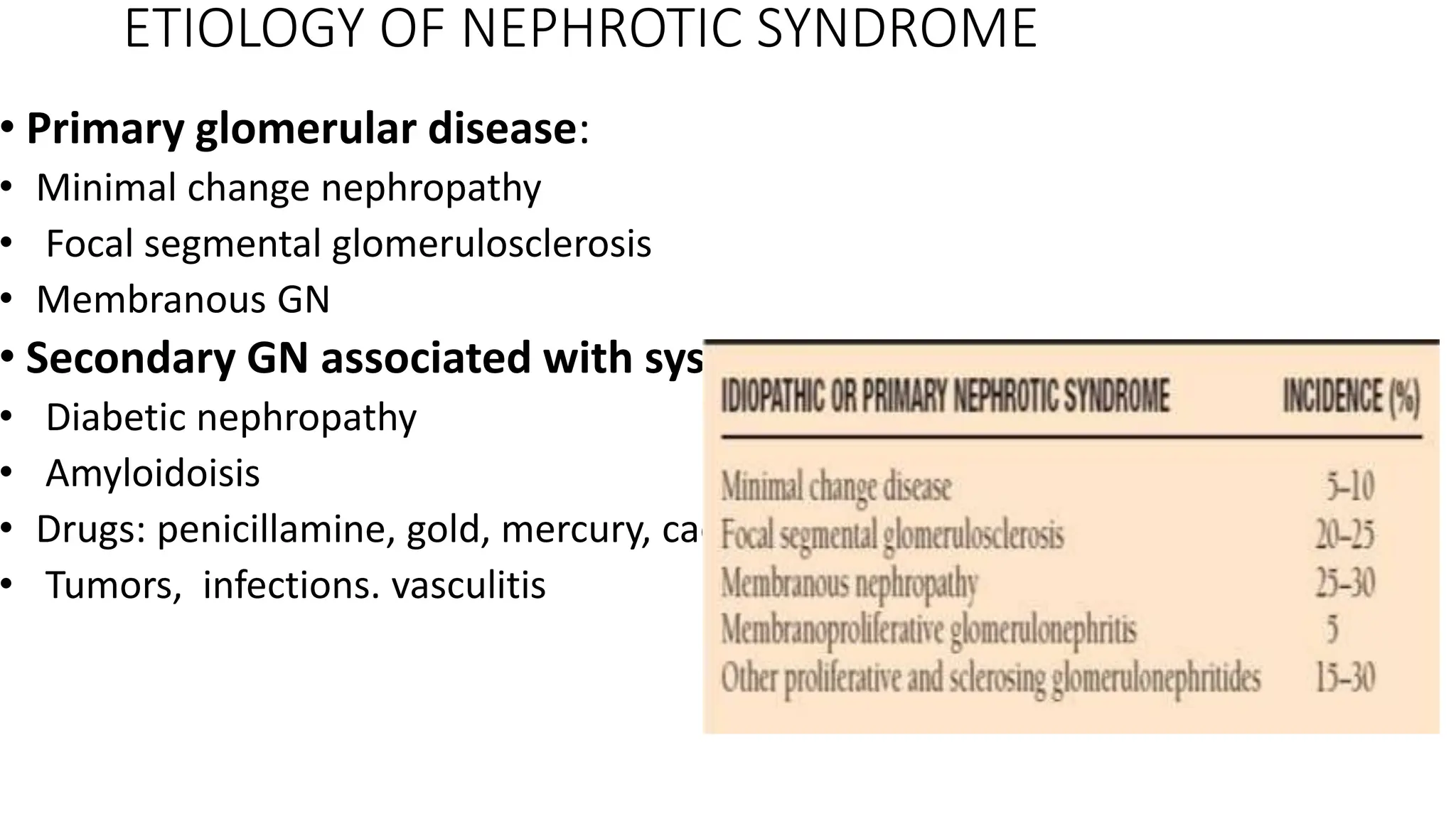
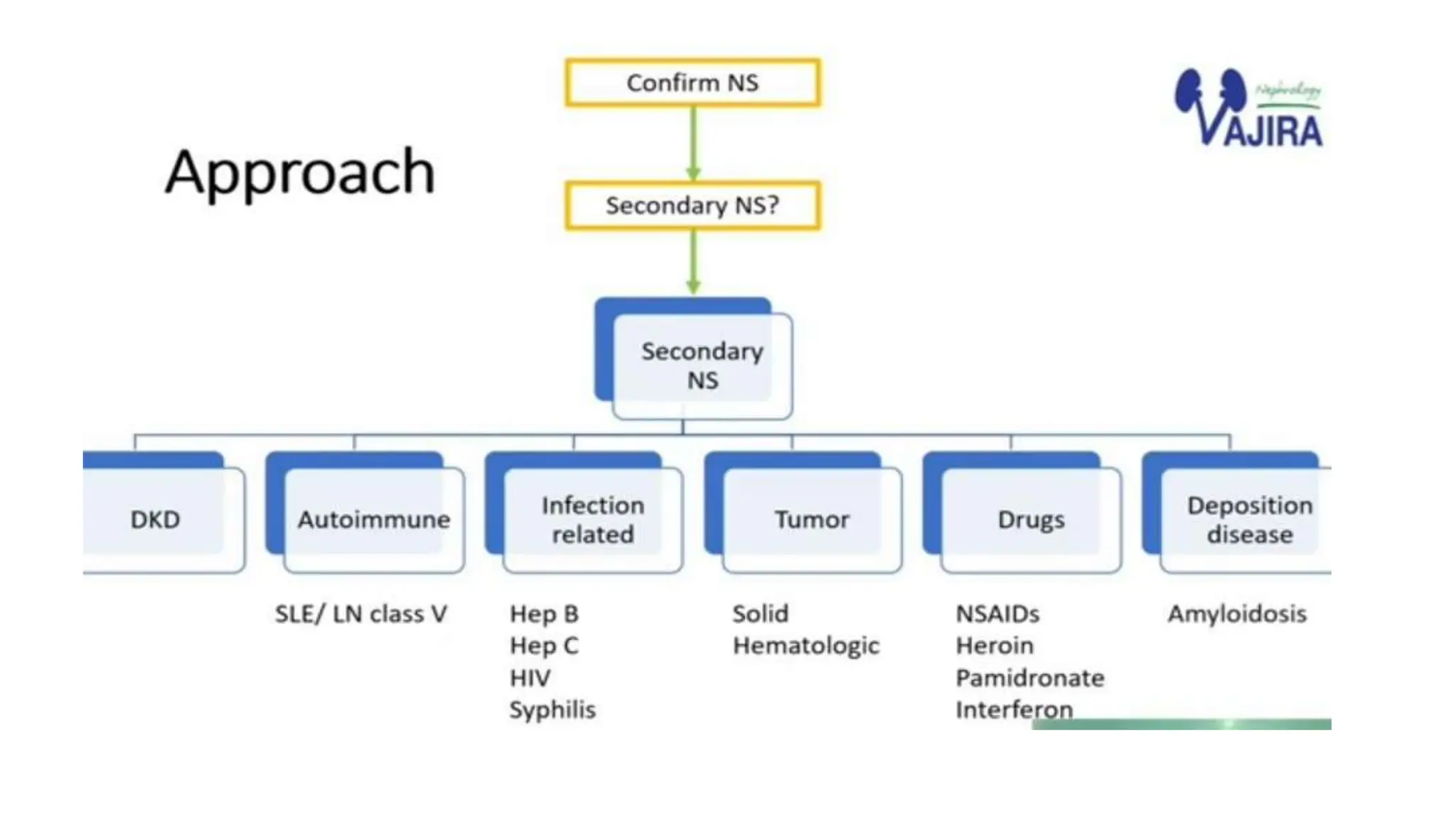
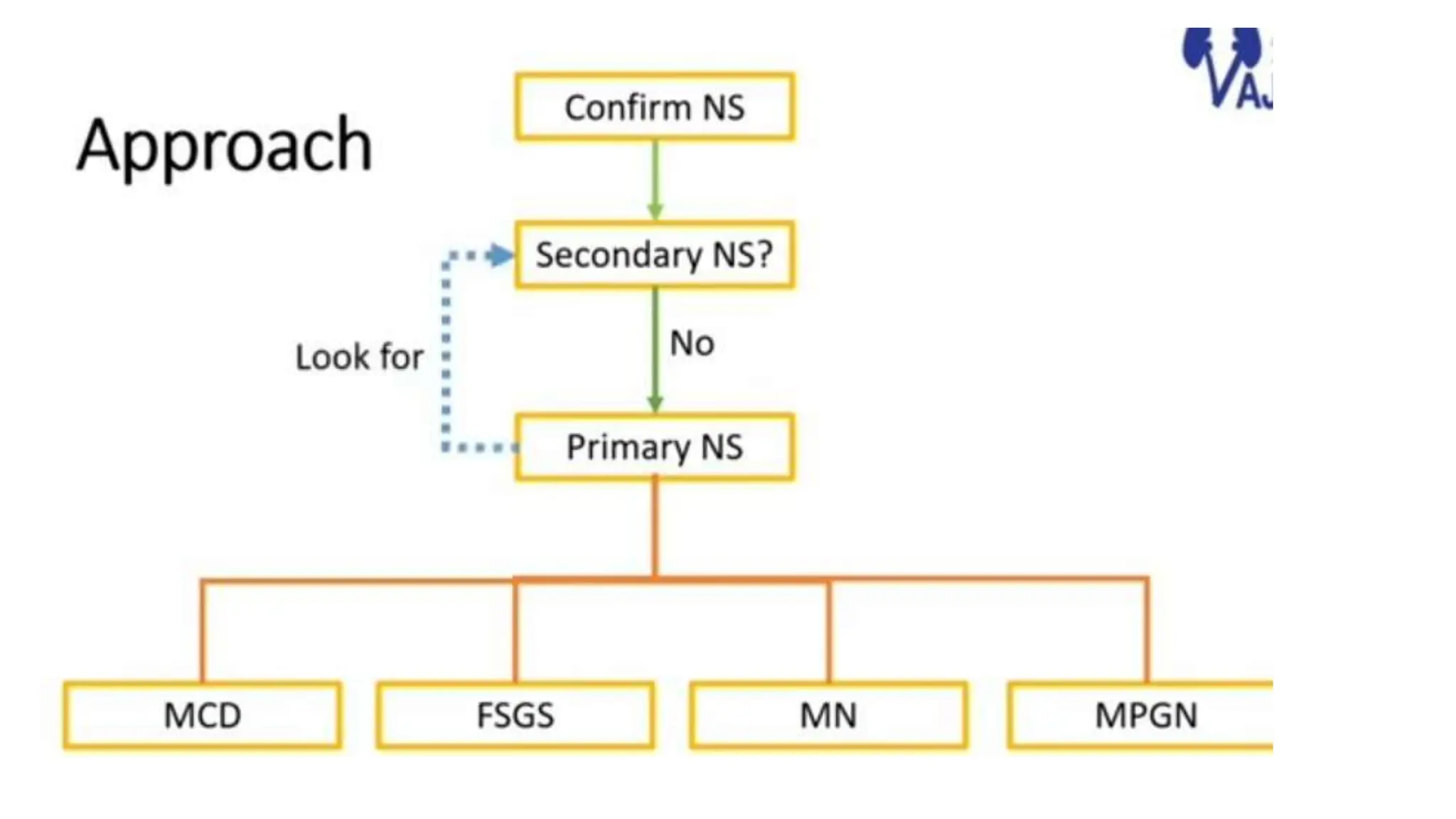
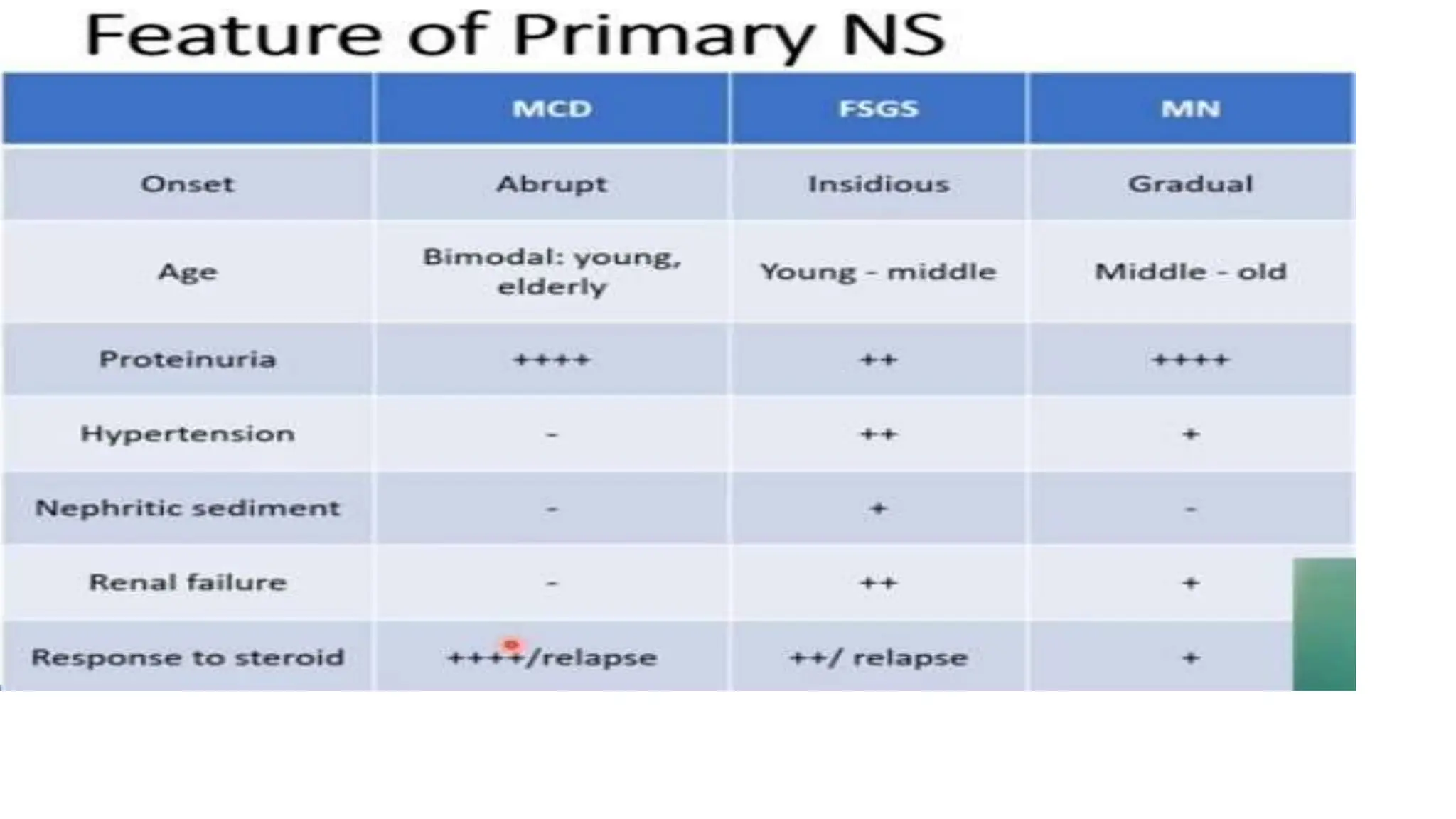
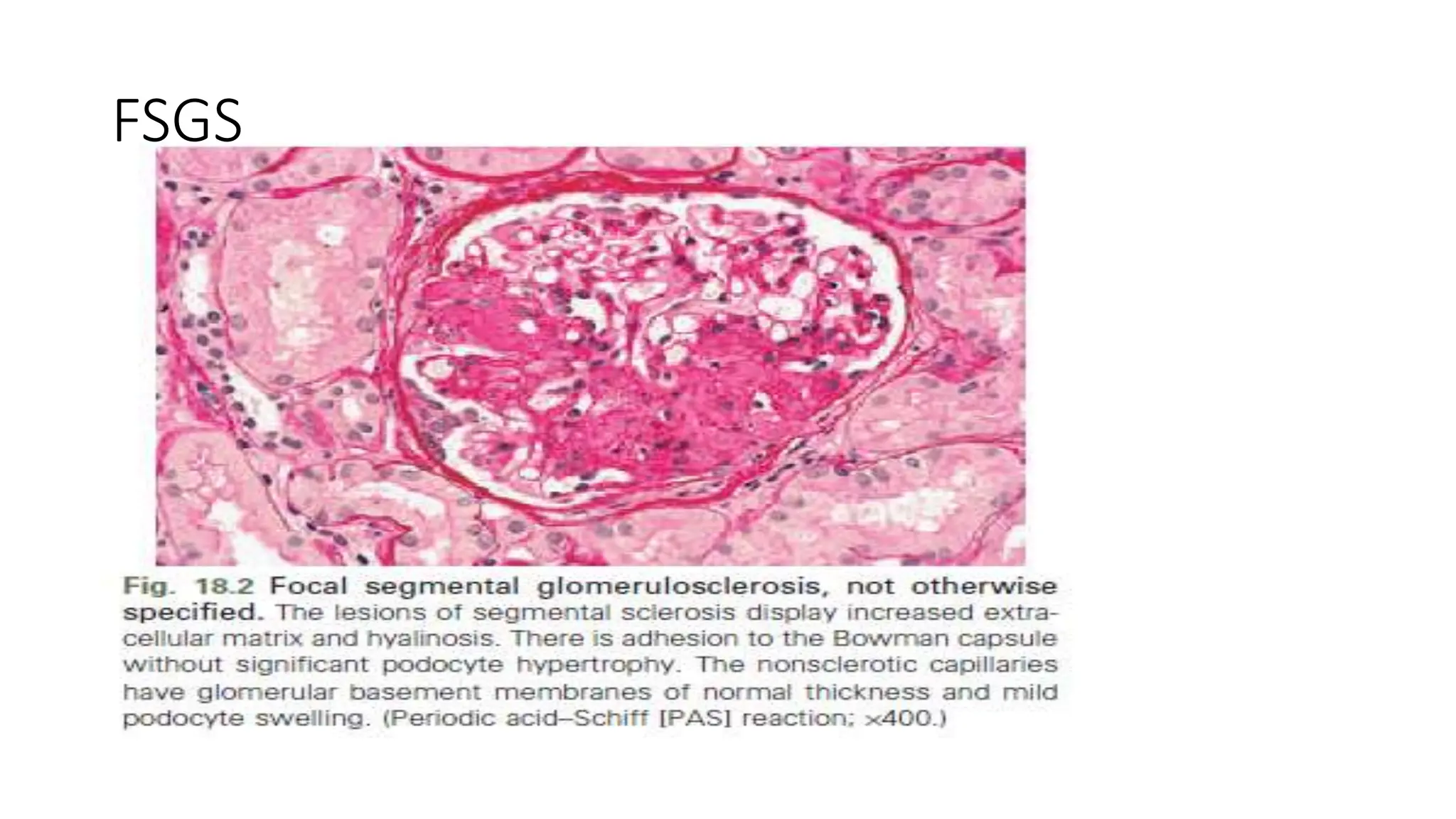
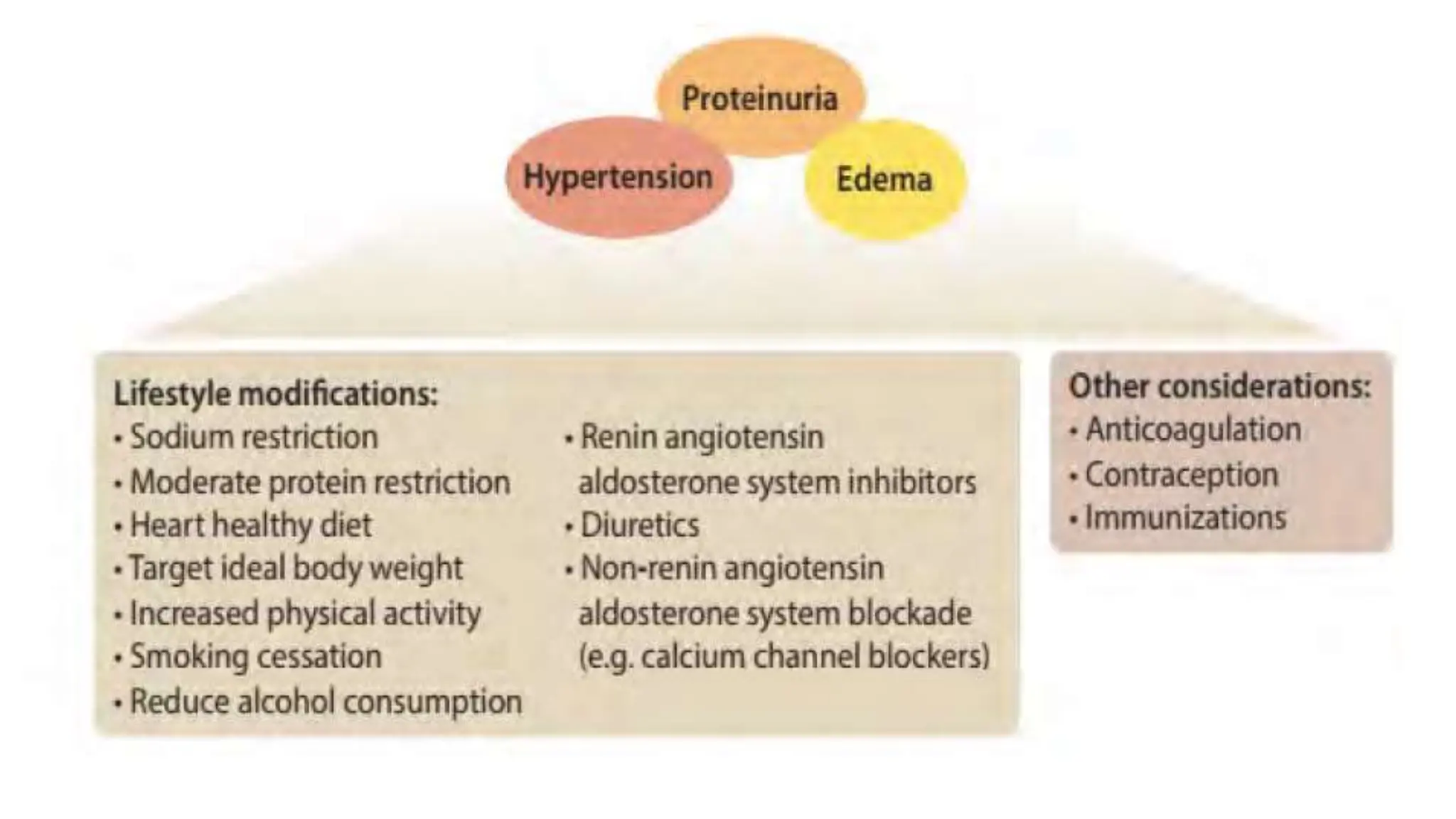
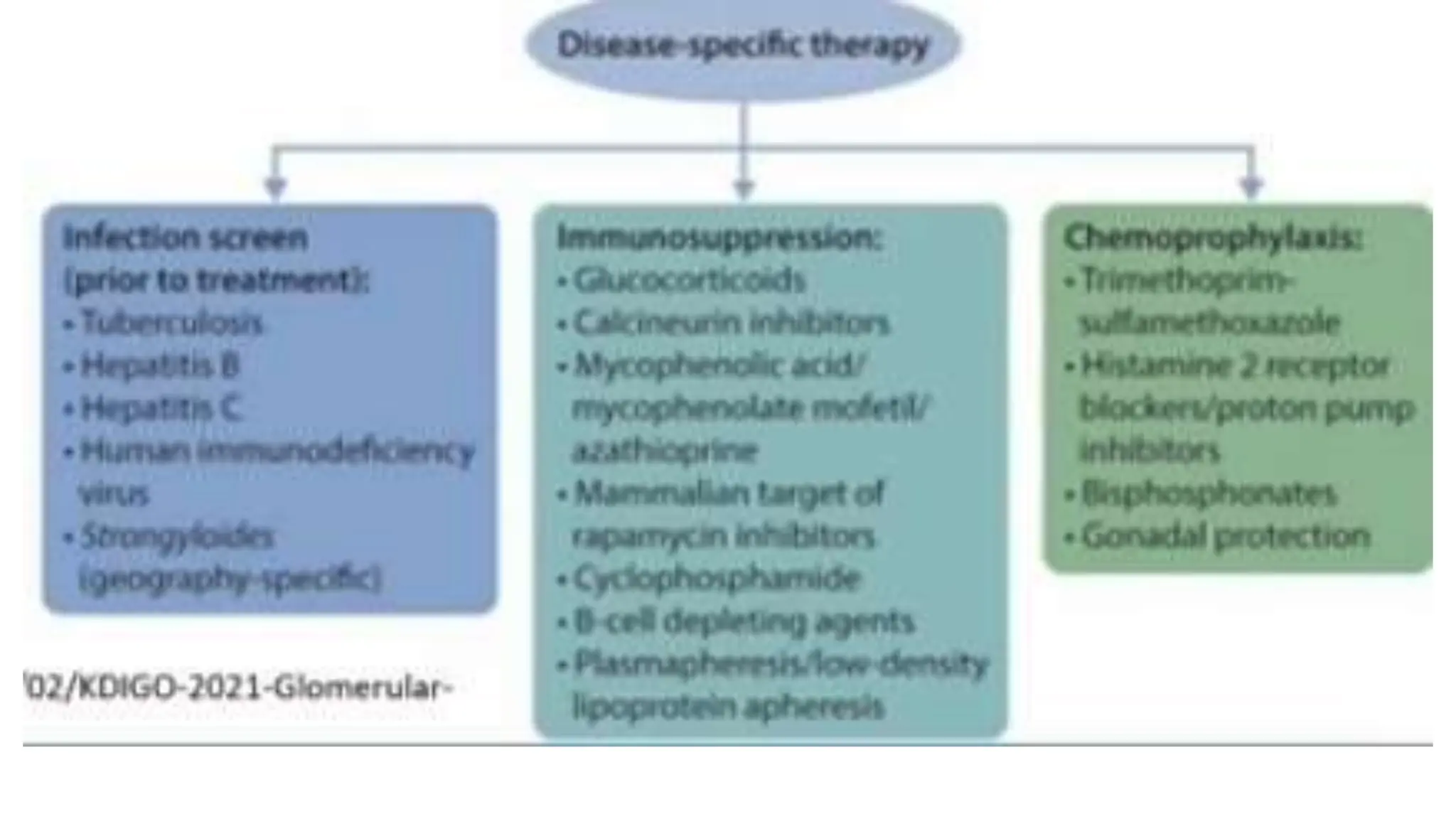
