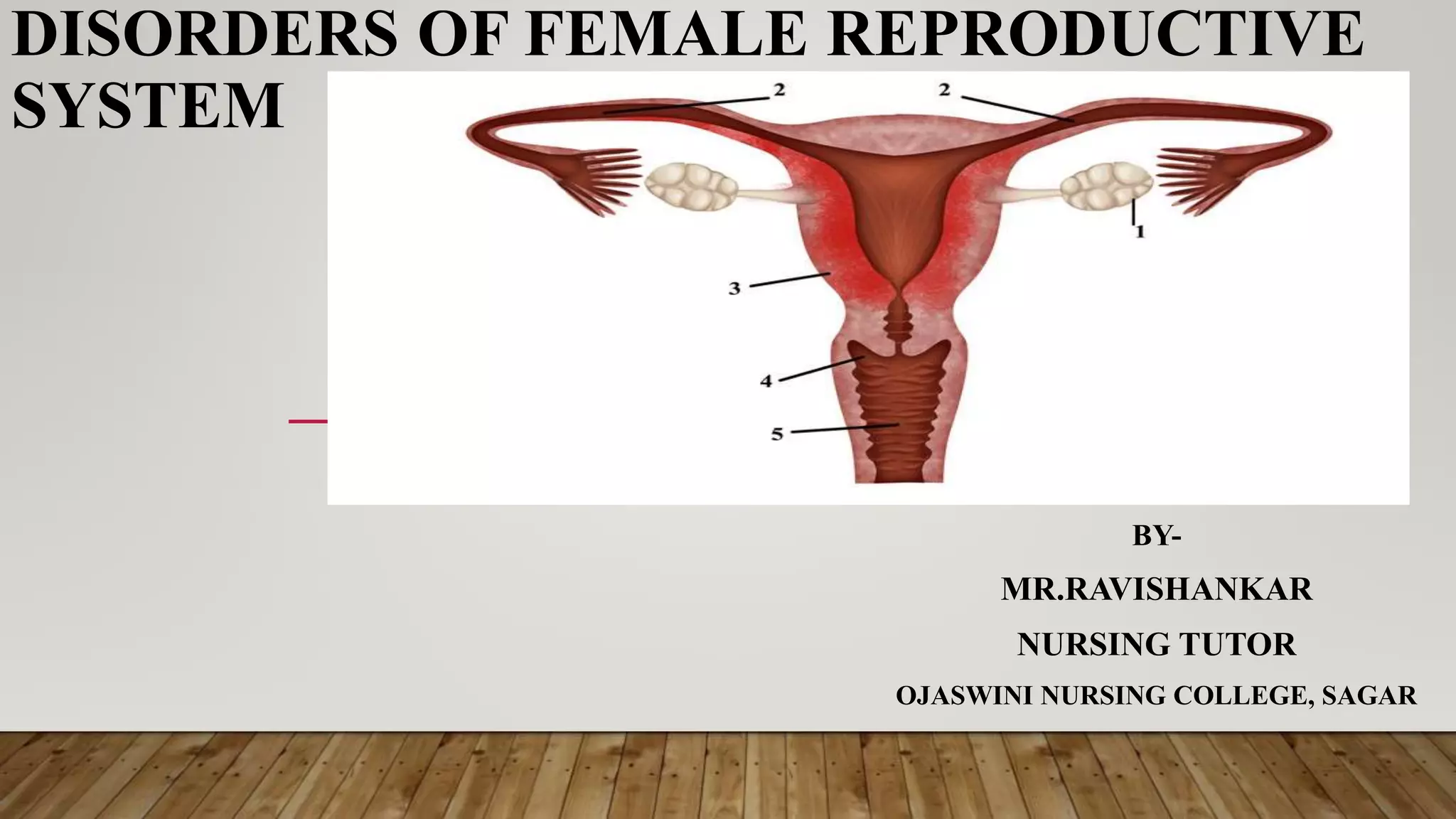
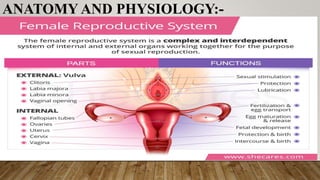
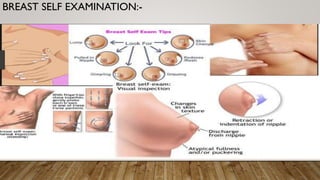
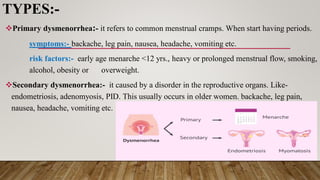
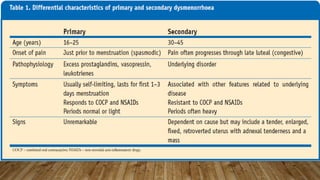
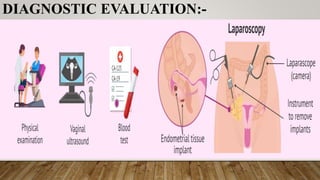
This document discusses disorders of the female reproductive system, including breast self-examination techniques and dysmenorrhea. It defines dysmenorrhea as painful menstruation with no identifiable pelvic pathology. There are two types - primary dysmenorrhea caused by common menstrual cramps, and secondary dysmenorrhea caused by disorders like endometriosis. The pathophysiology involves increased prostaglandins in the uterus leading to contraction, ischemia and pain. Management includes NSAIDs, oral contraceptives, antibiotics, and potentially hysterectomy or IUD insertion/removal.