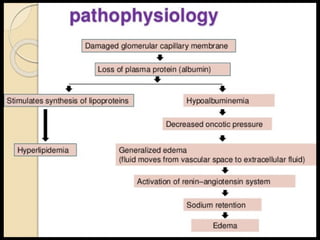
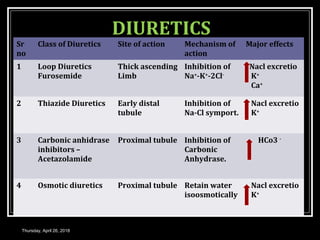
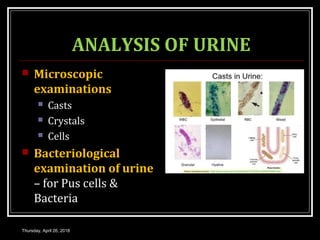
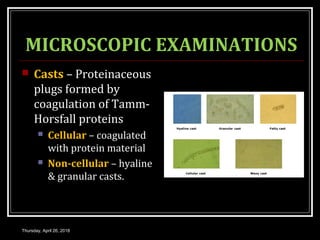
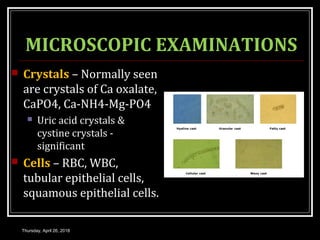
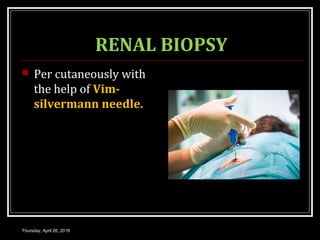
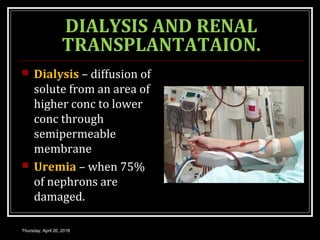
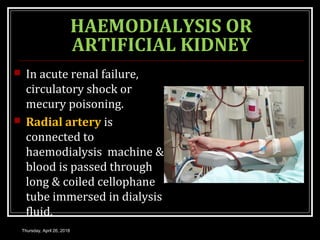
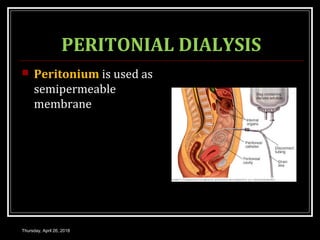
This document provides an overview of applied renal physiology and renal function tests by Dr. Nilesh Kate. It discusses the pathophysiology of common renal disorders like renal failure and nephrotic syndrome. It also describes various renal function tests including analysis of urine and blood, clearance tests to measure GFR and RPF, and radiological tests. Diagnostic techniques like renal biopsy are also mentioned. The document concludes with an overview of dialysis methods like hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis as well as renal transplantation.