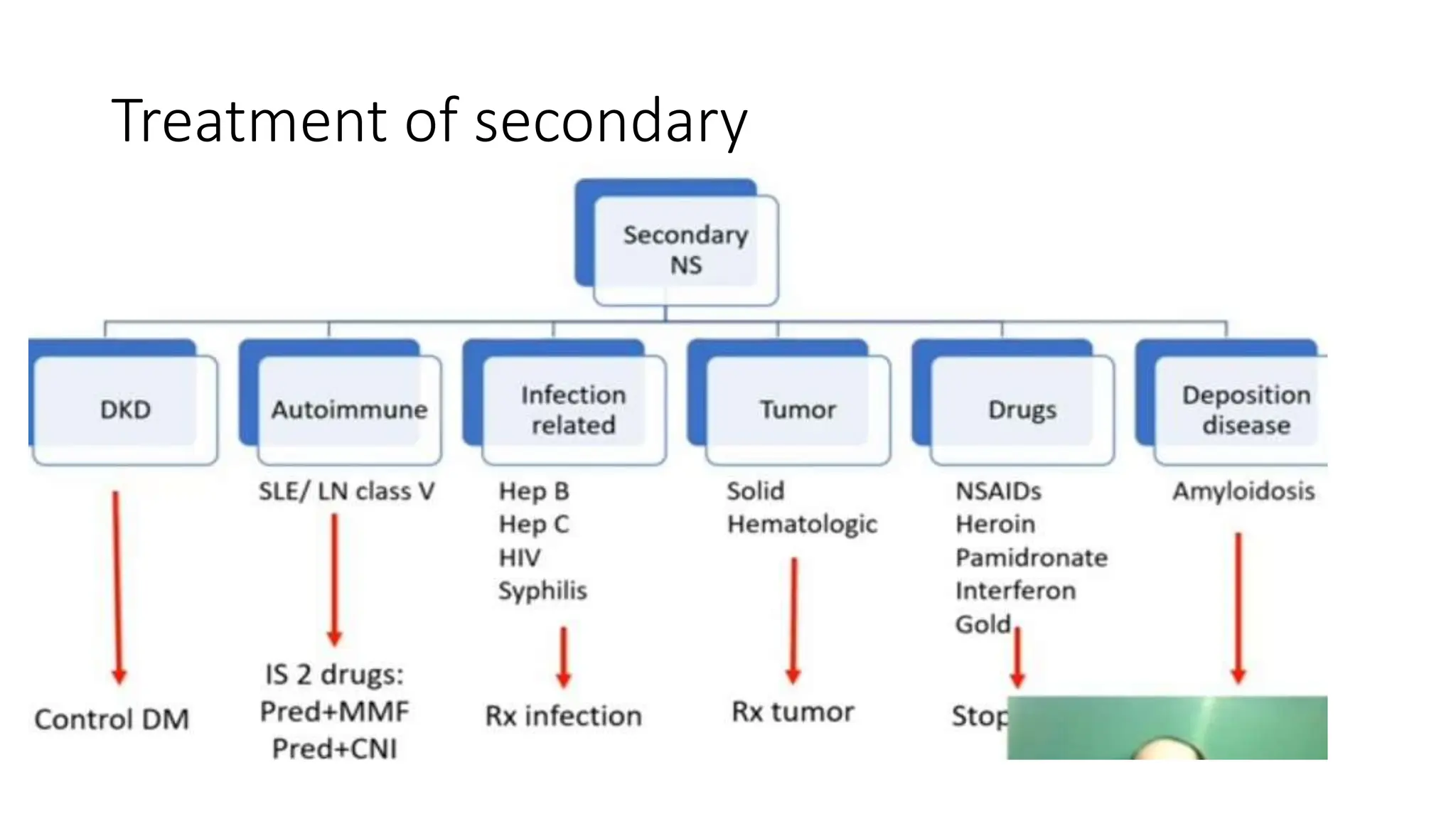
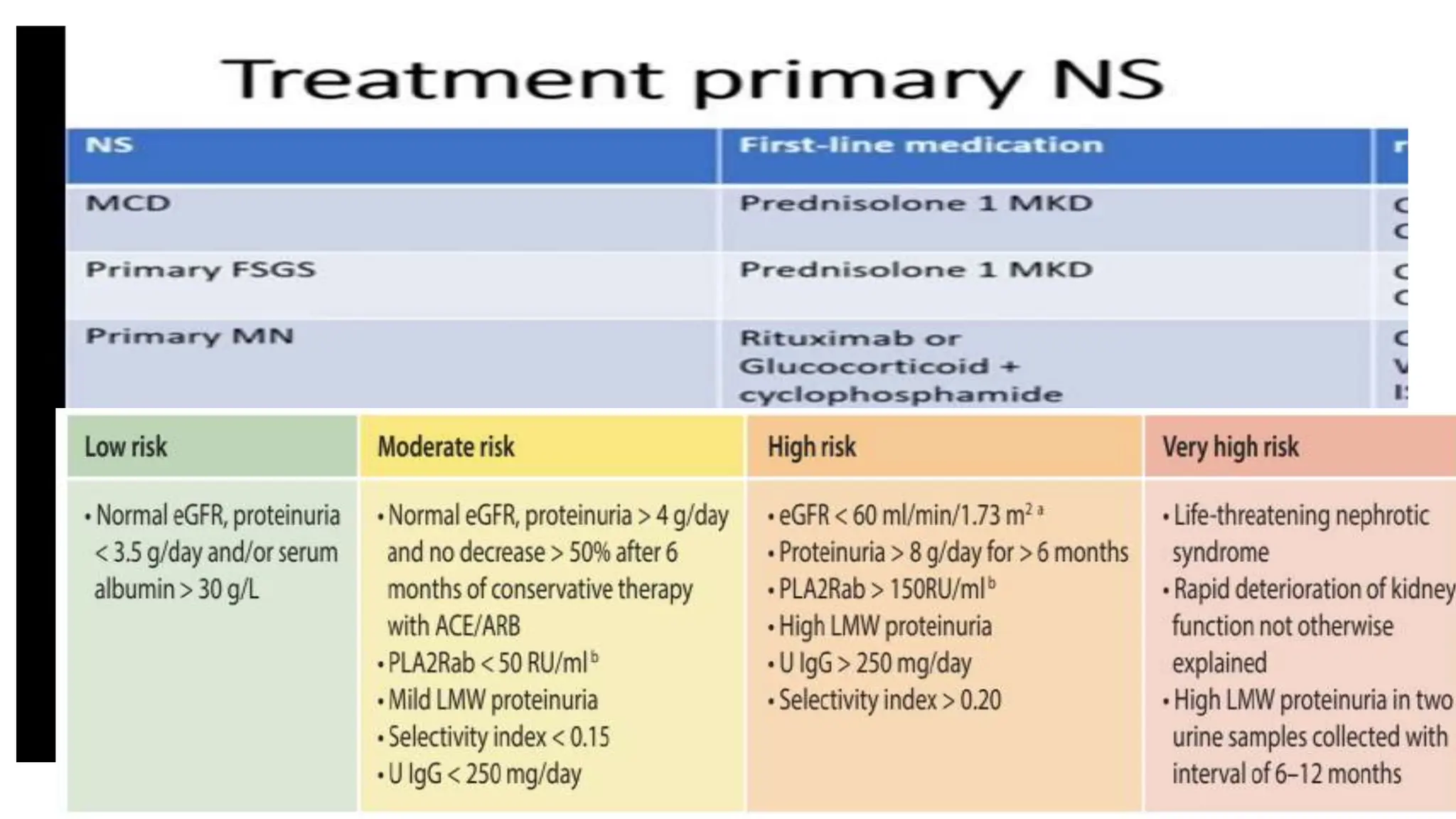
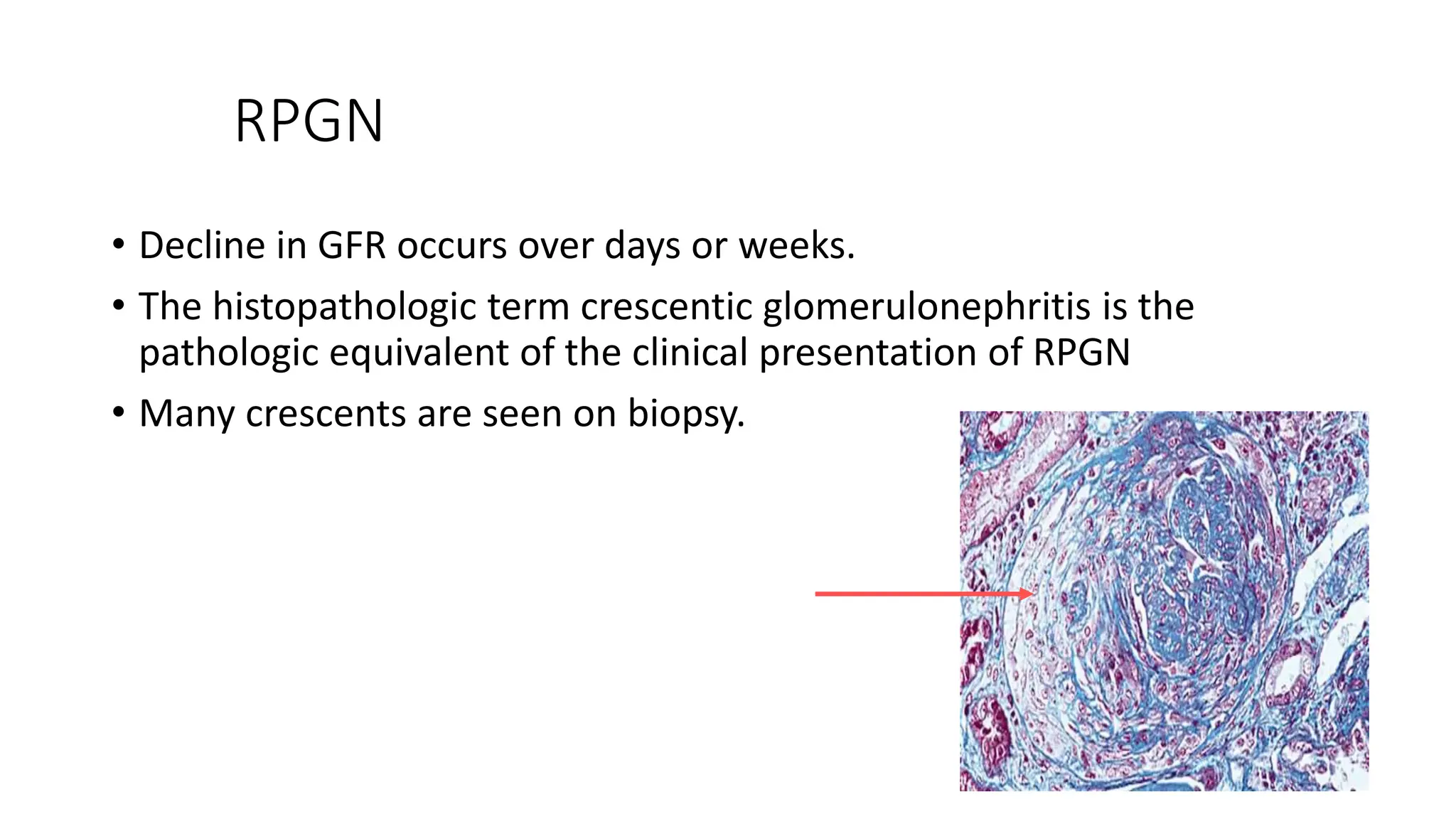
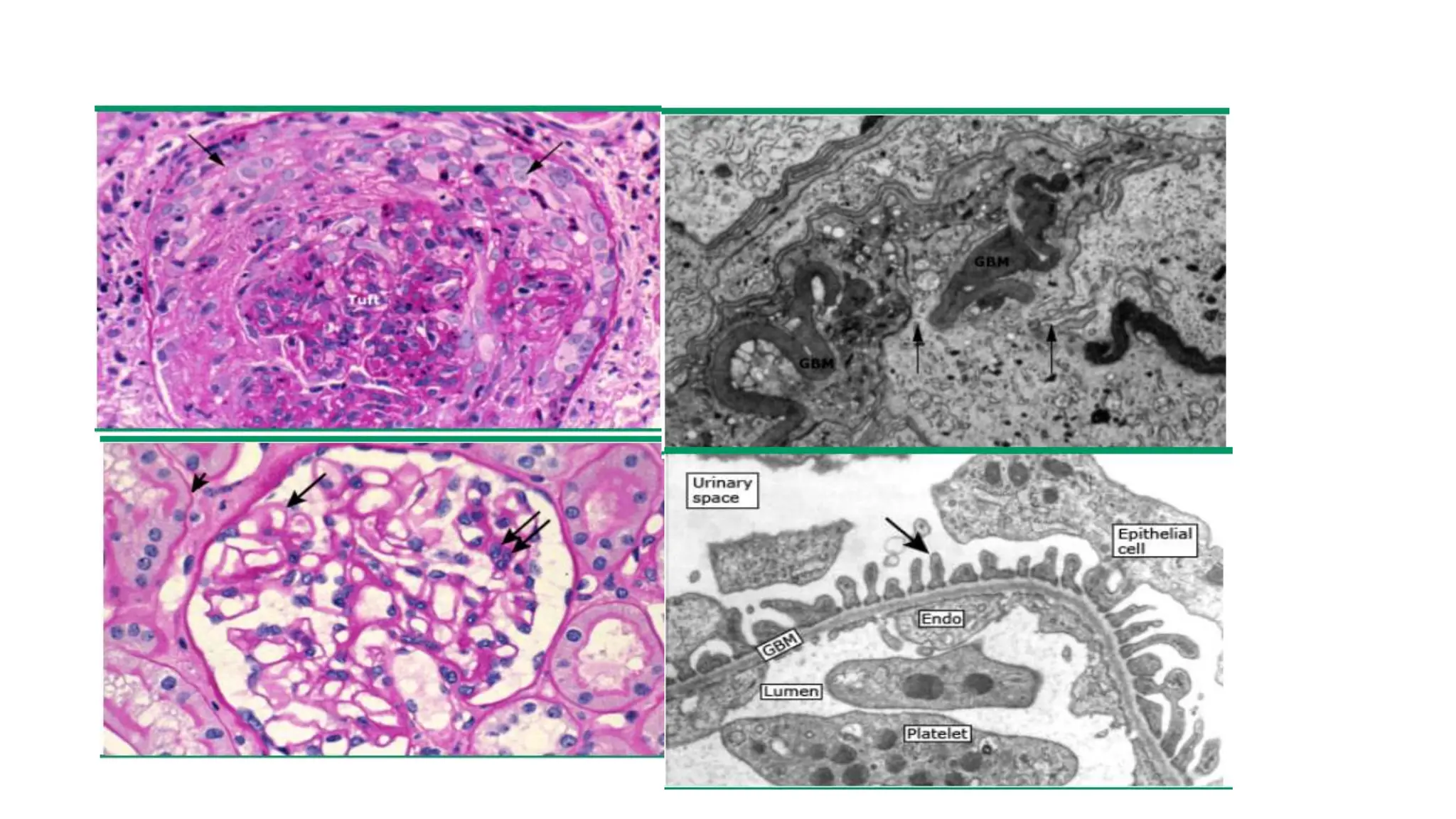
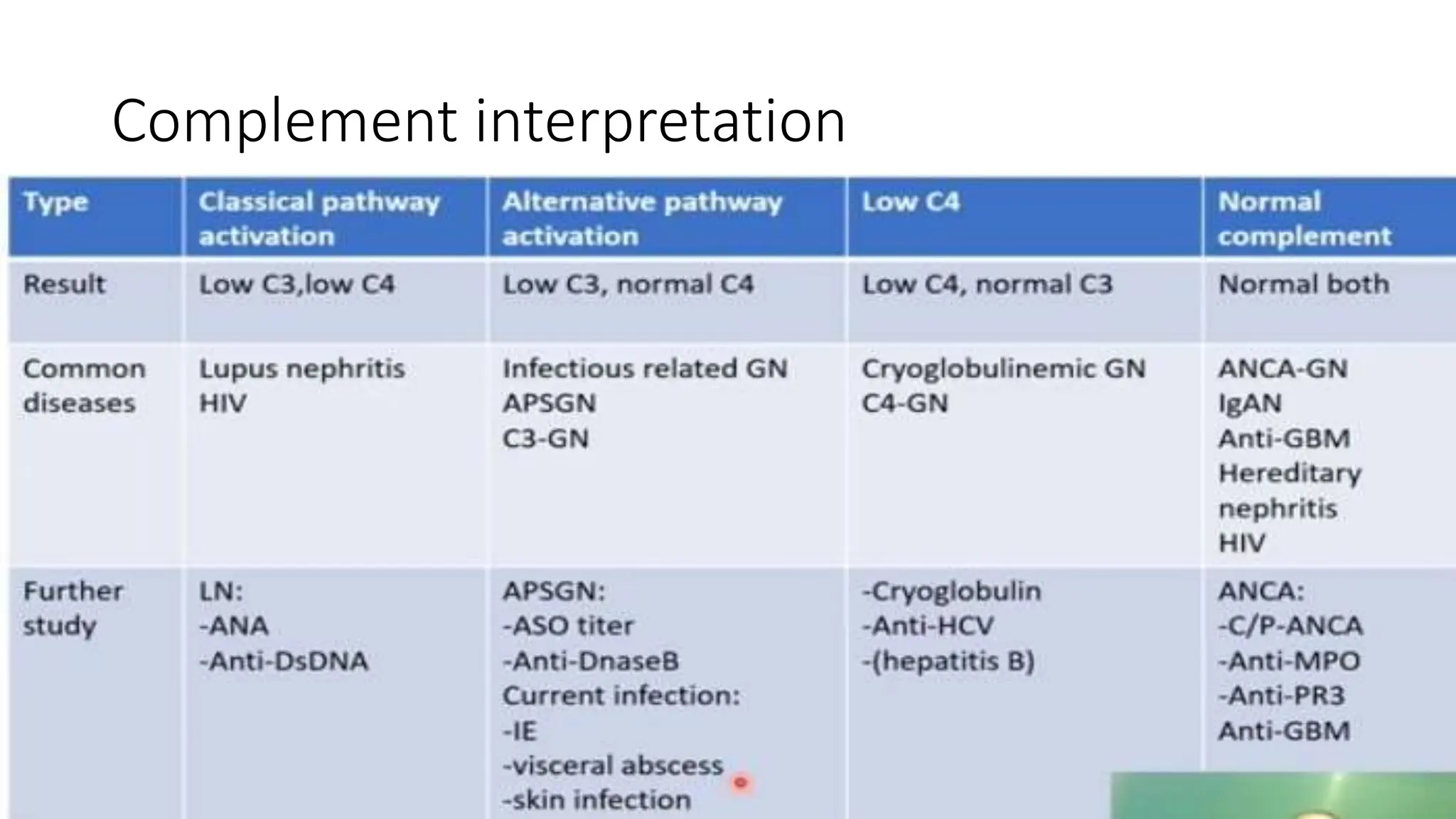
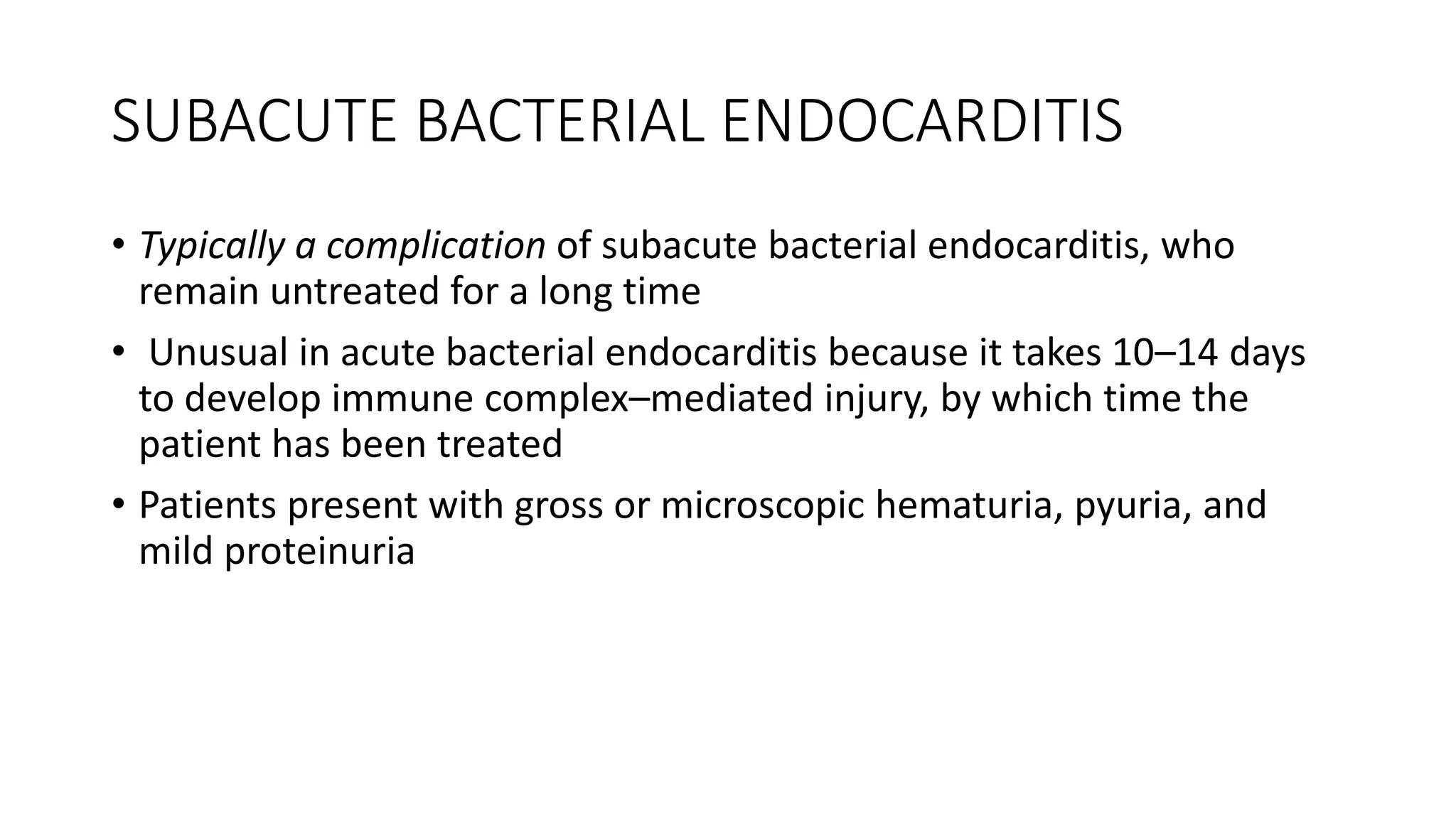
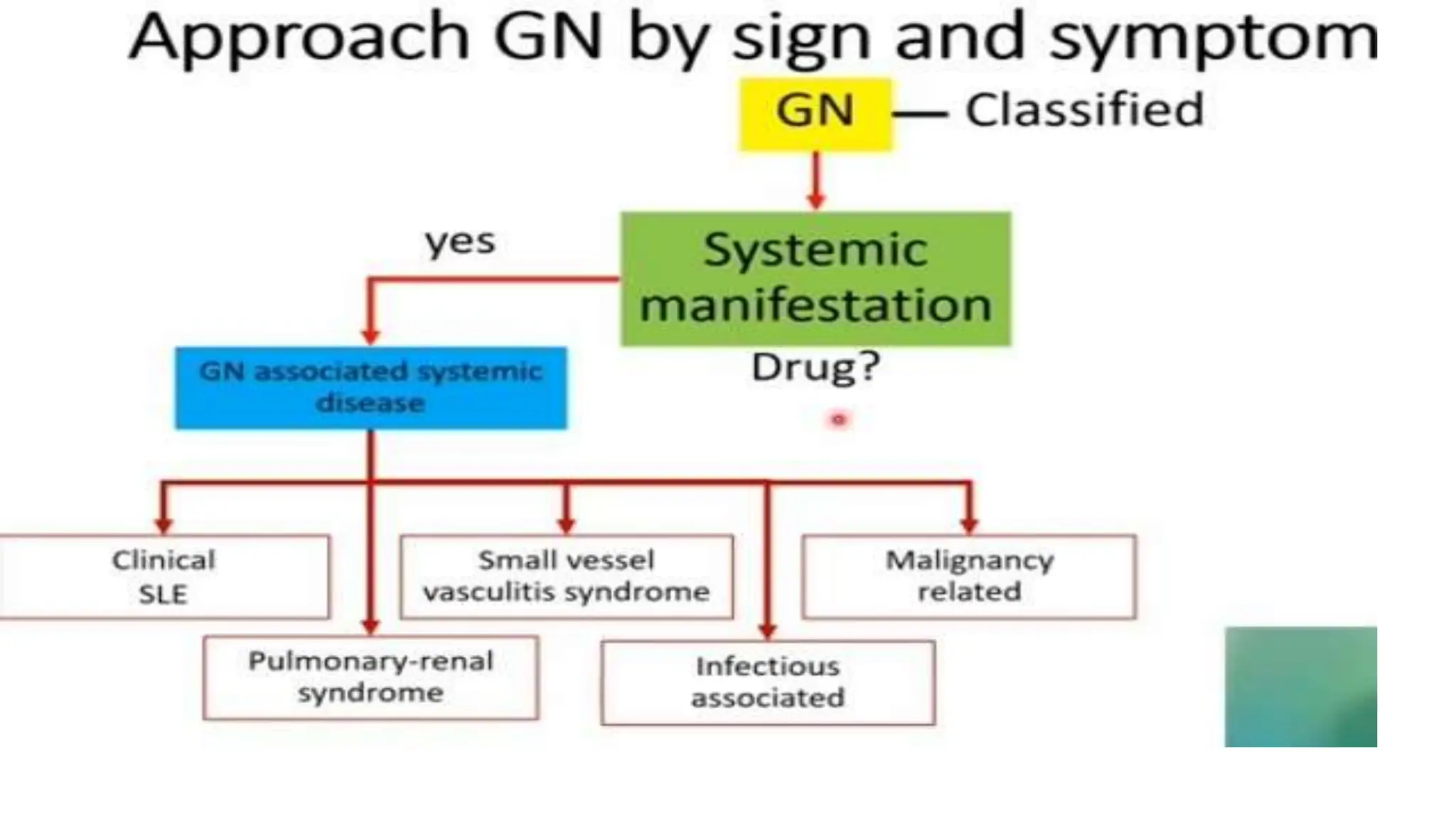
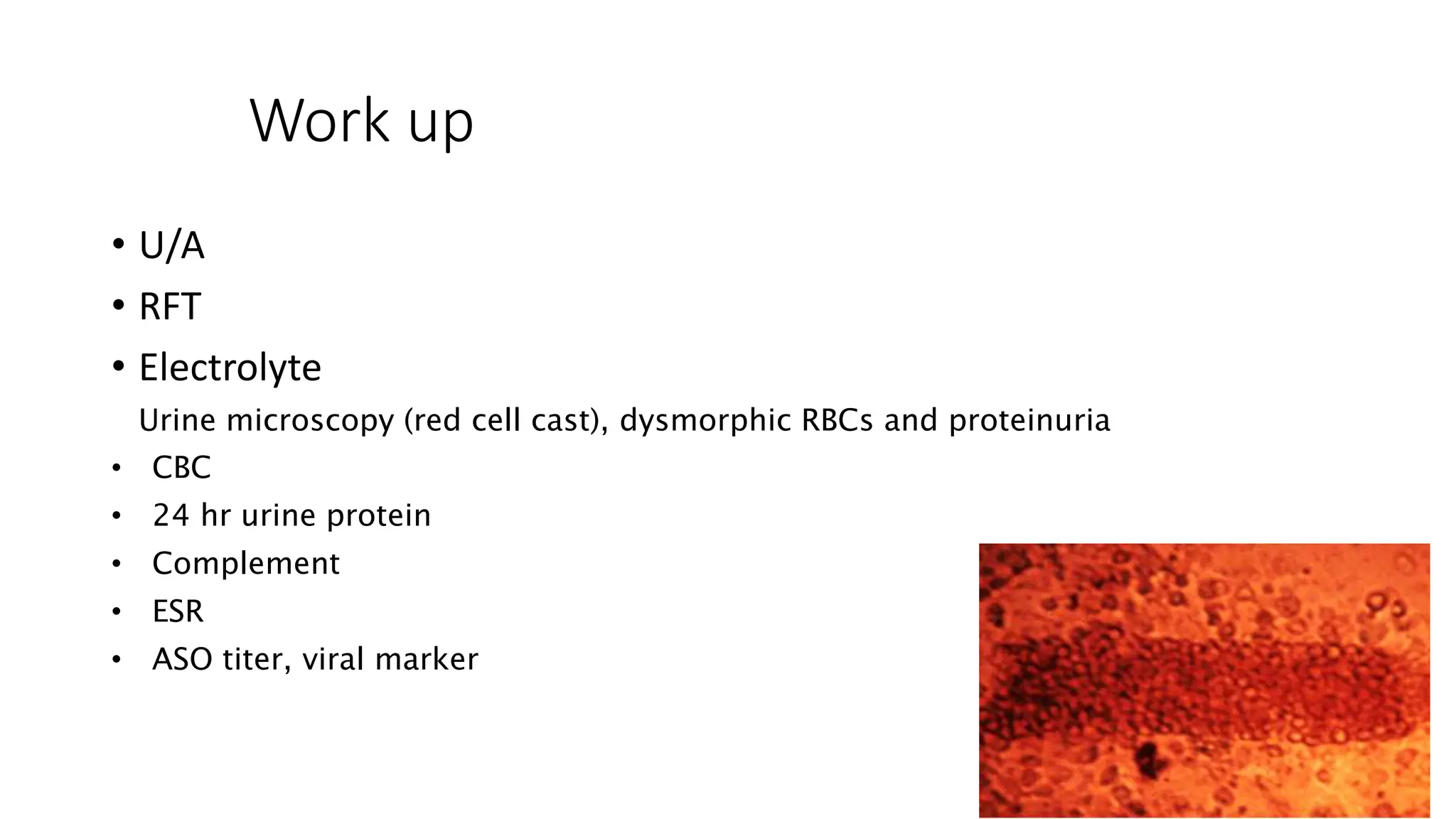
