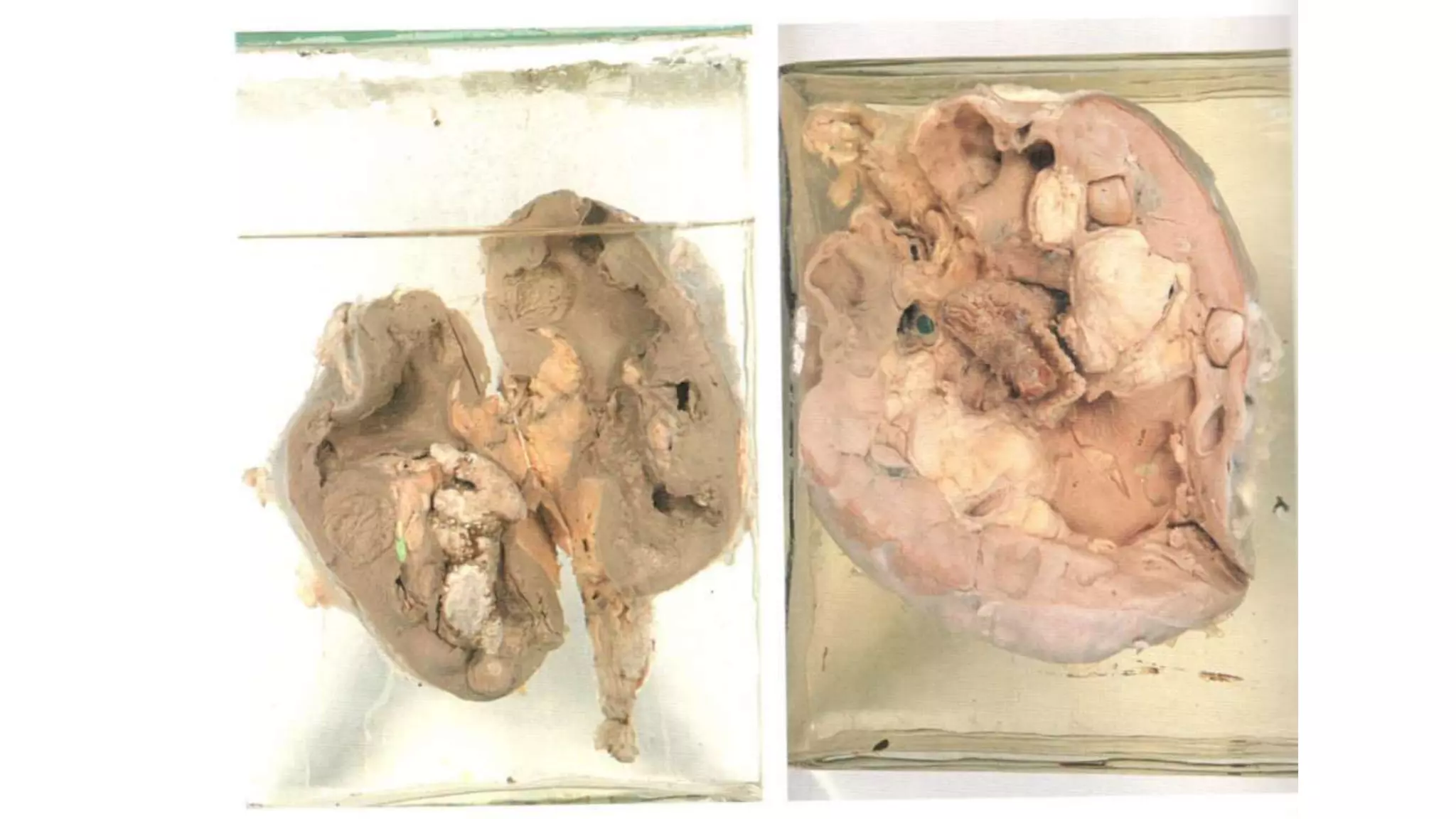
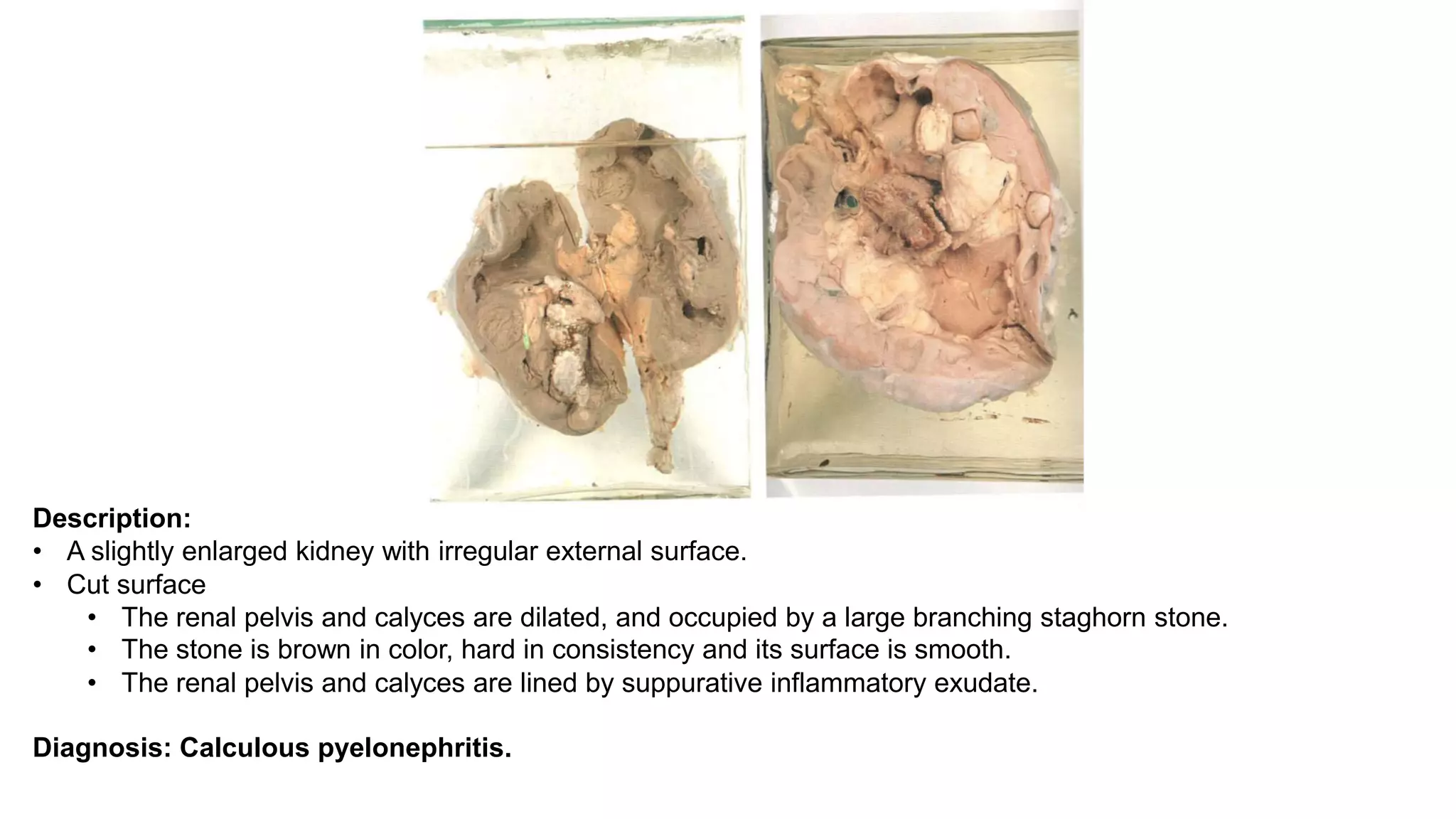
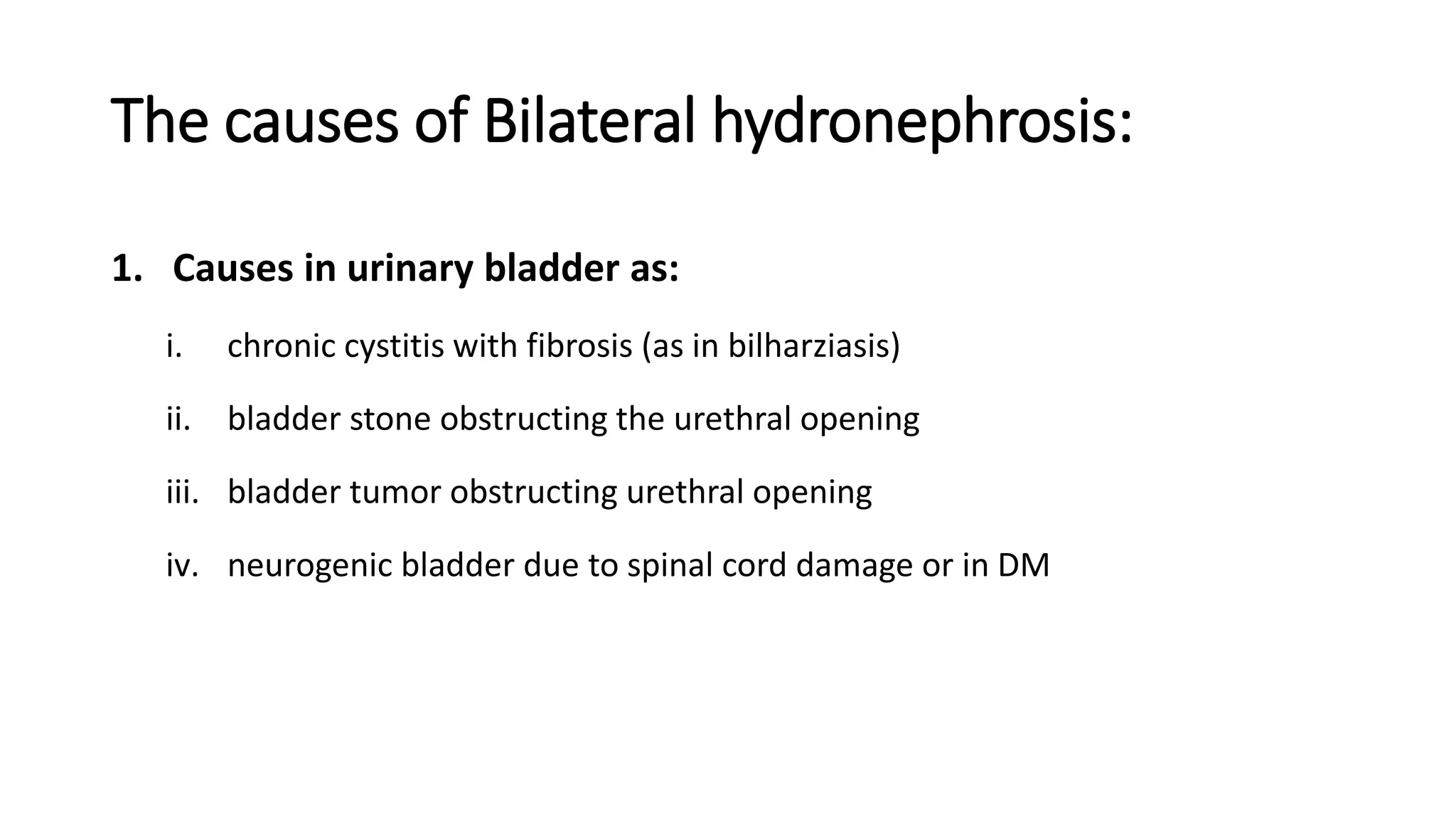
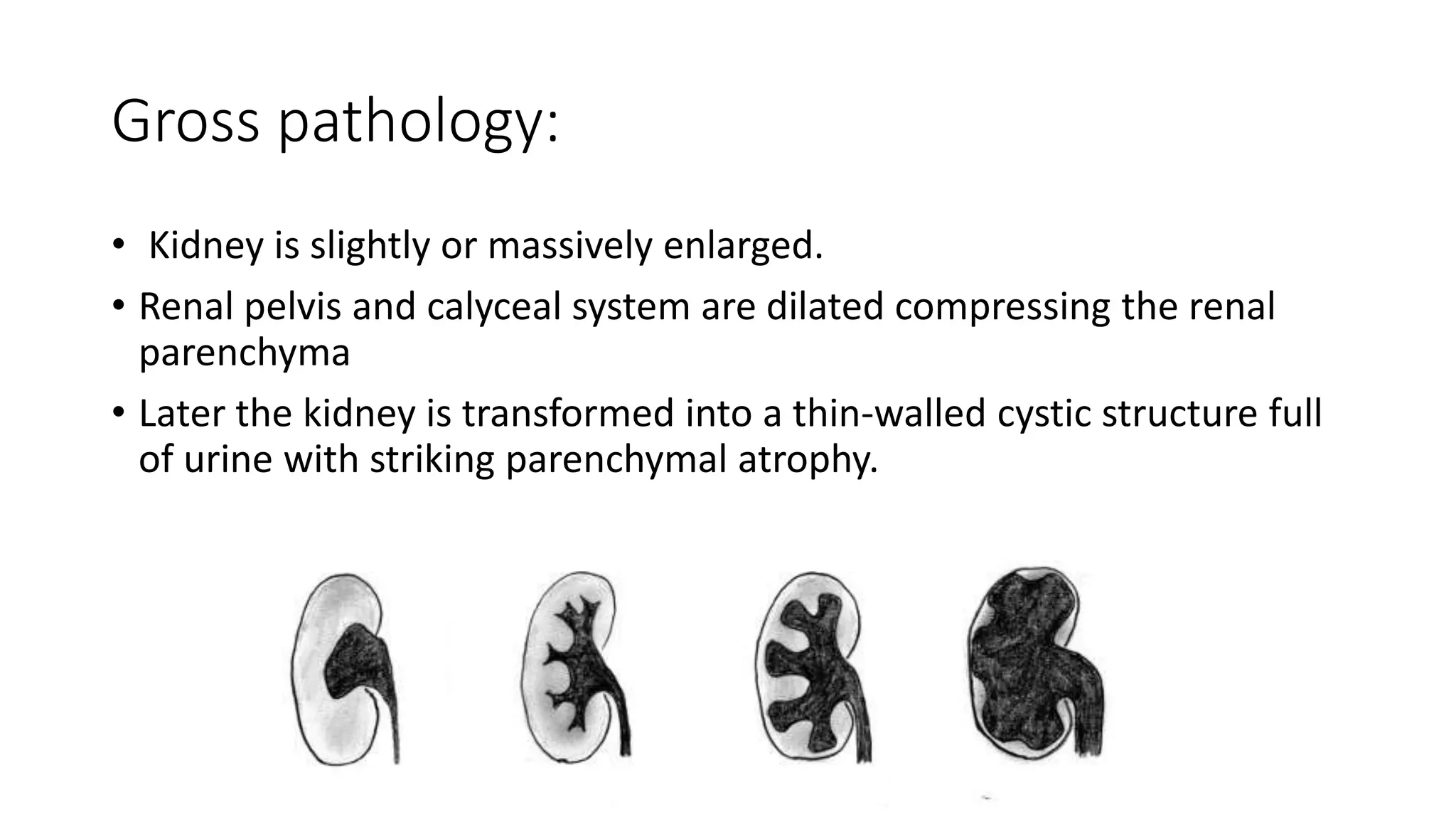
