Embed presentation
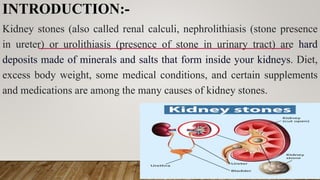

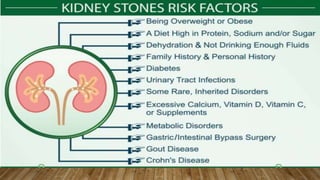
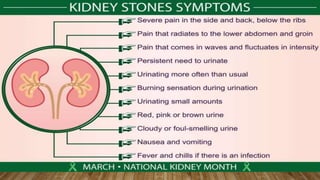

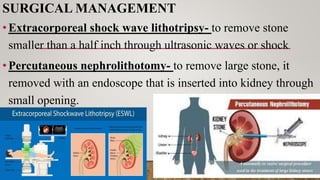
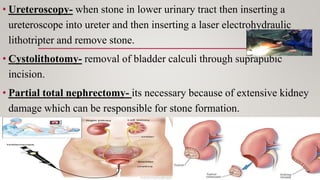


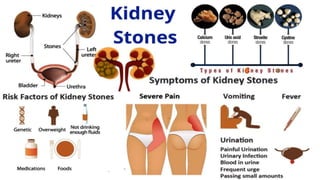

Kidney stones, also known as renal calculi, form inside the kidneys from minerals and salts in the urine. Risk factors include diet, excess weight, medical conditions, and certain supplements or medications. Diagnosis involves blood tests, urine tests, and imaging exams. Treatment depends on the size and location of the stone and may include increased fluid intake, pain medications, surgery to break up or remove stones, and lifestyle changes to prevent future stones.