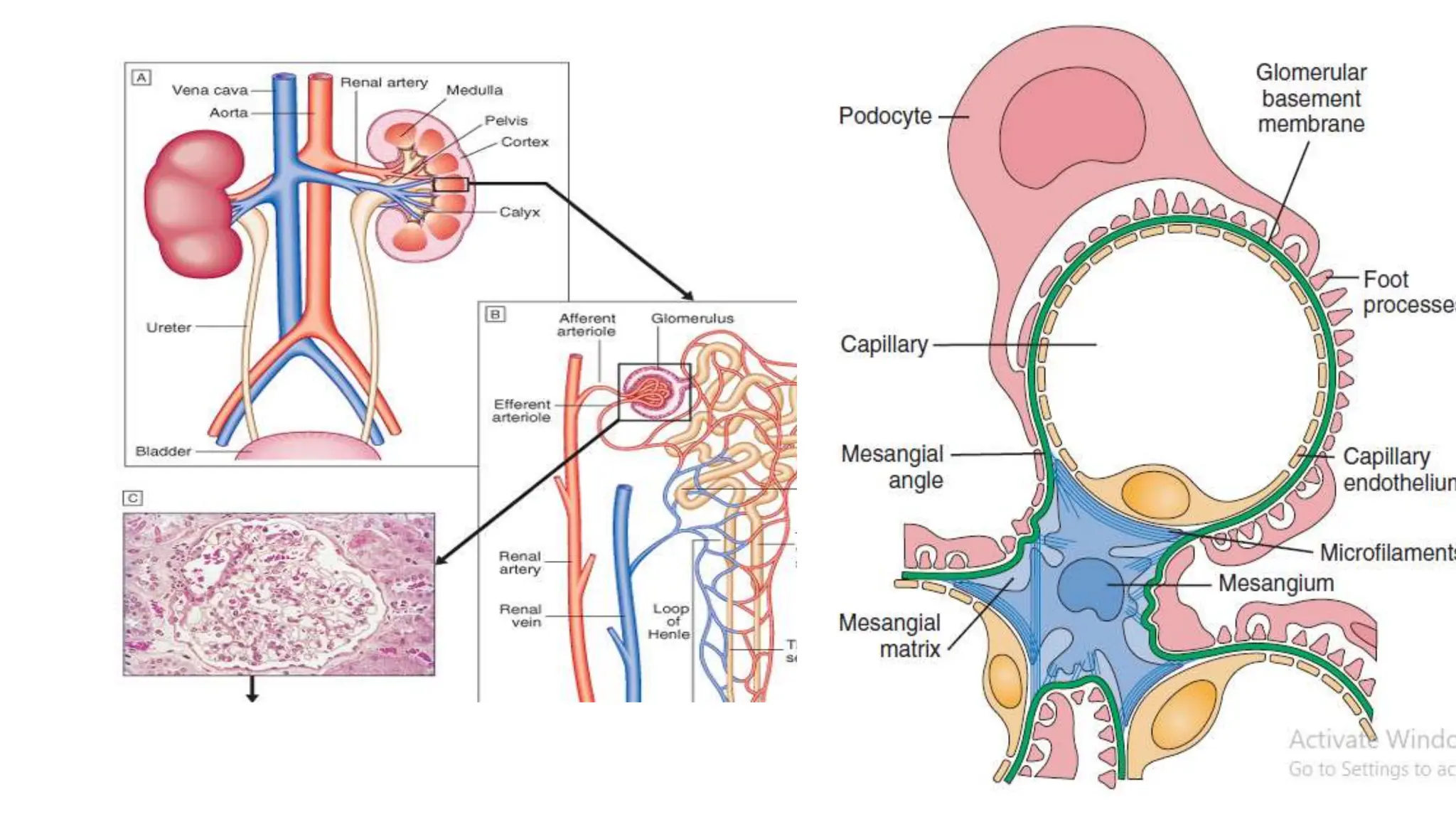
This document provides an overview of glomerular disease, including the pathogenesis, clinical evaluation, and treatment. It begins with an introduction to glomerular anatomy and physiology. Common causes of glomerular disease include genetic mutations, infections, autoimmunity, and