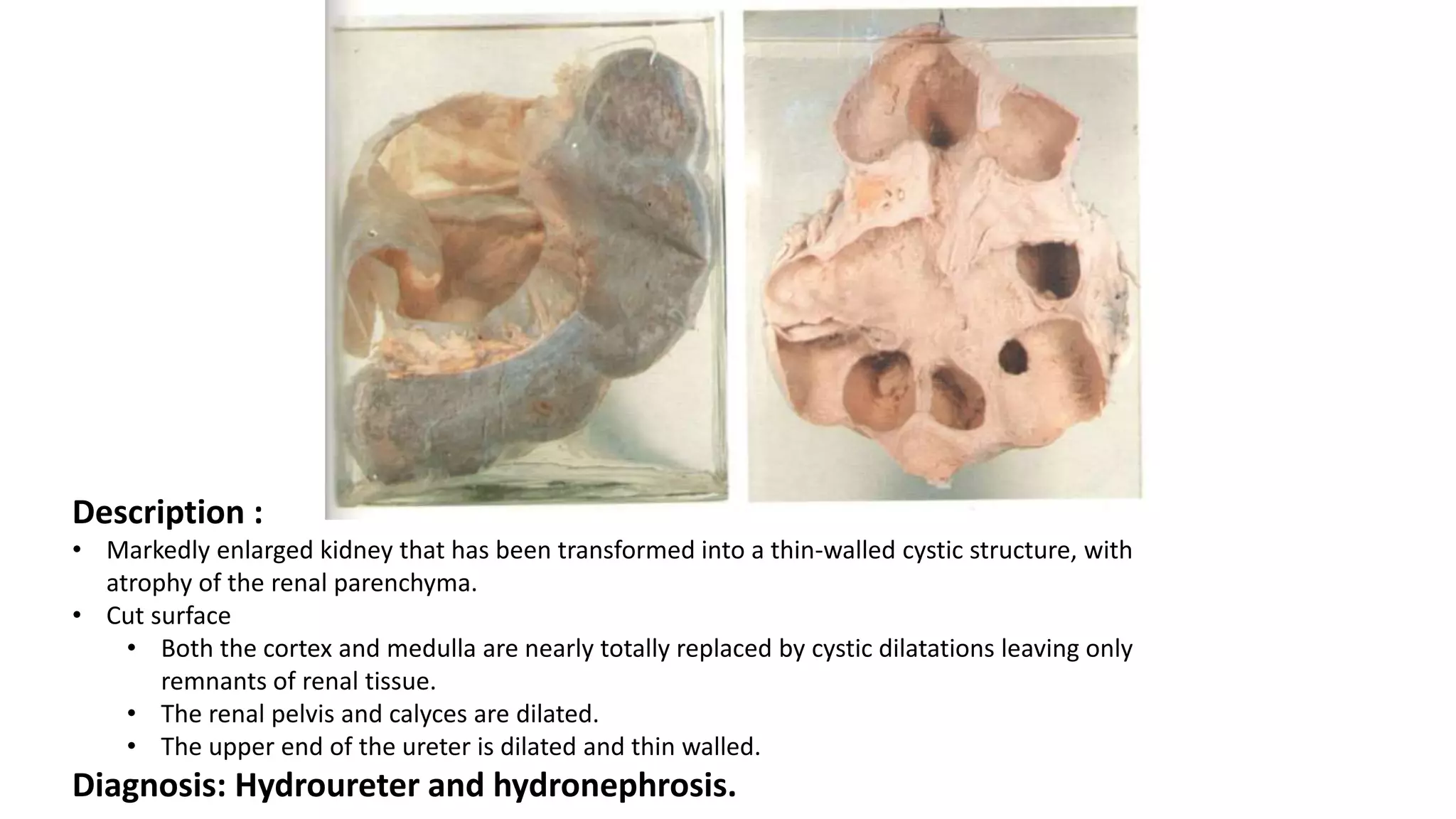
Renal pathology involves the study of the kidney and its structures. Glomerular injury can present as selective or non-selective proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, hematuria, nephritic syndrome, or rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by heavy proteinuria, hypoproteinemia, edema, and hyperlipidemia. Nephritic syndrome presents with hematuria, proteinuria, oliguria, azotemia, and hypertension. Glomerulonephritis can result from immune complex deposition, antibody-mediated injury, cell-mediated immunity, or complement activation. Both immune and non-immune mechanisms can lead to glomerular damage.






















































