atherosclerosis. Clinical presentations range from asymptomatic urine abnormalities to nephrotic syndrome. Evaluation involves history, physical exam, urine analysis, renal function tests, and sometimes renal biopsy. Main treatment approaches depend on the specific glomerular disease and include controlling hypertension and proteinuria, immunosuppression, and dialysis. Complications can include renal failure and chronic kidney disease if not properly treated.














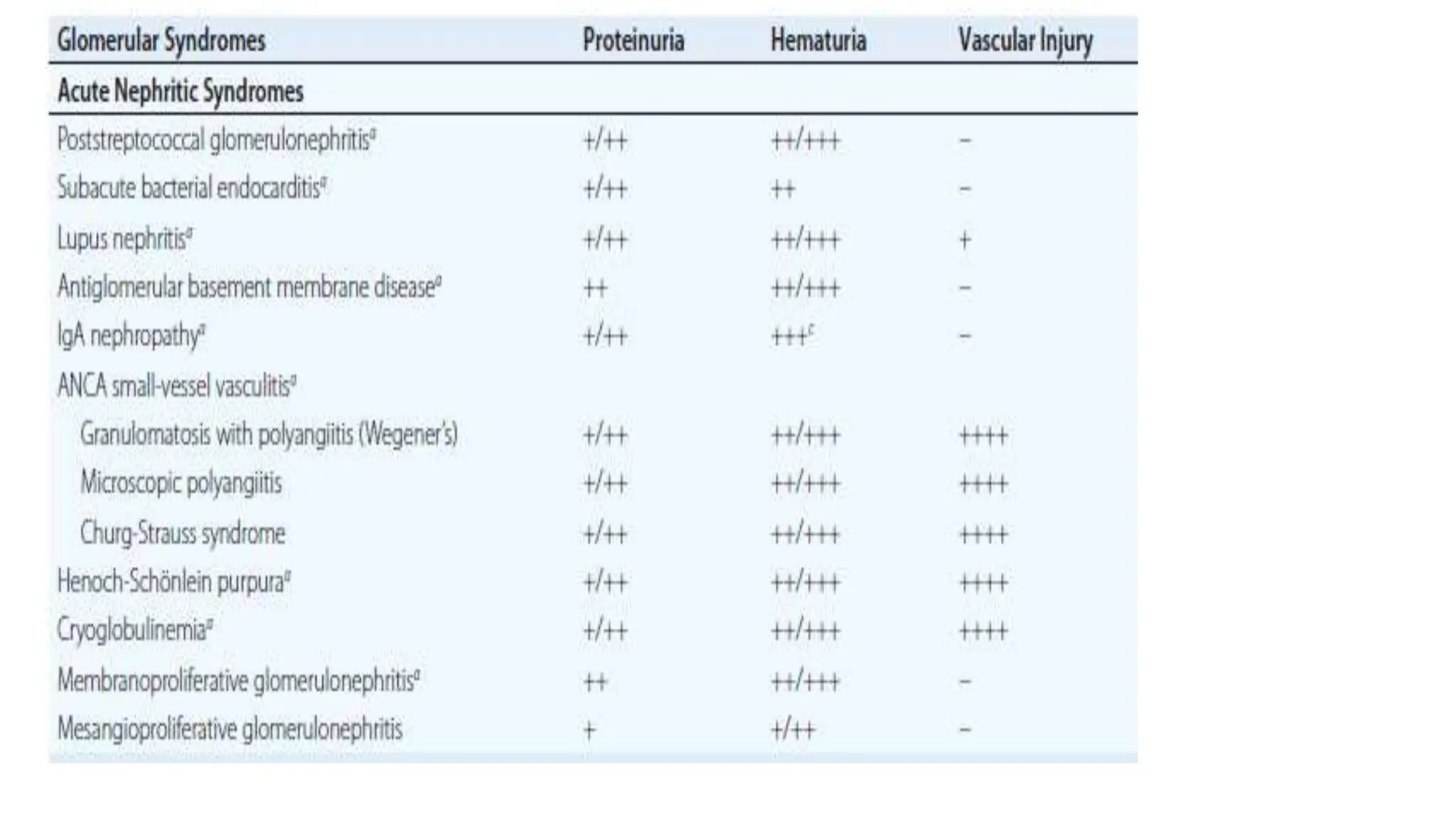
![Clinical syndromes
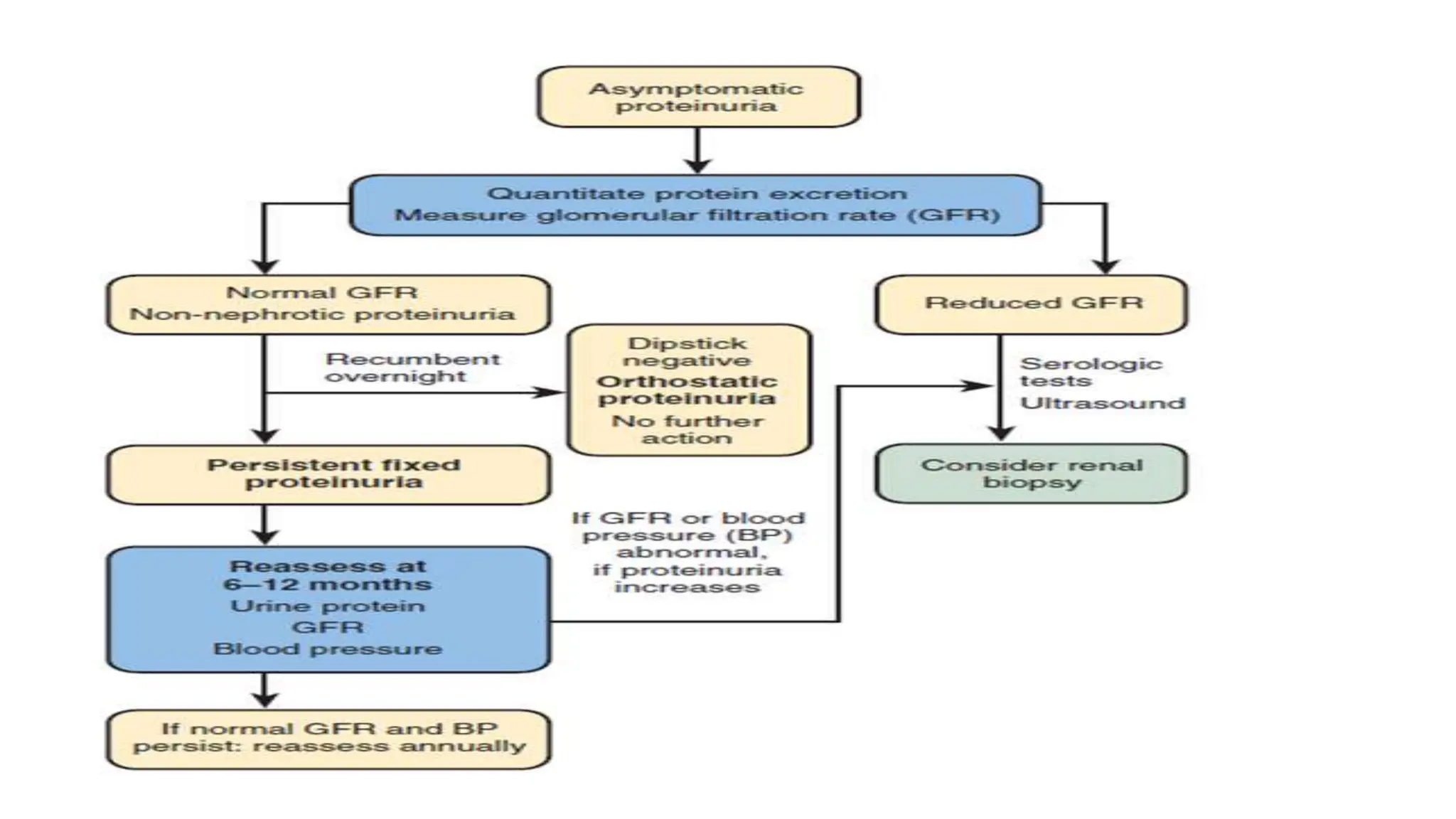
• Asymptomatic