![Classifications
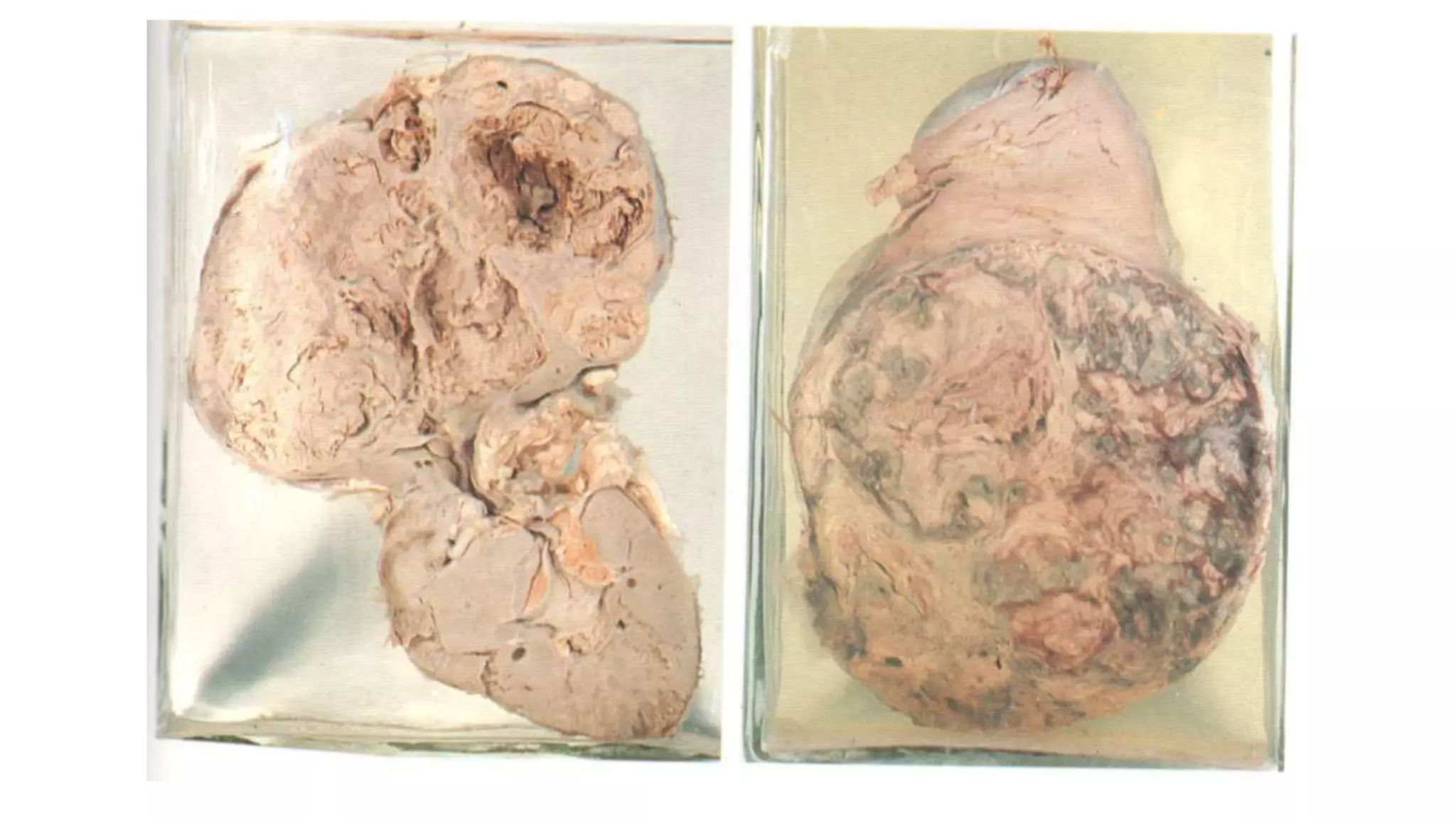
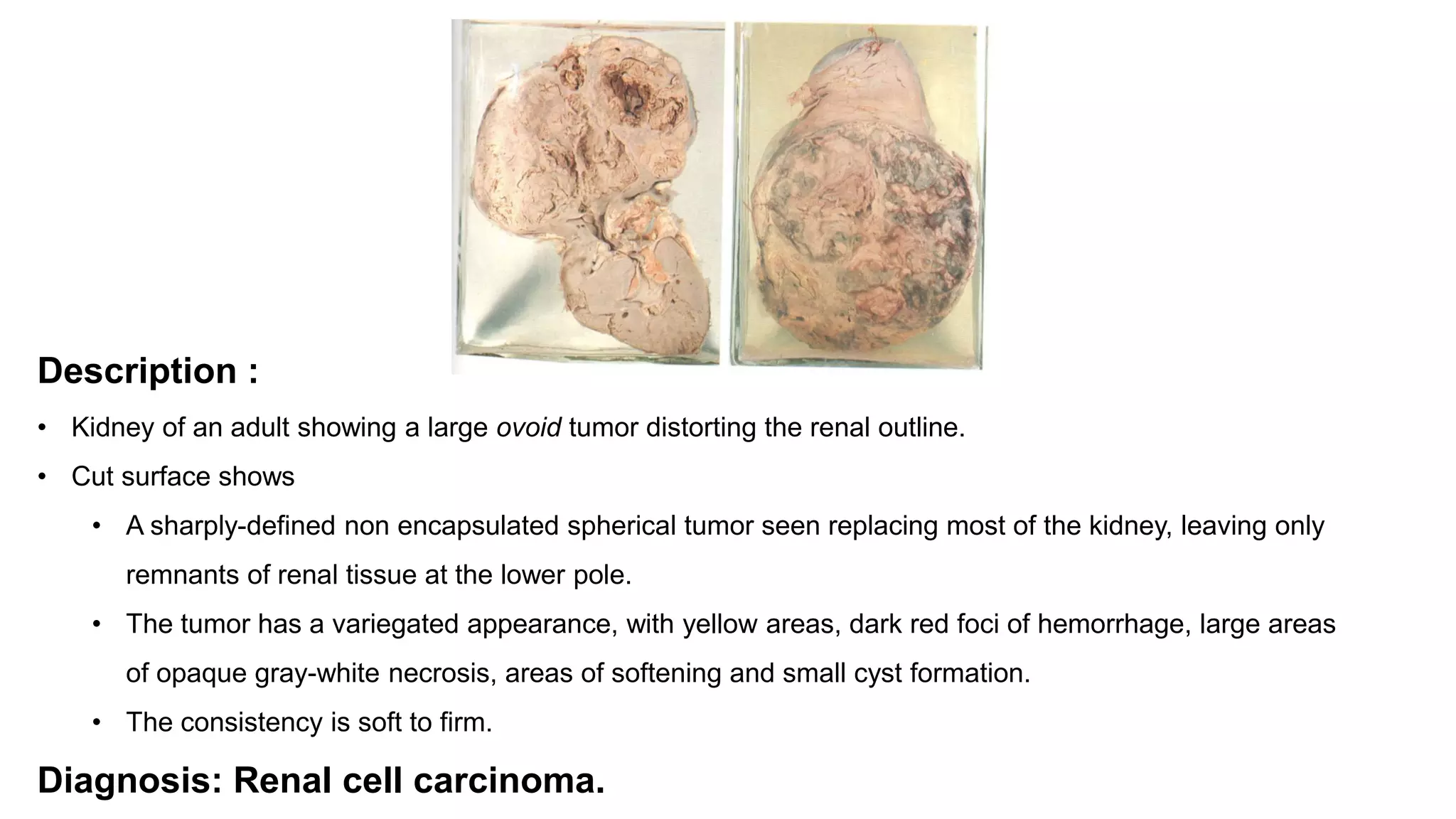