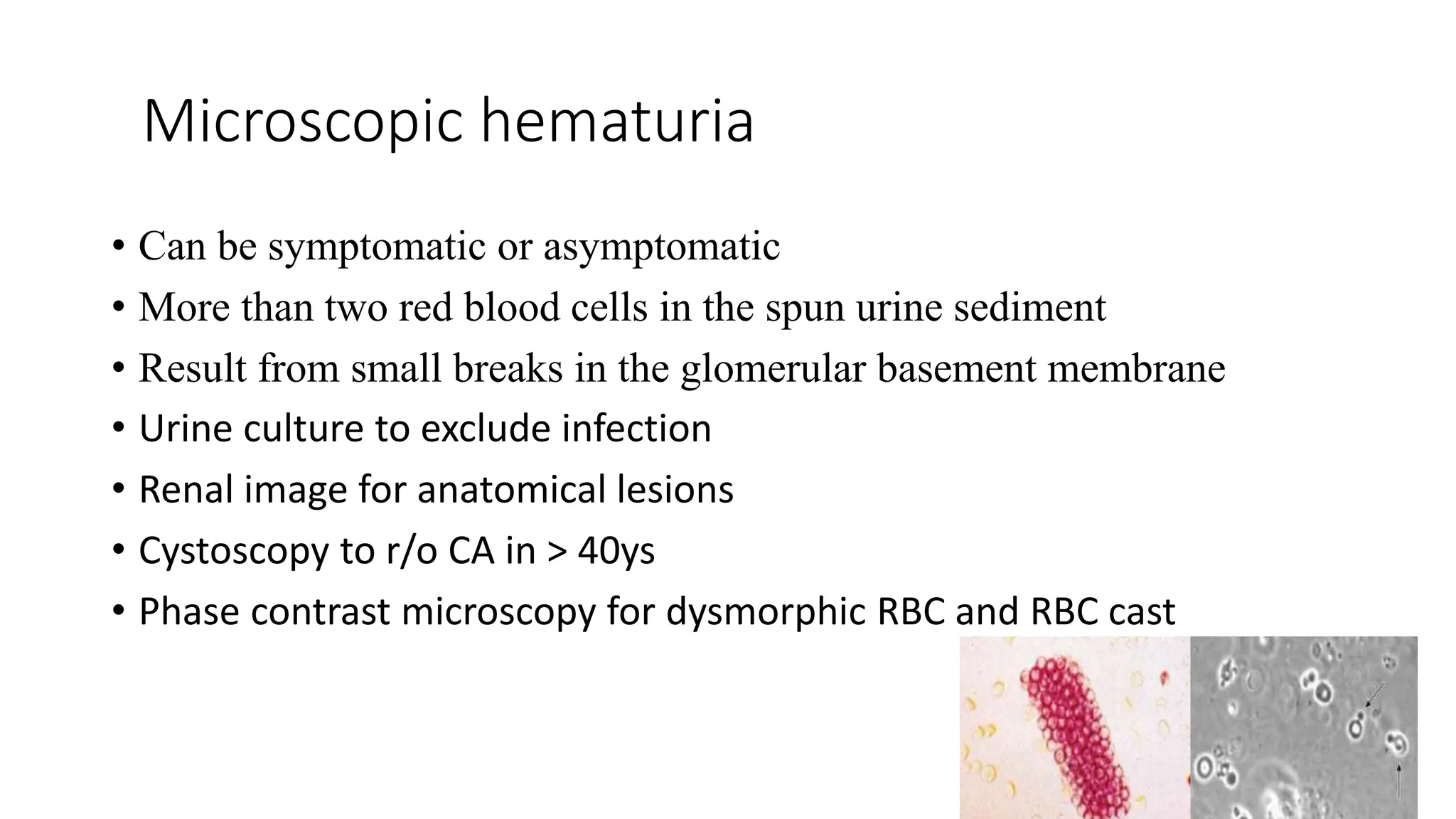
• Macroscopic hematuria
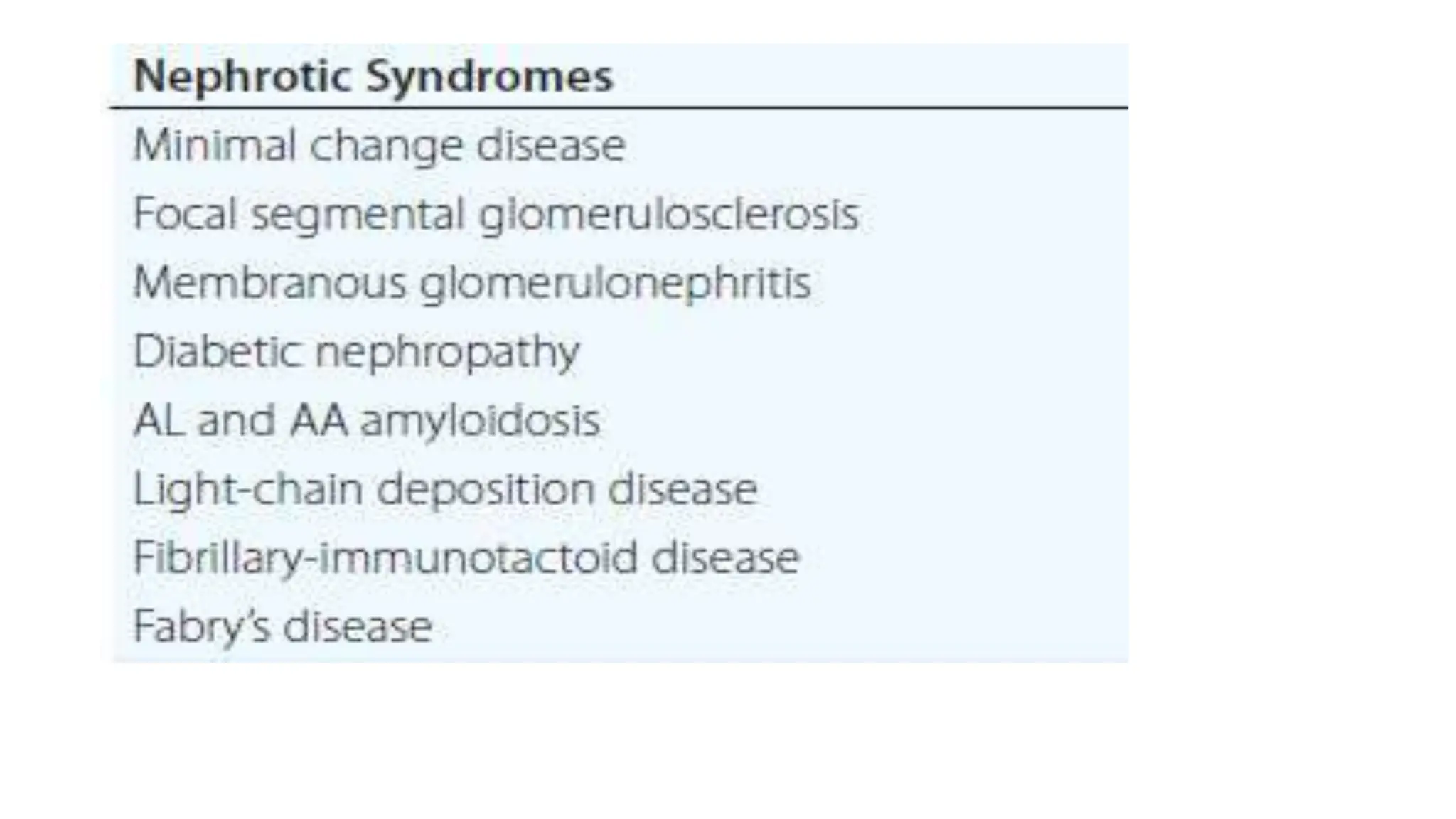
• Nephrotic syndrome
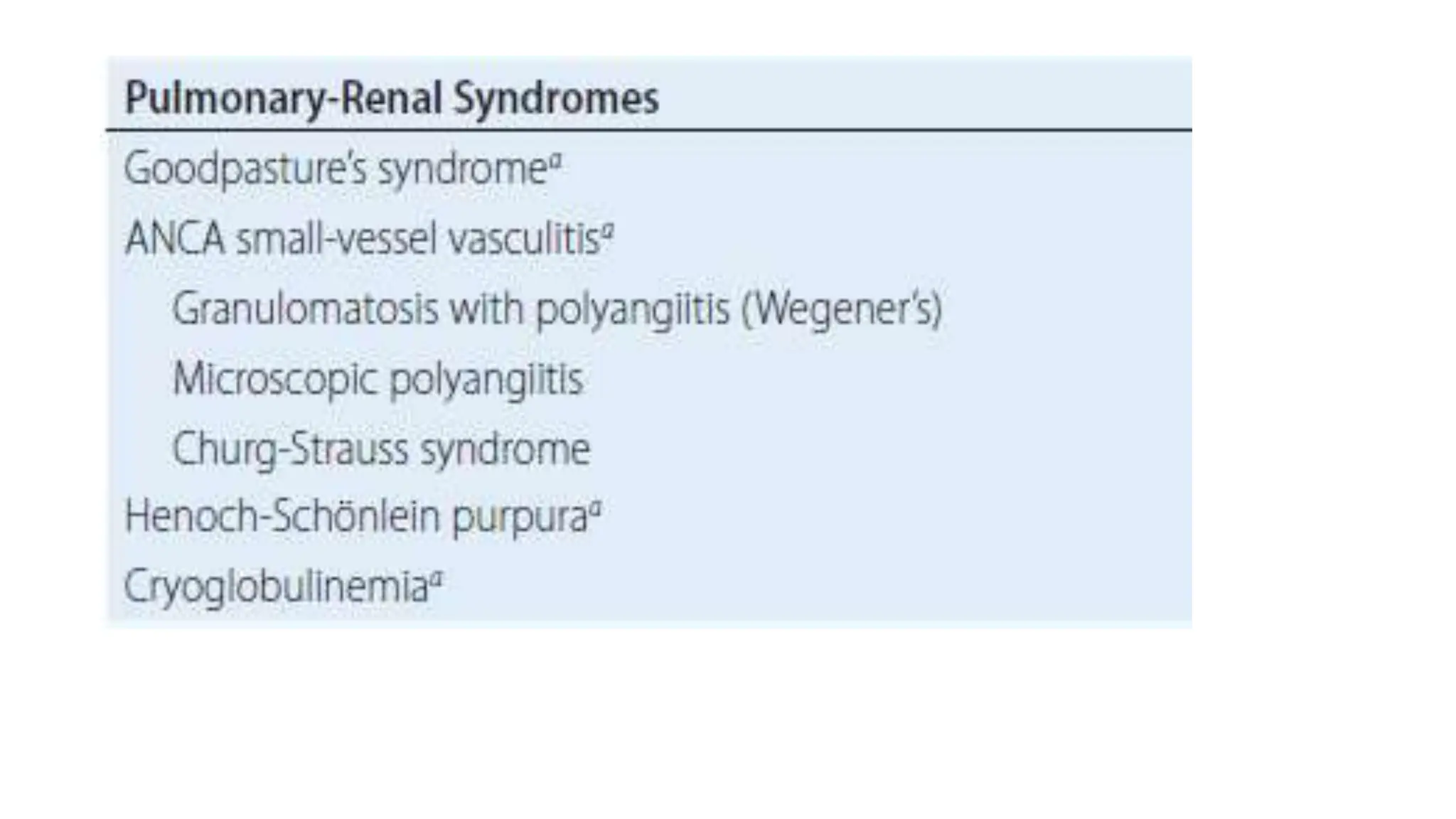
• Acute nephritic syndrome: AGN,RPGN
• Chronic glomerulonephritis [CKD]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glomerulardiseasesem-231005200303-723ddfd4/75/Glomerular-Disease-sem-pptx-17-2048.jpg)
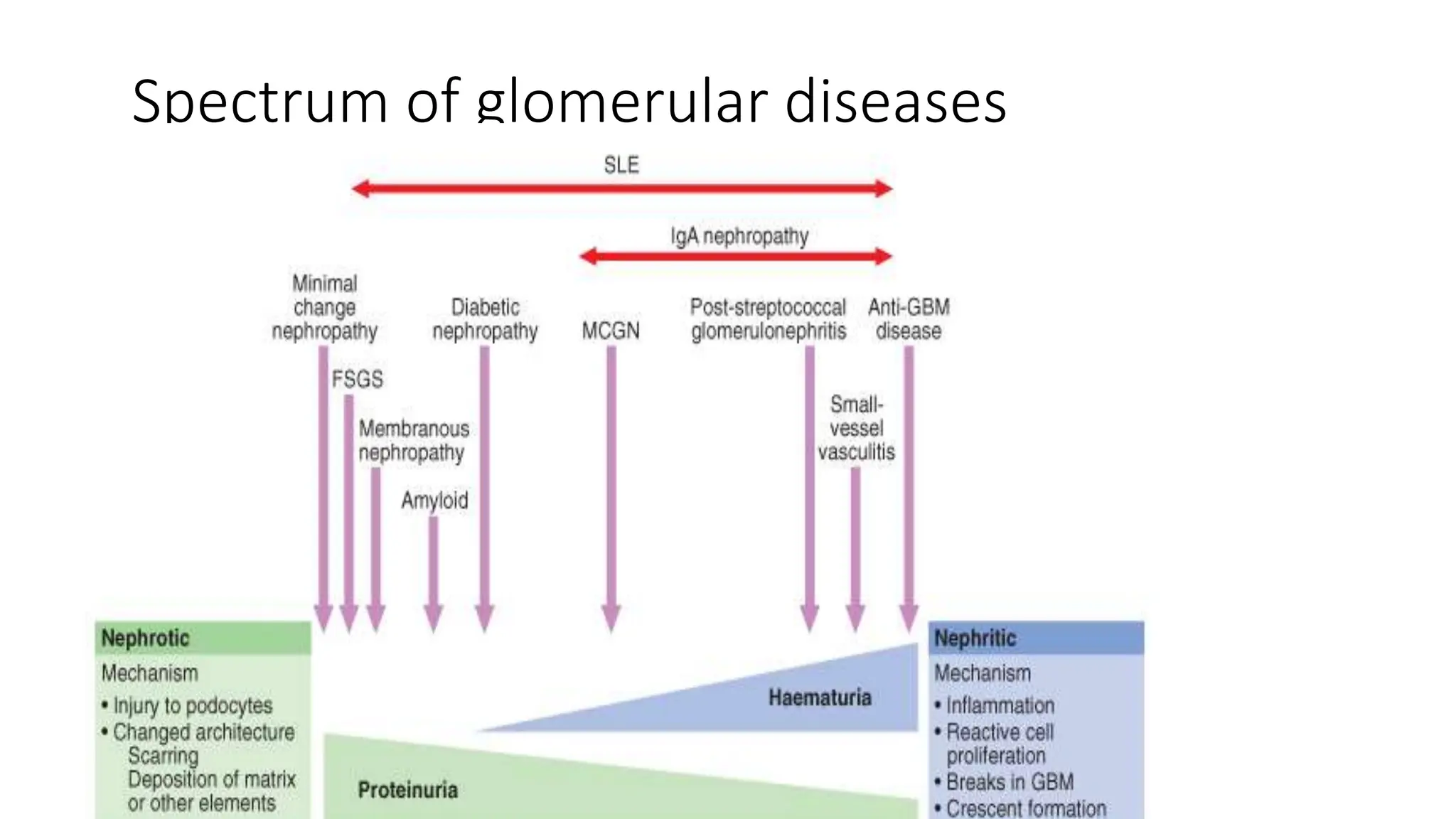


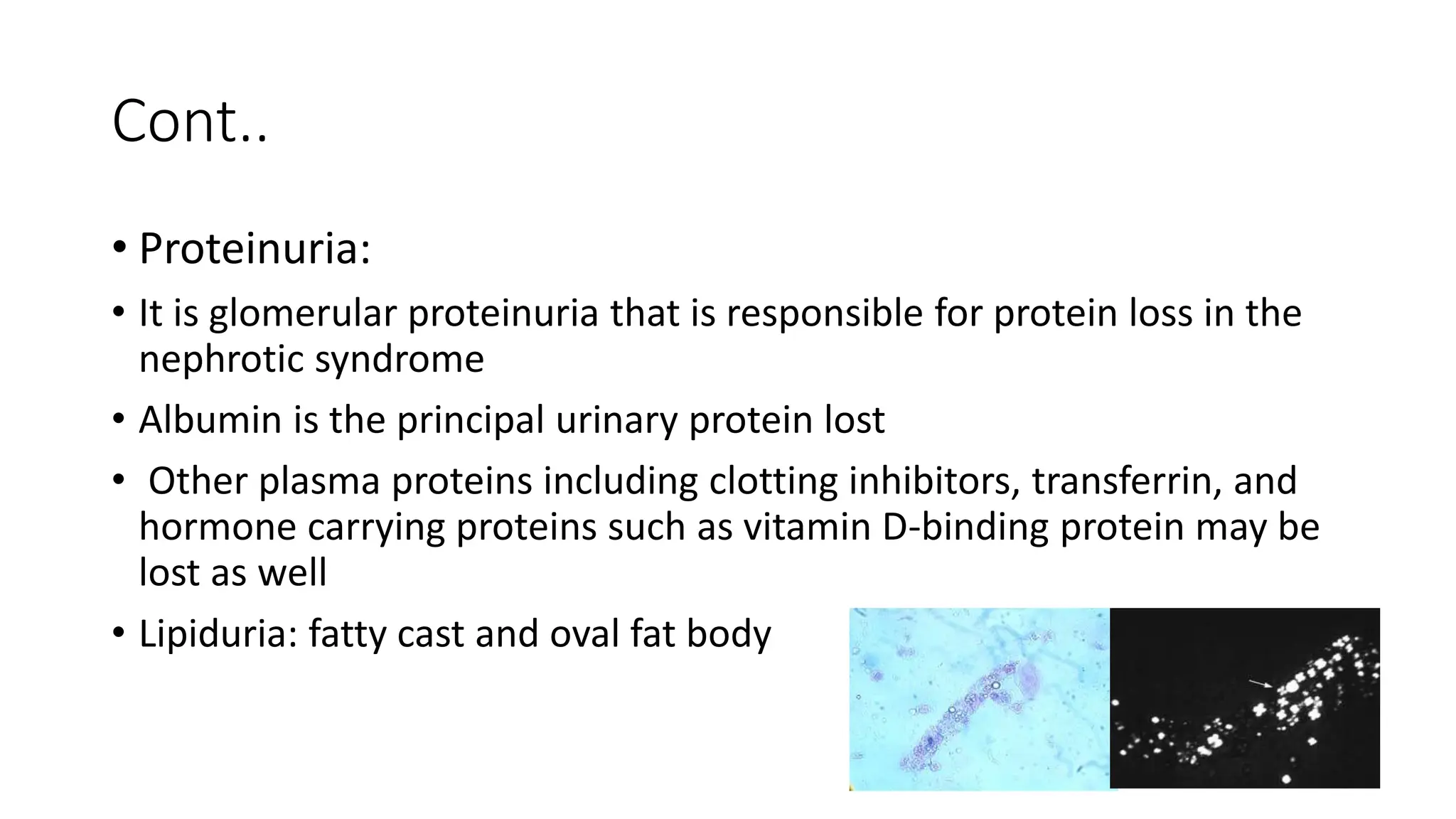
![Nephrotic Syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is pathognomonic of glomerular disease.
It is a clinical syndrome with a characteristic pentad