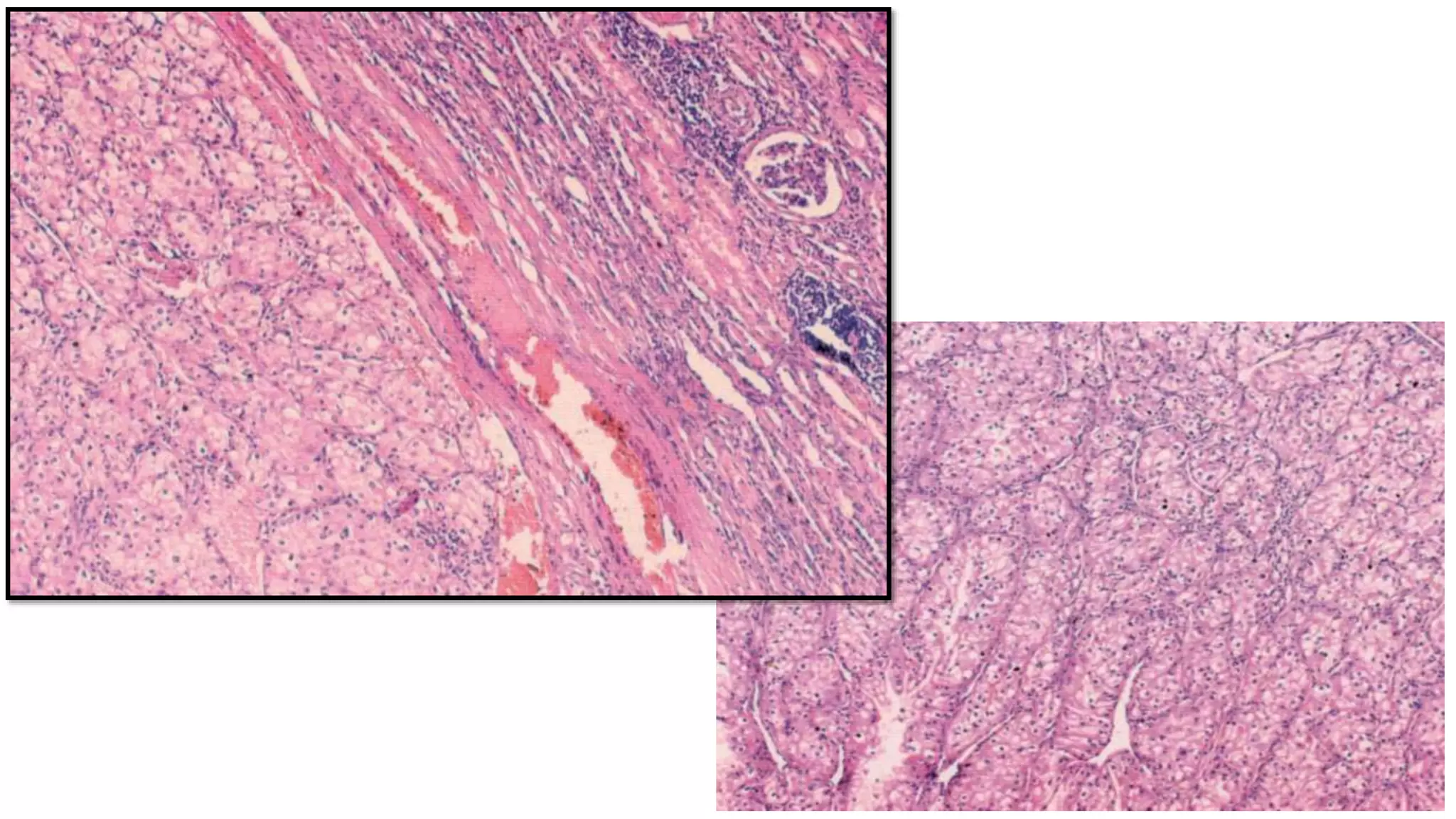
Tumors of renal
parenchyma
Benign "rare"
Oncocytoma Angiolipoma
Malignant
Renal cell
carcinoma
[hypernephroma]
Nephroblastoma
[wilms tumor]
Tumors of renal
pelvis
Urothelial tumors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1upload-161220213343/75/Renal-pathology-version-5-174-2048.jpg)