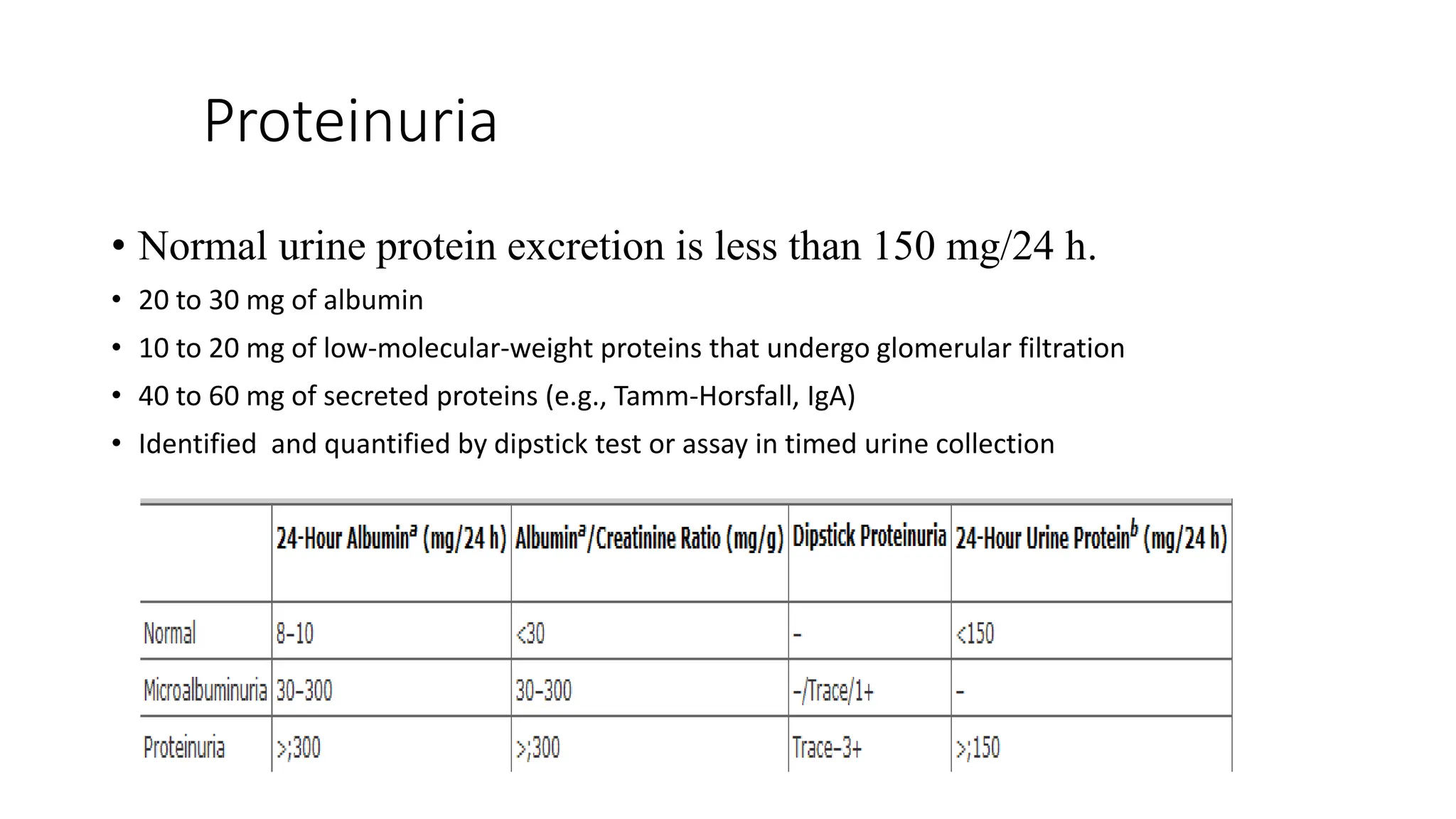
• Proteinuria > 3.5 g/day[24hr urine collection]
Hypoalbuminemia <3.5 g/dl
Edema
Hypercholesterolemia
Lipiduria](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glomerulardiseasesem-231005200303-723ddfd4/75/Glomerular-Disease-sem-pptx-28-2048.jpg)